Class Communicator<Provider, Remote>Abstract
Type Parameters
- Provider extends object | null | undefined
Type of features provided for remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy (view full)
- Communicator
Index
Constructors
Methods
Constructors
Protected constructor
- new
Communicator<Provider, Remote>(provider): Communicator<Provider, Remote> Initializer Constructor.
+Type Parameters
Parameters
- provider: Provider
An object providing features for remote system.
+
Returns Communicator<Provider, Remote>
- provider: Provider
Methods
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
Protected Abstract inspect
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
Protected Abstract send
- send
Data(invoke): Promise<void> A function sending data to the remote system.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data to send.
+
Returns Promise<void>
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: Provider
Class SharedWorkerAcceptor<Header, Provider, Remote>
SharedWorker acceptor for client.
+-
+
- available only in the Web Browser. +
The SharedWorkerAcceptor is a communicator class communicating with the remote client
+(SharedWorkerConnector) using RFC (Remote Function Call). The SharedAcceptor
+objects are always created by the SharedWorkerServer class whenever a remote client
+connects to its server.
To accept connection and start interaction with the remote client, call the accept
+method with special Provider. After the acceptance, don't forget to closing
+the connection after your business has been completed. Otherwise, you don't want to accept but
+reject the connection, call the reject method.
Also, when declaring this SharedWorkerAcceptor type, you've to define two template +arguments, Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from +the remote client after the connection.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote client.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote client, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of the header containing initial data.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for the remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy
Implements
- IWorkerSystem
Index
Accessors
Methods
Accessors
header
- get header(): Header
Header containing initialization data like activation.
+Returns Header
state
- get state(): WebAcceptor.State
Get state.
+Get current state of connection state with the remote client.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
REJECTING: Therejectmethod is on running.
+NONE: This instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+ACCEPTING: Theacceptmethod is on running.
+OPEN: The connection is online.
+CLOSING: Theclosemethod is on running.
+CLOSED: The connection is offline.
+
Returns WebAcceptor.State
Methods
accept
- accept(provider): Promise<void>
Parameters
- provider: Provider
Returns Promise<void>
Inherit Doc
close
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
reject
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: undefined | Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: undefined | Provider
Class SharedWorkerConnector<Header, Provider, Remote>
SharedWorker Connector
+-
+
- available only in the Web Browser. +
The SharedWorkerConnector is a communicator class, who can connect to an SharedWorker
+instance and communicate with it using RFC (Remote Function Call), considering the
+SharedWorker as a remote system (WorkerServer).
You can connect to an SharedWorker instance with connect() method. If the
+SharedWorker instance does not exist yet, a new SharedWorker instance would be newly
+created. After the creation, you have to let the SharedWorker program to open a sever
+using the SharedWorkerServer.open() method. Your connection would be linked with
+a SharedWorkerAcceptor object in the server.
After your business has been completed, you've to close the SharedWorker using one of
+them below. If you don't close that, vulnerable memory usage and communication channel
+would not be destroyed and it may cause the memory leak:
Also, when declaring this SharedWorkerConnector type, you've to define two template +arguments, Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the +remote client after the connection.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote system.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote system, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of the header containing initial data.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for the remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy
Implements
- IWorkerSystem
Index
Constructors
Accessors
Methods
Constructors
constructor
Accessors
header
- get header(): Header
Header containing initialization data like activation.
+Returns Header
state
- get state(): WebConnector.State
Get state.
+Get current state of connection state with the worker server.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
NONE: This instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+CONNECTING: Theconnectmethod is on running.
+OPEN: The connection is online.
+CLOSING: Theclosemethod is on running.
+CLOSED: The connection is offline.
+
Returns WebConnector.State
Methods
close
connect
- connect(jsFile, options?): Promise<void>
Connect to remote server.
+The connect() method tries to connect an
+SharedWorkerinstance. If the +SharedWorkerinstance is not created yet, theSharedWorkerinstance would be newly +created. After the creation, theSharedWorkerprogram must open that server using +the SharedWorkerServer.open() method.After you business has been completed, you've to close the
+SharedWorkerusing one of +them below. If you don't close that, vulnerable memory usage and communication channel +would not be destroyed and it may cause the memory leak:-
+
- close() +
- ShareDWorkerAcceptor.close() +
- SharedWorkerServer.close() +
Parameters
- jsFile: string
JS File to be SharedWorkerServer.
+ - options: Partial<SharedWorkerConnector.IConnectOptions> = {}
Detailed options like timeout.
+
Returns Promise<void>
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: Provider
Class SharedWorkerServer<Header, Provider, Remote>
SharedWorker server.
+-
+
- available only in the Web Browser. +
The SharedWorkerServer is a class representing a server server in a SharedWorker
+environment. Clients connecting to the SharedWorkerServer would communicate with this
+server through SharedWorkerAcceptor objects using RFC (Remote Function Call).
To open the server, use the open() method with a callback function which would be +called whenever a client has been connected. After your business, don't forget to closing +the connection using one of them below. If you don't close that, vulnerable memory usage +and communication channel would not be destroyed and it may cause the memory leak.
+ +Also, when declaring this SharedWorkerServer type, you've to define two template +arguments, Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the +remote client after the connection.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote client.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote client, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
Implements
Index
Constructors
constructor
Accessors
state
- get state(): WebServer.State
Get server state.
+Get current state of the websocket server.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
NONE: The `{@link SharedWorkerServer} instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+OPENING: The {@link SharedWorkerServer.open} method is on running.
+OPEN: The websocket server is online.
+CLOSING: The {@link SharedWorkerServer.close} method is on running.
+CLOSED: The websocket server is offline.
+
Returns WebServer.State
Methods
close
- close(): Promise<void>
Close server.
+Close all connections between its remote clients (SharedWorkerConnectors).
+It destories all RFCs (remote function calls) between this server and remote clients +(through
+Driver<Controller>) that are not returned (completed) yet. The destruction +causes all incompleted RFCs to throw exceptions.Returns Promise<void>
open
- open(handler): Promise<void>
Open shared worker server.
+Open a server through the shared worker protocol, with handler function determining +whether to accept the client's connection or not. After the server has been opened, clients +can connect to that websocket server by using the SharedWorkerServer class.
