INFO The current raidEX version is a work in progress proof-of-concept to investigate how a DEX could be built on top of Raiden. It is not production ready and should absolutely not be used with mainnet funds!
While there are already decentralized exchanges, they are built on the blockchain and inherit the performance restrictions of the global consensus systems, i.e. especially latency and limited transaction throughput. This results in a low liquidity for these exchanges.
The mentioned performance restrictions are overcome by off-chain state technology, i.e. the Raiden Network for Ethereum. As raidEX is based on the Ethereum platform and the Raiden Network, it is fully interoperable and leverages synergies with tokens and apps in the Ethereum ecosystem.
A high level introduction to the raidEX protocol can be found in the following issue.
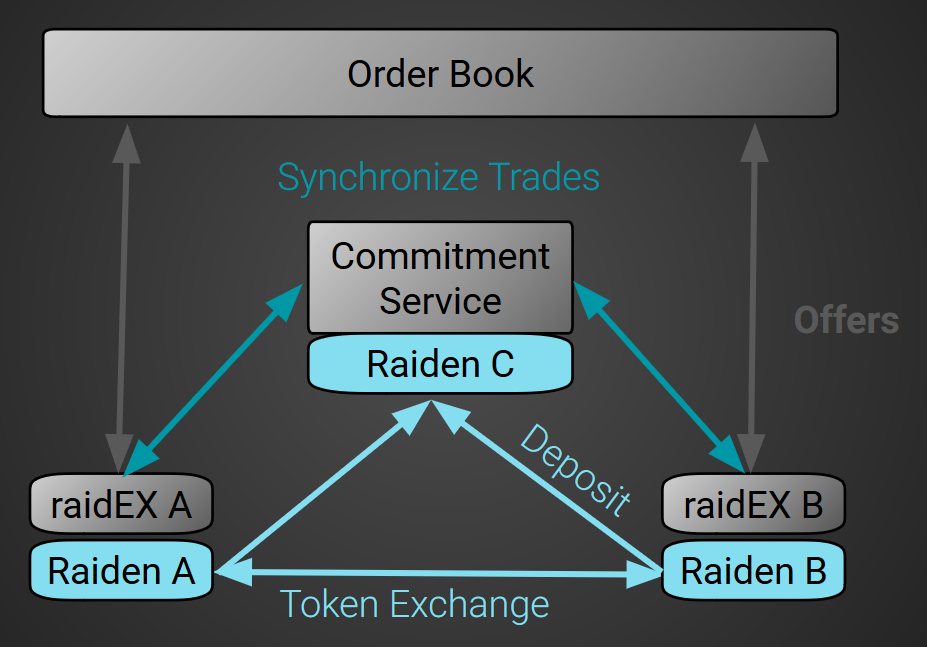
raidEX consists of several components
- Commitment Service
- Order Book
- raidEX nodes
- Raiden nodes
- Message Broker
When two parties want to engage in a trade the commitment service synchronizes the communication between them from the order creation until the settlement of a trade.
It is a trusted third party depository where traders provide a security that they are intending to engage in an exchange. On misbehavior this deposit could get slashed by the commitment service.
It acts as a notary upon commitment signing and settles the trade eventually by revealing the secret to the HTLC of the parties' payments via the raiden network.
In the happy case the commitment service returns the deposits minus a little fee for the service.
The intended goal is to reduce as much influence as possible from the commitment service. In the end it should only synchronize the communication and penalize on misbehavior.
Each raidEX node builds its own decentralized order book. It receives and publishes new orders from/to a public broadcast channel distributed via the message broker.
The raidEX node is the core instance implementing the raidEX protocol. It communicates with its respective raiden node, triggering payments and acknowledging when payments have been received. On the other end it communicates to other raidEX nodes or the commitment service via the message broker.
Every raidEX node as well as the commitment service need an underlying raiden node to transfer value. It is used to exchange assets via the raiden network or to deposit to the commitment service.
The message broker is a simple sub/pub model to exchange messages. raidEX nodes communicate via the message broker with the commitment service and to other raidEX nodes. It also reads and writes to/from the order book broadcast.
Raiden is the base layer of the raidEX protocol.
