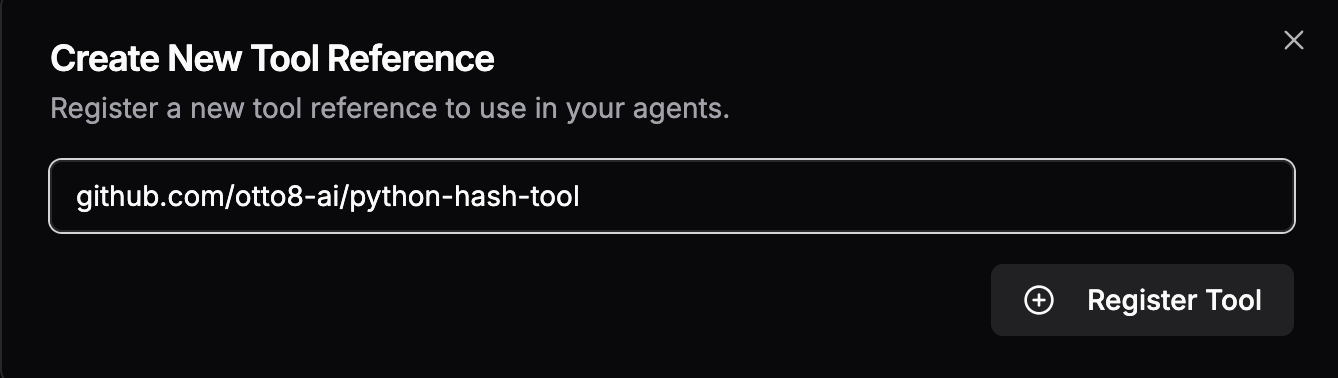
python-hash-tool contains a reference Python implementation of the Hash tool.
This guide walks through the structure and design of the tool and outlines the packaging requirements for Obot
To clone this repo and follow along, run the following command:
git clone [email protected]:obot-platform/python-hash-toolThe directory tree below highlights the files required to implement Hash in Python and package it for Obot.
python-hash-tool
├── hash.py
├── requirements.txt
└── tool.gpt
The tool.gpt file contains GPTScript Tool Definitions which describe a set of tools that can be used by agents in Obot.
Every tool repository must have a tool.gpt file in its root directory.
The tools defined in this file must have a Name and Description that will help agents understand what the tool does, what it returns (if anything), and all the Parameters it takes.
Agents use these details to figure out when and how to use the tool. We call the section of a tool definition that contains this info a Preamble.
We want the Hash tool to return the hash of some given data. It would also be nice to support a few different algorithms for the agent to choose from.
Let's take a look at the Preamble for Hash to see how that's achieved:
Name: Hash
Description: Generate a hash of data using the given algorithm and return the result as a hexadecimal string
Param: data: The data to hash
Param: algo: The algorithm to generate a hash with. Supports "sha256" and "md5". Default is "sha256"Breaking this down a bit:
- The
Preambleabove declares a tool namedHash - The
Paramfields enumerate the arguments that an agent must provide when callingHash,dataandalgo - In this case, the description of the
algoparameter outlines the valid options (sha256ormd5) and defines a default value (sha256) - The
Descriptionexplains whatHashreturns with respect to the given arguments; the hash ofdatausing the algorithm selected withalgo
Immediately below the Preamble is the Tool Body, which tells Obot how to execute the tool:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 ${GPTSCRIPT_TOOL_DIR}/hash.pyThis is where the magic happens.
To simplify, when an agent calls the Hash tool, Obot reads this line and then:
- Downloads the appropriate
Pythontoolchain - Sets up a working directory for the tool and creates a virtual environment
- Installs the dependencies from the
requirements.txt, if present - Projects the call arguments onto environment variables (
DATAandALGO) - Runs
python3 ${GPTSCRIPT_TOOL_DIR}/hash.py
Putting it all together, here's the complete definition of the Hash tool.
Name: Hash
Description: Generate a hash of data using the given algorithm and return the result as a hexadecimal string
Param: data: The data to hash
Param: algo: The algorithm to generate a hash with. Default is "sha256". Supports "sha256" and "md5".
#!/usr/bin/env python3 ${GPTSCRIPT_TOOL_DIR}/hash.pyThe snippet below (from the tool.gpt file) also provides the following metadata for use in Obot:
!metadata:*:categorywhich tags all tools in thetool.gptfile with theCryptocategory to promote organization and discovery!metadata:*:iconwhich assignshttps://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@phosphor-icons/core@2/assets/duotone/fingerprint-duotone.svgas the tool icon to all tools in thetool.gptfile
Note:
*is a wildcard pattern that applies the metadata to all tools in atool.gpt.