+When implementing the handler function with the SharedWorkerServer instance, calls +the SharedWorkerAcceptor.accept method if you want to accept the new client's +connection. Otherwise you dont't want to accept the client and reject its connection, just +calls the SharedWorkerAcceptor.reject instead.
+Parameters
- handler: ((acceptor) => Promise<void>)
Callback function called whenever client connects.
+- (acceptor): Promise<void>
Parameters
- acceptor: SharedWorkerAcceptor<Header, Provider, Remote>
Returns Promise<void>
Returns Promise<void>
- handler: ((acceptor) => Promise<void>)
Class WebAcceptor<Header, Provider, Remote>
Web Socket Acceptor.
+-
+
- available only in the NodeJS. +
The WebAcceptor is a communicator class interacting with the remote (web socket) client using
+RFC (Remote Function Call). The
+WebAcceptor objects are always created by the WebServer class whenever a remote client
+connects to its server.
To accept connection and start interaction with the remote client, call the accept
+method with special Provider. After the acceptance, don't forget to closing the
+connection after your busines has been completed. Otherwise, you don't want to accept but reject
+the connection, call the reject method.
Also, when declaring this WebAcceptor type, you've to define two template arguments, +Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the remote +client after the connection. I hope you and client not to omit it and utilize it as an +activation tool to enhance security.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote client.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote client, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of the header containing initial data.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for the remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy
Implements
- IWebCommunicator
Accessors
header
- get header(): Header
Header containing initialization data like activation.
+Returns Header
ip
- get ip(): string
IP Address of client.
+Returns string
path
- get path(): string
Path of client has connected.
+Returns string
state
- get state(): WebAcceptor.State
Get state.
+Get current state of connection state with the remote client.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
REJECTING: The WebAcceptor.reject method is on running.
+NONE: The WebAcceptor instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+ACCEPTING: The WebAcceptor.accept method is on running.
+OPEN: The connection is online.
+CLOSING: The WebAcceptor.close method is on running.
+CLOSED: The connection is offline.
+
Returns WebAcceptor.State
Methods
accept
- accept(provider): Promise<void>
Parameters
- provider: Provider
Returns Promise<void>
Inherit Doc
close
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
reject
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: undefined | Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: undefined | Provider
Static upgrade
Class WebConnector<Header, Provider, Remote>
Web Socket Connector.
+The WebConnector is a communicator class who can connect to websocket server and
+interact with it using RFC (Remote Function Call).
You can connect to the websocket server using connect() method. The interaction +would be started if the server is opened by WebServer.open() and the server +accepts your connection by WebAcceptor.accept().
+Note that, after you business has been completed, please close the connection using +close() or let the server to close itself. If you don't +close the connection in time, it may waste vulnerable resources of the server.
+Also, when declaring this WebConnector type, you've to define two template arguments, +Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the remote +client after the connection. I hope you and client not to omit it and utilize it as an +activation tool to enhance security.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote system.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote system, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of the header containing initial data.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for the remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy
Implements
- IWebCommunicator
Index
Constructors
Accessors
Methods
Constructors
constructor
Accessors
header
- get header(): Header
Header containing initialization data like activation.
+Returns Header
state
- get state(): WebConnector.State
Get state.
+Get current state of connection state with the websocket server.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
NONE: The WebConnector instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+CONNECTING: The WebConnector.connect method is on running.
+OPEN: The connection is online.
+CLOSING: The WebConnector.close method is on running.
+CLOSED: The connection is offline.
+
Returns WebConnector.State
url
- get url(): undefined | string
Connection URL.
+Returns undefined | string
Methods
close
connect
- connect(url, options?): Promise<void>
Connect to remote websocket server.
+Try connection to the remote websocket server with its address and waiting for the +server to accept the trial. If the server rejects your connection, then exception +would be thrown (in Promise.catch, as
+WebError).After the connection and your business has been completed, don't forget to closing the +connection in time to prevent waste of the server resource.
+Parameters
- url: string
URL address to connect.
+ - options: Partial<WebConnector.IConnectOptions> = {}
Detailed options like timeout.
+
Returns Promise<void>
- url: string
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: Provider
Class WebError
Web Socket Error.
+Reference
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/CloseEvent
+Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Hierarchy
- DomainError
- WebError
Index
Constructors
constructor
Properties
message
Optional stack
Readonly status
Static Optional prepare
Optional override for formatting stack traces
+Type declaration
- (err, stackTraces): any
Parameters
- err: Error
- stackTraces: CallSite[]
Returns any
Static stack
Accessors
name
- get name(): string
The error name.
+Returns string
Methods
toJSON
- toJSON(): object
Native function for
+JSON.stringify().The Exception.toJSON function returns only three properties; (name, message and stack). If you want to define a new sub-class extending the Exception and const the class to export additional props (or remove some props), override this Exception.toJSON method.
+Returns object
An object for
+JSON.stringify().
what
Static capture
Class WebServer<Header, Provider, Remote>
Web Socket Server.
+-
+
- available only in the NodeJS. +
The WebServer is a class who can open an websocket server. Clients connecting to the
+WebServer would communicate with this server through WebAcceptor objects using
+RFC (Remote Function Call).
To open the websocket server, call the open() method with your callback function which +would be called whenever a WebAcceptor has been newly created ay a client's connection.
+Also, when declaring this WebServer type, you've to define two template arguments, +Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the remote +client after the connection. I hope you and client not to omit it and utilize it as an +activation tool to enhance security.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote client.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote client, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
Implements
Index
Constructors
constructor
- new
Web Server<Header, Provider, Remote>(): WebServer<Header, Provider, Remote> Default Constructor for the
+wsserver..Create an websocket server (
+ws://).Type Parameters
Returns WebServer<Header, Provider, Remote>
- new
Web Server<Header, Provider, Remote>(key, cert): WebServer<Header, Provider, Remote> Initializer Constructor for the
+wssserver.Create a secured websocket server (
+wss://).Type Parameters
Parameters
- key: string
Key string.
+ - cert: string
Certification string.
+
Returns WebServer<Header, Provider, Remote>
- key: string
Accessors
state
- get state(): WebServer.State
Get server state.
+Get current state of the websocket server.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
NONE: The `{@link WebServer} instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+OPENING: The {@link WebServer.open} method is on running.
+OPEN: The websocket server is online.
+CLOSING: The {@link WebServer.close} method is on running.
+CLOSED: The websocket server is offline.
+
Returns WebServer.State
Methods
close
- close(): Promise<void>
Close server.
+Close all connections between its remote clients (WebConnectors).
+It destories all RFCs (remote function calls) between this server and remote clients +(through
+Driver<Controller>) that are not returned (completed) yet. The destruction +causes all incompleted RFCs to throw exceptions.Returns Promise<void>
open
- open(port, handler): Promise<void>
Open websocket server.
+Open a server through the web-socket protocol, with its port number and handler +function determining whether to accept the client's connection or not. After the server has +been opened, clients can connect to that websocket server by using the WebConnector +class.
+When implementing the handler function with the WebAcceptor instance, calls the +WebAcceptor.accept method if you want to accept the new client's connection. +Otherwise you dont't want to accept the client and reject its connection, just calls the +WebAcceptor.reject instead.
+Parameters
- port: number
Port number to listen.
+ - handler: ((acceptor) => Promise<void>)
Callback function for client connection.
+- (acceptor): Promise<void>
Parameters
- acceptor: WebAcceptor<Header, Provider, Remote>
Returns Promise<void>
Returns Promise<void>
- port: number
Class WorkerConnector<Header, Provider, Remote>
Worker Connector.
+The WorkerConnector is a communicator class, who can create an Worker instance and
+communicate with it using RFC (Remote Function Call), considering the Worker as a
+remote system (WorkerServer).
You can create an Worker instance with compile() or connect() method.
+Anyway, after creation of the Worker instance, the Worker program must open a server
+using the WorkerServer.open() method.
Note that, after your business, don't forget terminating the worker using close() +or WorkerServer.close(). If you don't terminate it, then vulnerable memory and +communication channel would not be destroyed and it may cause the memory leak.
+Also, when declaring this WorkerConnector type, you've to define two template arguments, +Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the remote +system after the connection. I hope you and server not to omit it and utilize it as an +activation tool to enhance security.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote system.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote system, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of header containing initialization data like activation.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy
Implements
- IWorkerSystem
Index
Constructors
Accessors
Methods
Constructors
constructor
- new
Worker Connector<Header, Provider, Remote>(header, provider, type?): WorkerConnector<Header, Provider, Remote> Initializer Constructor.
+For reference, you're planning to run a bundled JavaScript file, +and you're using the NodeJS environment, you can't use the
+"thread"+mode. You've to use the"process"mode instead.Type Parameters
Parameters
Returns WorkerConnector<Header, Provider, Remote>
Accessors
header
- get header(): Header
Header containing initialization data like activation.
+Returns Header
state
- get state(): WebConnector.State
Get state.
+Get current state of connection state with the worker server.
+List of values are such like below:
+-
+
NONE: This instance is newly created, but did nothing yet.
+CONNECTING: Theconnectmethod is on running.
+OPEN: The connection is online.
+CLOSING: Theclosemethod is on running.
+CLOSED: The connection is offline.
+
Returns WebConnector.State
Methods
close
compile
- compile(content, options?): Promise<void>
Compile server and connect to there.
+The compile method tries compile JS source code, creates
+Workerinstance +with that code connects to theWorker. To complete the compilation and connection, +theWorkerprogram must open that server using the WorkerServer.open() +method.Note that, after your business has been completed, you've to close the
+Workerusing +close() or WorkerServer.close(). If you don't close that, vulnerable +memory usage and communication channel would not be destroyed and it may cause the +memory leak.Parameters
- content: string
JS Source code to compile.
+ - options: Partial<WorkerConnector.IConnectOptions> = {}
Returns Promise<void>
- content: string
connect
- connect(jsFile, options?): Promise<void>
Connect to server.
+The connect() method tries to create an
+Workerinstance and connect to the +Worker. To complete the connection, theWorkerprogram must open that server using +the WorkerServer.open() method.Note that, after your business has been completed, you've to close the
+Workerusing +close() or WorkerServer.close(). If you don't close that, vulnerable +memory usage and communication channel would not be destroyed and it may cause the +memory leak.Parameters
- jsFile: string
JS File to be WorkerServer.
+ - options: Partial<WorkerConnector.IConnectOptions> = {}
Returns Promise<void>
- jsFile: string
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: Provider
Class WorkerServer<Header, Provider, Remote>
Worker Server.
+The WorkerServer is a class representing a Worker server who can communicate with
+remote client, parent and creator of the Worker (anyway WorkerConnector), using
+RFC (Remote Function Call).
Unlike other servers, WorkerServer can accept only a client (WorkerConnector)
+because the worker is dependent on its parent instance (web page, node or parent worker).
+Thus, WorkerServer does not have any acceptor and communicates with client (its parent)
+by itself.
To start communication with the remote client, call the open() method with special
+Provider. After your business, don't forget terminating this worker using close()
+or WorkerConnector.close() method. If you don't terminate it, then vulnerable
+memory and communication channel would be kept and it may cause the memory leak.
Also, when declaring this WorkerServer type, you've to define two template arguments, +Header and Provider. The Header type repersents an initial data gotten from the remote +system after the connection.
+The second template argument Provider represents the features provided for the remote system.
+If you don't have any plan to provide any feature to the remote system, just declare it as
+null.
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type Parameters
- Header
Type of header containing initialization data like activation.
+ - Provider extends object | null
Type of features provided for remote system.
+ - Remote extends object | null
Type of features supported by remote system, used for getDriver function.
+
Hierarchy (view full)
- Communicator<Provider | undefined, Remote>
- WorkerServer
Implements
Index
Constructors
constructor
Accessors
state
Methods
close
Protected destructor
- destructor(error?): Promise<void>
Destory the communicator.
+A destory function must be called when the network communication has been closed. +It would destroy all function calls in the remote system (by
+Driver<Controller>), +which are not returned yet.The error instance would be thrown to those function calls. If the disconnection is +abnormal, then write the detailed reason why into the error instance.
+Parameters
Optionalerror: ErrorAn error instance to be thrown to the unreturned functions.
+
Returns Promise<void>
get
- get
Driver<Controller, UseParametric>(): Driver<Controller, UseParametric> Get Driver for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The
+Controlleris an interface who defines provided functions from the remote +system. TheDriveris an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in +theControllerand provided byProviderin the remote system, possible.In other words, calling a functions in the
+Driver<Controller>, it means to call +a matched function in the remote system'sProviderobject.-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
- Controller extends object = NonNullable<Remote>
An interface for provided features (functions & objects) from the remote system (
+Provider). - UseParametric extends boolean = false
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+
Returns Driver<Controller, UseParametric>
A Driver for the RFC.
+
get
get
join
- join(): Promise<void>
Join connection.
+Wait until the connection to be closed.
+Returns Promise<void>
- join(ms): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or timeout.
+Wait until the connection to be clsoed until timeout.
+Parameters
- ms: number
The maximum milliseconds for joining.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or timeout.
+- ms: number
- join(at): Promise<boolean>
Join connection or time expiration.
+Wait until the connection to be closed until time expiration.
+Parameters
- at: Date
The maximum time point to join.
+
Returns Promise<boolean>
Whether awaken by disconnection or time expiration.
+- at: Date
open
- open(provider): Promise<void>
Open server with
+Provider.Open worker server and start communication with the remote system +(WorkerConnector).
+Note that, after your business, you should terminate this worker to prevent waste +of memory leak. Close this worker by yourself (close) or let remote client to +close this worker (WorkerConnector.close).
+Parameters
- provider: Provider
An object providing featrues for the remote system.
+
Returns Promise<void>
- provider: Provider
Protected reply
- reply
Data(invoke): void Data Reply Function.
+A function should be called when data has come from the remote system.
+When you receive a message from the remote system, then parse the message with your +special protocol and covert it to be an Invoke object. After the conversion, call +this method.
+Parameters
- invoke: Invoke
Structured data converted by your special protocol.
+
Returns void
- invoke: Invoke
set
- set
Provider(obj): void Set
+ProviderParameters
- obj: undefined | Provider
An object would be provided for remote system.
+
Returns void
- obj: undefined | Provider
tgrid
TGrid
Introduction
Full name of TGrid is TypeScript Grid Computing Framework.
+As its name suggests, TGrid is a useful framework for implementating Grid Computing in the TypeScript. With TGrid and its core concept Remote Funtion Call, you can make many computers to be a virtual computer.
+To know more, refer below links. If you are the first comer to the TGrid, I strongly recommend you to read the Guide Documents. In article level, I Basic Concepts and Learn from Examples sections would be good choices.
+-
+
- Repositories + +
- Documents
-
+
- API Documents +
- Guide Documents + +
- Release Notes +
+
1.2. Grid Computing
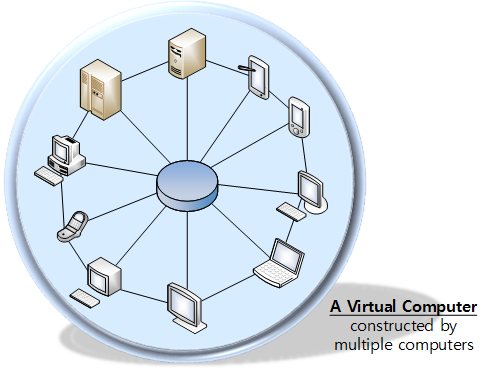
++Computers be a (virtual) computer
+
As its name suggests, TGrid is a useful framework for Grid Computing. However, perpective of Grid Computing in TGrid is something different. It doesn't mean just combining multiple computers uinsg network communication. TGrid insists the real Grid Computing must be possible to turning multiple computers into a virtual computer.
+Therefore, within framework of the TGrid, it must be possible to develop Grid Computing System as if there has been only a computer from the beginning. A program running on a computer and a Distributed +Processing System with millions, both of them must have similar program code. It's the real Grid Computing.
+Do you agree with me?
+1.3. Remote Function Call
TGrid realizes the Grid Computing through Remote Function Call. It literally calling remote system's functions are possible. With the Remote Function Call, you can access to objects of remote system as if they have been in my memory from the beginning.
+With TGrid and Remote Function Call, it's possible to handle remote system's objects and functions as if they're mine from the beginning. Do you think what that sentence means? Right, being able to call objects and functions of the remote system, it means that current and remote system are integrated into a single virtual computer.
+However, whatever Grid Computing and Remote Function Call are, you've only heard theoretical stories. Now, it's time to see the real program code. Let's see the demonstration code and feel the Remote Function Call. If you want to know more about the below demonstration code, read a section Learn from Examples wrote into the Guide Documents.
+composite-calculator/server.ts
import { WebServer } from "tgrid/protocols/web";
import { CompositeCalculator } from "../../providers/Calculator";
async function main(): Promise<void>
{
const server: WebServer<object, CompositeCalculator> = new WebServer();
await server.open(10102, async acceptor =>
{
await acceptor.accept(new CompositeCalculator());
});
}
main();
+composite-calculator/client.ts
import { WebConnector } from "tgrid/protocols/web/WebConnector";
import { Driver } from "tgrid/components/Driver";
import { ICalculator } from "../../controllers/ICalculator";
async function main(): Promise<void>
{
//----
// CONNECTION
//----
const connector: WebConnector<null, null> = new WebConnector(null, null);
await connector.connect("ws://127.0.0.1:10102");
//----
// CALL REMOTE FUNCTIONS
//----
// GET DRIVER
const calc: Driver<ICalculator> = connector.getDriver<ICalculator>();
// FUNCTIONS IN THE ROOT SCOPE
console.log("1 + 6 =", await calc.plus(1, 6));
console.log("7 * 2 =", await calc.multiplies(7, 2));
// FUNCTIONS IN AN OBJECT (SCIENTIFIC)
console.log("3 ^ 4 =", await calc.scientific.pow(3, 4));
console.log("log (2, 32) =", await calc.scientific.log(2, 32));
try
{
// TO CATCH EXCEPTION IS STILL POSSIBLE
await calc.scientific.sqrt(-4);
}
catch (err)
{
console.log("SQRT (-4) -> Error:", err.message);
}
// FUNCTIONS IN AN OBJECT (STATISTICS)
console.log("Mean (1, 2, 3, 4) =", await calc.statistics.mean(1, 2, 3, 4));
console.log("Stdev. (1, 2, 3, 4) =", await calc.statistics.stdev(1, 2, 3, 4));
//----
// TERMINATE
//----
await connector.close();
}
main();
+++ + ++1 + 6 = 7
7 * 2 = 14
3 ^ 4 = 81
log (2, 32) = 5
SQRT (-4) -> Error: Negative value on sqaure.
Mean (1, 2, 3, 4) = 2.5
Stdev. (1, 2, 3, 4) = 1.118033988749895 +
2. Strengths
2.1. Easy Development
Anyone can easily make a network system.
+It's difficult to make network system because many of computers are interacting together to accomplish a common task. Therefore, the word 'perfect' is inserted on every development processes; requirements must be analyzed perfectly, use-cases must be identified perfectly, data and network architectures must be designed, perfectly and mutual interaction test must be perfectly.
+++Something to Read
Blockchain's Network System, Steps to Hell
++
However, with TGrid and Remote Function Call, you can come true the true Grid Computing. Many computers interacting with network communication are replaced by only one virtual computer. Even Business Logic code of the virtual computer is same with another Business Logic code running on a single physical computer.
+Thus, you can make a network system very easily if you use the TGrid. Forget everything about the network; protocolcs and designing message structures, etc. You only concentrate on the Business Logic, the essence of what you want to make. Remeber that, as long as you use the TGrid, you're just making a single program running on a single (virtual) computer.
+2.2. Safe Implementation
By compilation and type checking, you can make network system safe.
+When developing a distributed processing system with network communication, one of the most embarrassing thing for developers is the run-time error. Whether network messages are correctly constructed and exactly parsed, all can be detected at the run-time, not the compile-time.
+Let's assume a situation; There's a distributed processing system build by traditional method and there's a critical error on the system. Also, the critical error wouldn't be detected until the service starts. How terrible it is? To avoid such terrible situation, should we make a test program validating all of the network messages and all of the related scenarios? If compilation and type checking was supported, everything would be simple and clear.
+TGrid provides exact solution about this compilation issue. TGrid has invented Remote Function Call to come true the real Grid Computing. What the Remote Function Call is? Calling functions remotly, isn't it a function call itself? Naturally, the function call is protected by TypeScript Compilter, therefore guarantees the Type Safety.
+Thus, with TGrid and Remote Function Call, you can adapt compilation and type checking on the network system. It helps you to develop a network system safely and conveniently. Let's close this chapter with an example of Safey Implementation.
+import { WebConnector } from "tgrid/protocols/web/WebConnector"
import { Driver } from "tgrid/components/Driver";
interface ICalculator
{
plus(x: number, y: number): number;
minus(x: number, y: number): number;
multiplies(x: number, y: number): number;
divides(x: number, y: number): number;
divides(x: number, y: 0): never;
}
async function main(): Promise<void>
{
//----
// CONNECTION
//----
const connector: WebConnector<null, null> = new WebConnector(null, null);
await connector.connect("ws://127.0.0.1:10101");
//----
// CALL REMOTE FUNCTIONS
//----
// GET DRIVER
const calc: Driver<ICalculator> = connector.getDriver<ICalculator>();
// CALL FUNCTIONS REMOTELY
console.log("1 + 6 =", await calc.plus(1, 6));
console.log("7 * 2 =", await calc.multiplies(7, 2));
// WOULD BE COMPILE ERRORS
console.log("1 ? 3", await calc.pliuowjhof(1, 3));
console.log("1 - 'second'", await calc.minus(1, "second"));
console.log("4 / 0", await calc.divides(4, 0));
}
main();
++++$ tsc
src/index.ts:33:37 - error TS2339: Property 'pliuowjhof' does not exist on type 'Driver<ICalculator>'.
console.log("1 ? 3", await calc.pliuowjhof(1, 3));
src/index.ts:34:53 - error TS2345: Argument of type '"second"' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number'.
console.log("1 - 'second'", await calc.minus(1, "second"));
src/index.ts:35:32 - error TS2349: Cannot invoke an expression whose type lacks a call signature. Type 'never' has no compatible call signatures.
console.log("4 / 0", await calc.divides(4, 0)); +
2.3. Network Refactoring
Critical changes on network systems can be resolved flexibly.
+In most case of developing network distributed processing system, there can be an issue that, necessary to major change on the network system. In someday, neccessary to refactoring in network level would be come, like software refactoring.
+The most representative of that is the performance issue. For an example, there is a task and you estimated that the task can be done by one computer. However, when you actually started the service, the computation was so large that one computer was not enough. Thus, you should distribute the task to multiple computers. On contrary, you prepared multiple computers for a task. However, when you actually started the service, the computation was so small that just one computer is sufficient for the task. Sometimes, assigning a computer is even excessive, so you might need to merge the task into another computer.