If you didn't use Raiden before, you can
- Checkout the developer portal
- Look at the documentation
- Learn more by watching explanatory videos
- Read the blog posts on Medium
To run the code in this repository, you need to
The raidEX project is currently configured to be used on the Kovan Testnet.
To run Raiden on Kovan, you need to
-
Get Kovan Ether (KETH) on the following Kovan Faucet.
-
Send KETH to the WETH contract address (
0xd0A1E359811322d97991E03f863a0C30C2cF029C) to get Wrapped Eth (WETH)
Currently raidEX supports one trading pair. The default trading pair is set to be WETH and Raiden Testnet Token (RTT) on the Kovan Testnet:
- WETH Contract Address:
0xd0A1E359811322d97991E03f863a0C30C2cF029C - RTT Contract Address:
0x92276aD441CA1F3d8942d614a6c3c87592dd30bb
Fees to the commitment service are paid in Raiden Testnet Token (RTT) which can be minted. You can adapt the following utility to mint RTTs.
Clone the repository from Github
git clone [email protected]:raiden-network/raidex.git`
Create a virtualenv for raidEX (requires python3.6) and install all python dependencies there.
# go to the raidex directory
cd raidex
# create virtual environment
python3.6 -m venv venv
#activate virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
Install with
python setup.py develop
For the current version, Raiden, the Message Broker and the Commitment Service need to run before starting the raidEX node. Currently the raidEX Node is configured to be used in Kovan Testnet.
Info: In order to have a full trading experience it is necessary to run at least two raidEX nodes (traders). Each node relies on its own raiden node instance. Also the commitment service needs its own raiden node running. Please make sure to use different port settings for all instances and use unique keystores for every raidEX node including the commitment service.
# go to the raidex directory
cd raidex
#Activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
#Run the Message Broker with
python raidex/message_broker/server.py
Start Raiden as described in the Raiden Installation Guide.
Info: Run Raiden with the same keystore file as your corresponding raidEX node later on.
If you want to run the commitment service by yourself, you need to start a new Raiden Node for the commitment service.
Info: Run the Commitment Service with the same keystore file as the corresponding Raiden Node.
Run a Raiden Node for the commitment service as described above. Choose a different port and keystore for the commitment service.
Start the Commitment Service
# go to the raidex directory
cd raidex
# activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# run the commitment service
python raidex/commitment_service/__main__.py --trader-port *PATH_TO_RAIDEN_NODE* --keyfile *PATH_TO_KEYFILE* --pwfile *PATH_TO_PASSWORD_FILE*`
In order to be able to pay the fees to the Commitment Service a Raiden Channel from the user's node to the commitment service node must be created and topped up. A convinient way to create channels is using the Raiden WebUI (by default http://localhost:5001). Currently fees are getting payed in Raiden Testnet Token (RTT).
Open a channel to the CS and deposit RTT as described in Raiden WebUI Tutorial
After running the Raiden Node, the message broker and the commitment service you can start the raidEX Node.
# go to the raidex directory
cd raidex
# activate virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# start the Raidex Node
raidex --api --keyfile=*PATH_TO_KEYFILE* --pwfile=*PATH_TO_PASSWORD_FILE* --trader-port=*PORT_TO_RAIDEN_NODE* --api-port=*RAIDEX_API_PORT*
Install all dependecies (see ./webui/README.md) of the raidEX WebUI.
Start the raidEX WebUI.
cd webui
ng serve
Start the WebUI as described in the Web Application Tutorial
For testing please use pytest
# go to the raidex directory
cd raidex
# activate virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# run tests
pytest raidex/tests/
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
Also have a look at the raidEX Development Guide for more info.
Distributed under the MIT License.
Dev Chat: Gitter
Twitter: @raiden_network
Website: Raiden Network
Mail: [email protected]
The Raiden project is led by brainbot labs Est.
Disclaimer: Please note, that even though we do our best to ensure the quality and accuracy of the information provided, this publication may contain views and opinions, errors and omissions for which the content creator(s) and any represented organization cannot be held liable. The wording and concepts regarding financial terminology (e.g. “payments”, “checks”, “currency”, “transfer” [of value]) are exclusively used in an exemplary way to describe technological principles and do not necessarily conform to the real world or legal equivalents of these terms and concepts.