---
!metadata:*:category
Crypto
---
!metadata:*:icon
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@phosphor-icons/core@2/assets/duotone/fingerprint-duotone.svg
Note: Metadata can be applied to a specific tool by either specifying the exact name (e.g. !metadata:Hash:category) or by adding the metadata directly to a tool's Preamble
Name: Hash
Metadata: category: Crypto
Metadata: icon: https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@phosphor-icons/core@2/assets/duotone/fingerprint-duotone.svgComplete tool.gpt
---
Name: Hash
Description: Generate a hash of data using the given algorithm and return the result as a hexadecimal string
Param: data: The data to hash
Param: algo: The algorithm to generate a hash with. Supports "sha256" and "md5". Default is "sha256"
#!/usr/bin/env python3 ${GPTSCRIPT_TOOL_DIR}/hash.py
---
!metadata:*:category
Crypto
---
!metadata:*:icon
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@phosphor-icons/core@2/assets/duotone/fingerprint-duotone.svgThe hash.py file executed by the Tool Body is the concrete implementation of the tool's business logic.
Let's walk through the code to understand how it works.
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except Exception as err:
# Print err to stdout to return the error to the agent
print(f'Error: {err}')
sys.exit(1)Starting at the bottom, the main function is called in a try block so that any runtime exceptions caught are written to stdout.
This is important because everything written to stdout is returned to the agent when the tool call is completed, while everything written to stderr is discarded.
Using this pattern ensures that when a tool call fails, the calling agent is informed of the failure.
Moving on, the main function implements the core logic of the Hash tool.
SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS = ['sha256', 'md5']
def main():
# Extract the tool's `data` argument from the env
data = os.getenv('DATA')
if not data:
raise ValueError('A data argument must be provided')
# Extract the tool's `algo` argument from the env and default to `sha256`
algo = os.getenv('ALGO', 'sha256')
if algo not in SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS:
# Return the supported algorithms in the error message to help agents choose a valid
# algorithm the next time they call this tool
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported hash algorithm: {algo} not in {SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS}')
#...It starts off by extracting the tool's arguments from the respective environment variables and validates them.
When an argument is invalid, the function raises an exception that describes the validation issue in detail.
The goal is to provide useful information that an agent can use to construct valid arguments for future calls.
For example, when an invalid algo argument is provided, the code returns an error that contains the complete list of valid algorithms.
After validating the tool arguments, it calculates the hash and writes a JSON object to stdout. This object contains the hash and the algorithm used to generate it.
# ...
# Generate the hash
hash_obj = hashlib.new(algo)
hash_obj.update(data.encode('utf-8'))
# Return the hash along with the algorithm used to generate it.
# Providing more information in the tool's response makes it easier for agents to keep
# track of the context.
print(json.dumps({
'algo': algo,
'hash': hash_obj.hexdigest()
}))Note: Producing structured data with extra contextual info (e.g. the algorithm) is considered good form. It's a pattern that improves the Agent's ability to correctly use the tool's result over time.
Complete hash.py
import hashlib
import json
import os
import sys
SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS = ['sha256', 'md5']
def main():
# Extract the tool's `data` argument from the env
data = os.getenv('DATA')
if not data:
raise ValueError('A data argument must be provided')
# Extract the tool's `algo` argument from the env and default to `sha256`
algo = os.getenv('ALGO', 'sha256')
if algo not in SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS:
# Return the supported algorithms in the error message to help assistants choose a valid
# algorithm the next time they call this tool
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported hash algorithm: {algo} not in {SUPPORTED_HASH_ALGORITHMS}')
# Generate the hash
hash_obj = hashlib.new(algo)
hash_obj.update(data.encode('utf-8'))
# Return the hash along with the algorithm used to generate it.
# Providing more information in the tool's response makes it easier for assistants to keep
# track of the context.
print(json.dumps({
'algo': algo,
'hash': hash_obj.hexdigest()
}))
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except Exception as err:
# Print err to stdout to return the error to the assistant
print(f'Error: {err}')
sys.exit(1)Before adding a tool to Obot, verify that the Python business logic works on your machine.
To do this, run through the following steps in the root of your local fork:
-
Set up a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate -
Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate -
Install and freeze dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt pip freeze > requirements.txt -
Run the tool with some test arguments:
Command Output DATA='foo' python3 hash.py{ "algo": "sha256", "hash": "2c26b46b68ffc68ff99b453c1d30413413422d706483bfa0f98a5e886266e7ae" }python3 hash.pyError: A data argument must be providedDATA='foo' ALGO='md5' python3 hash.py{ "algo": "md5", "hash": "acbd18db4cc2f85cedef654fccc4a4d8" }DATA='foo' ALGO='whirlpool' python3 hash.pyError: Unsupported hash algorithm: whirlpool not in ['sha256', 'md5']
Before a tool can be used by an agent, an admin must first add the tool to Obot by performing the steps below:
To use the Hash tool in an agent, open the agent's Edit page, then: