The random module provides access to functions that support many operations. The most important thing is that it allows you to generate random numbers.
is an in-built module of Python which is used to generate random numbers. in a given range Pick a random element from a :
- list
- pick a random card from a deck
- flip a coin etc.
pov: When making your password database more secure or powering a random page feature of your website.
The Random module contains some very useful functions.
- Randint is function Randint accepts:
- two parameters: a lowest and a highest number. What it do?
- Generate integers between 1,5. The first value should be less than the second.
import random
print random.randint(0, 5)
This will output either 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5.
- Random If you want a larger number, you can multiply it.
For example, a random number between 0 and 100:
import random
random.random() * 100
- Choice Generate a random value from the sequence sequence.
random.choice( ['red', 'black', 'green'] ). The choice function can often be used for choosing a random element from a list.
import random
myList = [2, 109, False, 10, "Lorem", 482, "Ipsum"]
random.choice(myList)
- Shuffle The shuffle function, shuffles the elements in list in place, so they are in a random order.
from random import shuffle
x = [[i] for i in range(10)]
shuffle(x)
Output:
# print x gives [[9], [2], [7], [0], [4], [5], [3], [1], [8], [6]]
# of course your results will vary
- Randrange Generate a randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step)
random.randrange(start, stop[, step])
import random
for i in range(3):
print random.randrange(0, 101, 5)
In Software Testing risk analysis is the process of identifying the risks in applications or software that you built and prioritizing them to test.
Why use Risk Analysis?
-
Using risk analysis at the beginning to highlights the potential problem areas.
-
After knowing about the risk areas, it helps the developers and managers to mitigate the risks
-
Now, you might think what could be the possible risks that you could encounter? Well here is a list:
- Use of new hardware
- Use of new technology
- Use of new automation tool
- The sequence of code
- Availability of test resources for the application
- The time that you allocated for testing
- A defect leakage due to the complexity or size of the application
- Urgency from the clients to deliver the project
- Incomplete requirements
- Conduct Risk Assessment review meeting
- Use maximum resources to work on high-risk areas
- Create a Risk Assessment database for future use
- Identify and notice the risk magnitude indicators: high, medium, low.
- High: means the effect of the risk would be very high and non-tolerable. The company might face loss.
- Medium: it is tolerable but not desirable. The company may suffer financially but there is a limited risk.
- Low: it is tolerable. There lies little or no external exposure or no financial loss.
There are different sets of risks included in the risk identification process. Those are as follows:
-
Business Risks: This risk is the most common risk associated with our topic.
-
Testing Risks: You should be well acquainted with the platform you are working on, along with the software testing tools being used.
-
Premature Release Risk: a fair amount of knowledge to analyze the risk associated with releasing unsatisfactory or untested software is required
-
Software Risks: You should be well versed with the risks associated with the software development process.
There are three perspectives of Risk Assessment:
- Effect:To assess risk by Effect. In case you identify a condition, event or action and try to determine its impact.
- Cause:To assess risk by Cause is opposite of by Effect.
- Likelihood:To assess risk by Likelihood is to say that there is a probability that a requirement won’t be satisfied.
There are three steps:
- Searching the risk
- Analyzing the impact of each individual risk
- Measures for the risk identified
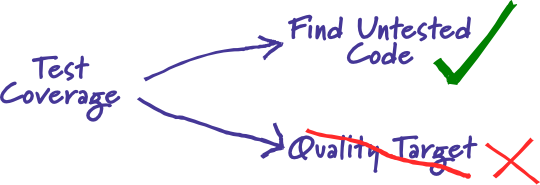
Test coverage is defined as a metric in Software Testing that measures the amount of testing performed by a set of test
- Finding the area of a requirement not implemented by a set of test cases
- Helps to create additional test cases to increase coverage
- Identifying a quantitative measure of test coverage, which is an indirect method for quality check
- Identifying meaningless test cases that do not increase coverage
- Test coverage can be done by exercising the static review techniques like peer reviews, inspections, and walkthrough
- By transforming the ad-hoc defects into executable test cases
you are doing enough testing if the following is true:
1.You rarely get bugs that escape into production, and
2.You are rarely hesitant to change some code for fear it will cause production bugs.
- It can assure the quality of the test
- It can help identify what portions of the code were actually touched for the release or fix
- It can help to determine the paths in your application that were not tested
- Prevent Defect leakage
- Time, scope and cost can be kept under control
Back to 2009 they mesure how arrive faster internet or the pigeon they found the pigeon arrive faster than the internet HOW MASURE BIG O:
Big O is essentially an equation that describes
- What's the runtime of this?one way you can describe it is O Claculate Big O:
- first one is if you have two different steps in your algorithm, you add up those steps.
- second rule is that you drop constants
- The third rule is that if you have different inputs you're usually going to use different variables to represent them.