+ |
+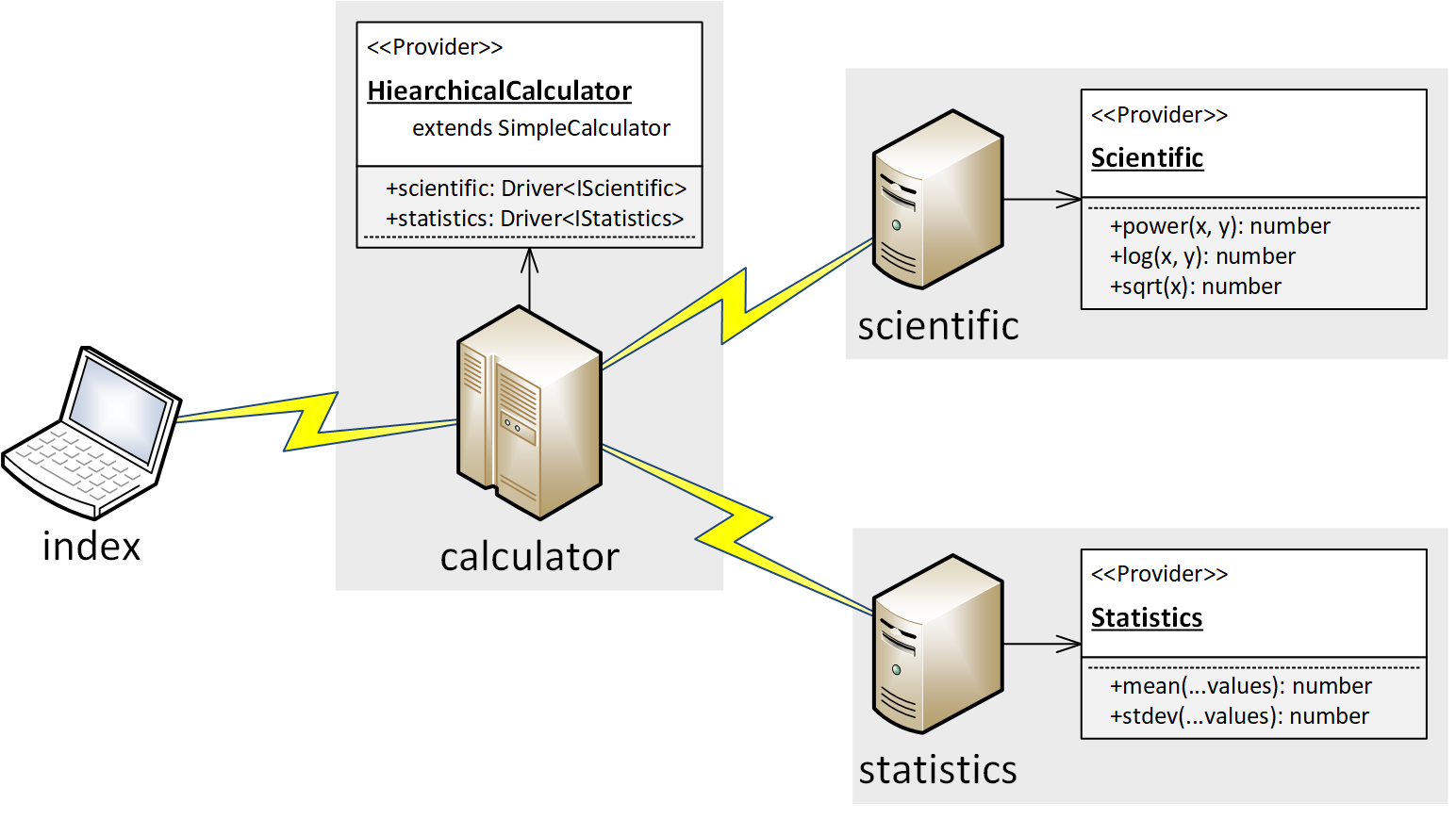 |
+
|---|---|
| Composite Calculator | +Hierarchical Calculator | +
I'll explain this Network Refactoring, caused by performance issue, through an example case that is very simple and clear. In a distributed processing system, there was a computer that providing a calculator. However, when this system was actually started, amount of the computations was so enormous that the single computer couldn't afford the computations. Thus, decided to separate the computer to three computers.
+-
+
scientific: scientific calculator server
+statistics: statistics calculator server
+calculator: mainframe server-
+
- four arithmetic operations are computed by itself +
- scientific and statistics operations are shifted to another computers +
- and intermediates the computation results to client +
+
If you solve this Network Refactoring by traditional method, it would be a hardcore duty. At first, you've to design a message protocol used for neetwork communication between those three computers. At next, you would write parsers for the designed network messges and reprocess the events according to the newly defined network architecture. Finally, you've to also prepare the verifications for those developments.
+++Things to be changed
++
+- Network Architecture
+- Message Protocol
+- Event Handling
+- Business Logic Code
+
However, if you use the TGrid and Remote Function Call, the issue can't be a problem. In the TGrid, each computer in the network system is just one object. Whether you implement the remote calculator in one computer or distribute operations to three computers, its Business Logic code must be the same, in always.
+I also provide you the best example for this performance issue causing the Network Refactoring. The first demonstration code is an implementation of a single calculator server and the second demonstration code is an implementation of a system distributing operations to three servers. As you can see, although principle structure of network system has been changed, you don't need to worry about it if you're using the TGrid and Remote Function Call.
+ +3. Opportunities
3.1. Blockchain
++Detailed Content: Appendix > Blockchain
+
With TGrid, you can develop Blockchain easily.
+It's a famous story that difficulty of developing blockchain is very high. Not only because of the high wages of the blockchain developers, but also from a technical point of view, blockchain is actually very difficult to implement. But, if you ask me what is such difficult, I will answer that not Business Logic* but Network System.
+The Network System used by blockchain is a type of great distributed processing system, conostructed by millions of computers interacting with network communication. The great distributed processing systems like the blockchain always present us the tremendous difficulties. The word 'perfect' is inserted on every development processes; requirements must be analyzed perfectly, use-cases must be identified perfectly, data and network architectures must be designed, perfectly and mutual interaction test must be perfectly.
+On contrary, Business Logic of the blockchain is not such difficult. Core elements of the blockchain are, as the name suggest, the first is 'Block' and the second is 'Chain'. The 'Block' is about defining and storing data and the 'Chain' is about policy that how to reach to an agreement when writing data to the 'Block'.
+| Component | +Conception | +Description | +
|---|---|---|
| Block | +Data Structure | +Way to defining and storing data | +
| Chain | +Requirements | +A policy for reaching to an agreement | +
Let's assume that you are developing the 'Block' and 'Chain' as a program running only on a single computer. In this case, you just need to design the data structure and implement code storing the data on disk. Also, you would analyze the requirements (policy) and implement them. Those skills are just the essentials for programmers. In other word, Business Logic of blockchain is something that any skilled programmers can implement.
+-
+
- To develop the Block and Chain:
-
+
- Ability to design Data Structure +
- Ability to store Data on Device +
- Ability to analyze policy (requirements) +
- Ability to implement them +
+
Do you remember? With TGrid and Remote Function Call, you can come true the true Grid Computing. Many computers interacting with network communication are replaced by only one virtual computer. Even Business Logic code of the virtual computer is same with another Business Logic code running on a single physical computer.
+Thus, if you adapt the TGrid and Remote Function Call, difficulty of the blockchain development would be dropped to the level of [Business Logic](https://tgrid.com/en/appendix/blockchain.html rather than Network System. Forget complex Network System and just focus on the essence of what you want to develop; the [Business Logic](https://tgrid.com/en/appendix/blockchain.html.
+3.2. Public Grid
++Related Project: Tutorial > Projects > Grid Market
+
With TGrid, you can procure resources for Grid Computing from unspecified crowds, very easily and inexpensively.
+When composing traditional Grid Computing, of course, many computers should be prepared. As the number of computers required increases, so does the infrastructure and costs associated with procuring them. Also, you've to install programs and configure settings for the network communication on the prepared computers. Such duties increase your efforts and let you to be tired. Is it so nature?
+| Name | +Consumer | +Supplier | +
|---|---|---|
| Who | +Developer of Grid Computing | +Unspecified crowds connecting to the Internet | +
| What | +Consumes resources of the Suppliers | +Provides resources to Consumer | +
| How | +Deliver program code to Suppliers | +Connect to special URL by Internet Browser | +
However, TGrid even can economize such costs and efforts dramatically. You can procure resources for Grid Computing from the unspecified crowds. Those unspecified crowds do not need to prepare anything like installing some program or configuring some setting. The only need those unspecified crowds is just connecting to special URL by Internet Browser.
+The program that each Supplier should run is provided by the Consumer as JavaScript code. Each Supplier would act its role by the JavaScript code. Of course, interactions with Supplier and Consumer (or with a third-party computer) would use the Remote Function Call, so they are just one virtual computer.
+++Base language of the TGrid is TypeScript and compilation result of the TypeScript is the JavaScript file. As JavaScript is a type of script language, it can be executed dinamiccaly. Therefore, the Supplier can execute the program by script code delivered by the Consumer.
+
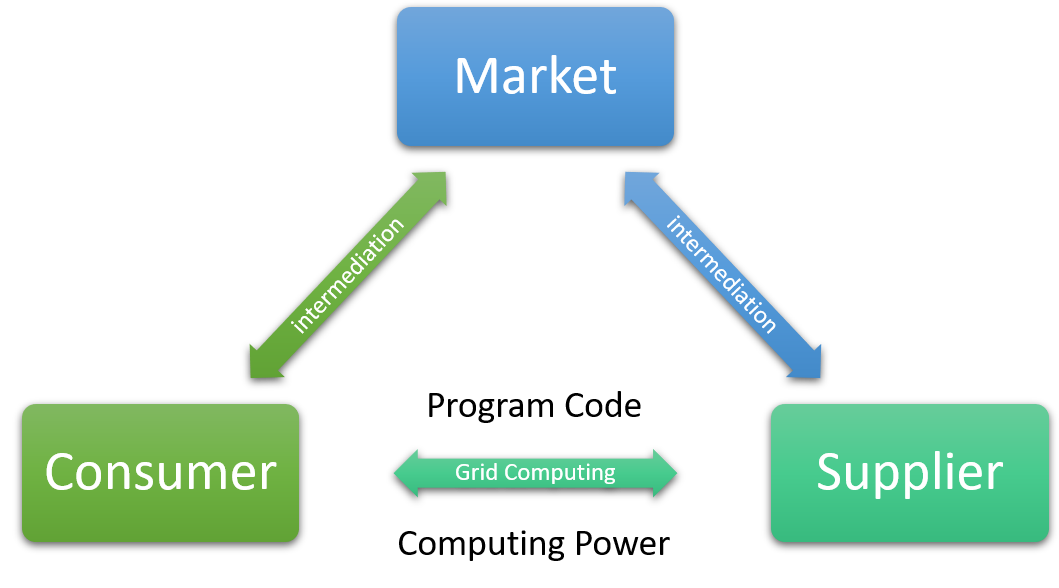
Grid Market is one of the most typical example case for the Public Grid, a demo project for tutorial learning. In this demo project, Consumer also procures resources from the Suppliers for composing the Grid Computing system. Supplier also provides its resources just by connecting to the special URL by Internet Browser, too. Of course, in the Grid Market, the program that Supplier would run still comes from the Consumer.
+However, there's a special thing about the Grid Market, it is that there is a cost for the Consumer to procure the Suppliers' resources. Also, intermediary Market exists and it charges fee for mediation between the Consumer and Supplier.
+-
+
Market: Intermediary market for the Suppliers and Consumers.
+Consumer: Purchase resources from the *Suppliers.
+Supplier: Sells its own resources to the Consumer.
+
3.3. Market Expansions
The Grid Computing market would be grown up day by day.
+The future belongs to those who prepare. Prepare the future by TGrid and Remote Function Call. Also, I hope you to hold some changes from the future.
+Interface IConnectOptions
Connection options for the SharedWorkerConnector.connect.
+ Index
Properties
Properties
timeout
Milliseconds to wait the shared-worker server to accept or reject it. If omitted, the waiting would be forever.
+Interface IConnectOptions
Connection options for the WebConnector.connect.
+ Index
Properties
Properties
timeout
Milliseconds to wait the web-socket server to accept or reject it. If omitted, the waiting would be forever.
+Interface IConnectOptions
Connection options for the WorkerConnector.connect.
+Properties
exec
Arguments only for the NodeJS environments.
+timeout
Milliseconds to wait the worker server to accept or reject it. If omitted, the waiting would be forever.
+tgrid
Index
Namespaces
Classes
Type Aliases
Variables
Namespace Invoke
Index
Interfaces
Namespace WebAcceptor
Index
Enumerations
Namespace WebConnector
Index
Enumerations
Interfaces
Namespace WebServer
Index
Enumerations
Namespace default
Index
References
Communicator
Re-exports CommunicatorDriver
Re-exports DriverInvoke
Re-exports InvokePrimitive
Re-exports PrimitivePromisive
Re-exports PromisiveShared
Re-exports SharedWorkerAcceptorShared
Re-exports SharedWorkerConnectorShared
Re-exports SharedWorkerServerWeb
Re-exports WebAcceptorWeb
Re-exports WebConnectorWeb
Re-exports WebErrorWeb
Re-exports WebServerWorker
Re-exports WorkerConnectorWorker
Re-exports WorkerServerType alias Driver<Controller, Parametric>
Driver RFC (Remote Function Call).
+The Controller is an interface who defines provided functions from the remote system.
+The Driver is an object who makes to call remote functions, defined in the
+Controller and provided by Provider in the remote system, possible.
In other words, calling a functions in the Driver<Controller>, it means to call a
+matched function in the remote system's Provider object.
-
+
Controller: Definition only
+Driver: Remote Function Call
+
Type Parameters
Template: UseParametric
Whether to convert type of function parameters to be compatible with their pritimive.
+Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type alias Invoke
Message structure for RFC (Remote Function Call).
+Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Type alias Primitive<T>
Primitive type of JSON.
+Primitive<T> is a TMP (Type Meta Programming) type which converts
+its argument as a primitive type within framework JSON.
If the target argument is a built-in class which returns its origin primitive type
+through the valueOf() method like the String or Number, its return type would
+be the string or number. Otherwise, the built-in class does not have the
+valueOf() method, the return type would be an empty object ({}).
Otherwise, the target argument is a type of custom class, all of its custom method
+would be erased and its prototype would be changed to the primitive object.
+Therefore, return type of the TMP type finally be the primitive object.
In addition, if the target argument is a type of custom class and it has a special
+method toJSON(), return type of this Primitive would be not Primitive<Instance>
+but Primitive<ReturnType<Instance.toJSON>>.
| Before | +After | +
|---|---|
Boolean |
+boolean |
+
Number |
+number |
+
String |
+string |
+
Class |
+object |
+
Class with toJSON() |
+Primitive<ReturnType<Class.toJSON>> |
+
| Native Class | +never | +
| Others | +No change | +
Type Parameters
Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+Author
Kyungsu Kang - https://github.com/kakasoo
+Author
Michael - https://github.com/8471919
+Type alias Promisive<Instance, UseParametric>
[P in keyof Instance]: Instance[P] extends Function
? Functional<Instance[P], UseParametric>
: ValueOf<Instance[P]> extends object
? Instance[P] extends object
? Promisive<Instance[P], UseParametric>
: never
: never
} & IRemoteObject>>
Promisify an object type.
+It promisifies all member types. When a member type is:
+-
+
- function: returns
Promise(R->Promise<R>).
+ - object: promisifies recursively (
O->Promisify<O>).
+ - atomic value: be ignored (be
nevertype).
+
Type Parameters
Variable Driver
+
+ Copyright 2018 - {new Date().getFullYear()}{" "} + + Samchon + {" "} + & Contributors + + ), + }, + useNextSeoProps() { + return { + defaultTitle: "TGrid Guide Documents", + titleTemplate: "TGrid Guide Documents - %s", + additionalLinkTags: [ + { + rel: "apple-touch-icon", + sizes: "180x180", + href: "/favicon/apple-touch-icon.png", + }, + { + rel: "manifest", + href: "/favicon/site.webmanifest", + }, + ...[16, 32].map((size) => ({ + rel: "icon", + type: "image/png", + sizes: `${size}x${size}`, + href: `/favicon/favicon-${size}x${size}.png`, + })), + ], + additionalMetaTags: [ + { + property: "og:image", + content: "/og.jpg", + }, + { + property: "og:type", + content: "object", + }, + { + property: "og:title", + content: "Typia Guide Documents", + }, + { + property: "og:description", + content: "Superfast Runtime Validator with only one line", + }, + { + property: "og:site_name", + content: "Typia Guide Documents", + }, + { + property: "og:url", + content: "https://tgrid.com", + }, + { + name: "twitter:card", + content: "summary", + }, + { + name: "twitter:image", + content: "https://tgrid.com/og.jpg", + }, + { + name: "twitter:title", + content: "TGrid Guide Documents", + }, + { + name: "twitter:description", + content: "Superfast Runtime Validator with only one line", + }, + { + name: "twitter:site", + content: "@SamchonGithub", + }, + ], + }; + }, +}; + +export default config; diff --git a/website/tsconfig.json b/website/tsconfig.json new file mode 100644 index 0000000..18cde56 --- /dev/null +++ b/website/tsconfig.json @@ -0,0 +1,31 @@ +{ + "compilerOptions": { + "target": "es5", + "lib": [ + "dom", + "dom.iterable", + "esnext" + ], + "allowJs": true, + "skipLibCheck": true, + "strict": true, + "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, + "noEmit": true, + "incremental": true, + "esModuleInterop": true, + "module": "esnext", + "moduleResolution": "node", + "resolveJsonModule": true, + "isolatedModules": true, + "jsx": "preserve", + "downlevelIteration": true, + }, + "include": [ + "next-env.d.ts", + "**/*.ts", + "**/*.tsx" + ], + "exclude": [ + "node_modules" + ] +} diff --git a/website/tsconfig.webpack.json b/website/tsconfig.webpack.json new file mode 100644 index 0000000..fd76ce4 --- /dev/null +++ b/website/tsconfig.webpack.json @@ -0,0 +1,31 @@ +{ + "compilerOptions": { + "target": "es5", + "lib": [ + "dom", + "dom.iterable", + "esnext" + ], + "allowJs": true, + "skipLibCheck": true, + "strict": true, + "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, + "outDir": "./bin", + "incremental": true, + "esModuleInterop": true, + "module": "esnext", + "moduleResolution": "node", + "resolveJsonModule": true, + "isolatedModules": true, + "jsx": "preserve", + "downlevelIteration": true, + }, + "include": [ + "next-env.d.ts", + "raw", + "src", + ], + "exclude": [ + "node_modules" + ] +} diff --git a/website/typedoc.json b/website/typedoc.json new file mode 100644 index 0000000..ebc0cf9 --- /dev/null +++ b/website/typedoc.json @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +{ + "tsconfig": "../tsconfig.json", + "entryPoints": [ + "../src/index.ts", + ], + "out": "./public/api" +} \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/website/webpack.config.js b/website/webpack.config.js new file mode 100644 index 0000000..a588f8f --- /dev/null +++ b/website/webpack.config.js @@ -0,0 +1,37 @@ +const path = require("path"); +const webpack = require("webpack"); + +module.exports = { + entry: ["./src/compilers/index.ts"], + output: { + path: path.join(__dirname, "public", "compilers"), + filename: "index.js", + chunkFormat: false, + }, + optimization: { + minimize: true, + }, + + mode: "development", + target: "web", + module: { + rules: [ + { + test: /\.ts$/, + exclude: /node_modules/, + loader: "ts-loader", + options: { + configFile: "tsconfig.webpack.json", + }, + }, + ], + }, + resolve: { + extensions: [".tsx", ".ts", ".js"], + }, + plugins: [ + new webpack.ProvidePlugin({ + process: "process/browser", + }), + ], +};


The basic communicator.
+The
+Communicatoris an abstract class taking full charge of network communication. +Protocolized communicators like WebConnector are realized by extending this +Communicatorclass.You want to make your own communicator using special protocol, extends this
+Communicator+class. After the extending, implement your special communicator by overriding those methods.+- inspectReady
+- replyData
+- sendData
+
+Author
Jeongho Nam - https://github.com/samchon
+