diff --git a/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/__init__.py b/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e69de29bb2
diff --git a/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder.py b/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..69eca7add1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder.py
@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+import torch
+from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
+from pyspark.ml.functions import predict_batch_udf
+from pyspark.ml import Transformer
+from pyspark.ml.param.shared import HasInputCol, HasOutputCol, Param, Params
+from pyspark.sql.types import (
+ ArrayType,
+ FloatType,
+)
+
+
+class HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(Transformer, HasInputCol, HasOutputCol):
+ """
+ Custom transformer that extends PySpark's Transformer class to
+ perform sentence embedding using a model with optional TensorRT acceleration.
+ """
+
+ NUM_OPT_ROWS = 100 # Constant for number of rows taken for model optimization
+
+ BATCH_SIZE_DEFAULT = 64
+
+ # Define additional parameters
+ runtime = Param(
+ Params._dummy(),
+ "runtime",
+ "Specifies the runtime environment: cpu, cuda, or tensorrt",
+ )
+ batchSize = Param(Params._dummy(), "batchSize", "Batch size for embeddings", int)
+ modelName = Param(Params._dummy(), "modelName", "Full Model Name parameter")
+
+ def __init__(
+ self,
+ inputCol=None,
+ outputCol=None,
+ runtime=None,
+ batchSize=None,
+ modelName=None,
+ ):
+ """
+ Initialize the HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder with input/output columns and optional TRT flag.
+ """
+ super(HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder, self).__init__()
+
+ # Determine the default runtime based on CUDA availability
+ default_runtime = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
+
+ # Override the provided runtime if CUDA is not available
+ effective_runtime = runtime if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
+
+ self._setDefault(
+ runtime=default_runtime,
+ batchSize=self.BATCH_SIZE_DEFAULT,
+ )
+ self._set(
+ inputCol=inputCol,
+ outputCol=outputCol,
+ runtime=effective_runtime,
+ batchSize=batchSize if batchSize is not None else self.BATCH_SIZE_DEFAULT,
+ modelName=modelName,
+ )
+ self.optData = None
+ self.model = None
+ # Placeholder for the DataFrame row count check
+ self.row_count = 0 # This should be set when the DataFrame is available
+
+ # Setter method for batchSize
+ def setBatchSize(self, value):
+ self._set(batchSize=value)
+ return self
+
+ # Getter method for batchSize
+ def getBatchSize(self):
+ return self.getOrDefault(self.batchSize)
+
+ # Sets the runtime environment for the model.
+ # Supported values: 'cpu', 'cuda', 'tensorrt'
+ def setRuntime(self, value):
+ """
+ Sets the runtime environment for the model.
+ Supported values: 'cpu', 'cuda', 'tensorrt'
+ """
+ # if value not in ["cpu", "cuda", "onnxrt", "tensorrt"]:
+ if value not in ["cpu", "cuda", "tensorrt"]:
+ raise ValueError(
+ "Invalid runtime specified. Choose from 'cpu', 'cuda', 'tensorrt'"
+ )
+ self.setOrDefault(self.runtime, value)
+
+ def getRuntime(self):
+ return self.getOrDefault(self.runtime)
+
+ # Setter method for modelName
+ def setModelName(self, value):
+ self._set(modelName=value)
+ return self
+
+ # Getter method for modelName
+ def getModelName(self):
+ return self.getOrDefault(self.modelName)
+
+ def setRowCount(self, row_count):
+ self.row_count = row_count
+ # Override the runtime if row count is less than 100 or CUDA is not available
+ if self.row_count < 100 or not torch.cuda.is_available():
+ self.set(self.runtime, "cpu")
+ return self
+
+ # Optimize the model using Model Navigator with TensorRT configuration.
+ def _optimize(self, model):
+ import tensorrt as trt
+ import model_navigator as nav
+
+ conf = nav.OptimizeConfig(
+ target_formats=(nav.Format.TENSORRT,),
+ runners=("TensorRT",),
+ optimization_profile=nav.OptimizationProfile(
+ max_batch_size=self.BATCH_SIZE_DEFAULT
+ ),
+ custom_configs=[
+ nav.TorchConfig(autocast=True),
+ nav.TorchScriptConfig(autocast=True),
+ nav.TensorRTConfig(
+ precision=(nav.TensorRTPrecision.FP16,),
+ onnx_parser_flags=[trt.OnnxParserFlag.NATIVE_INSTANCENORM.value],
+ ),
+ ],
+ )
+
+ def _get_dataloader():
+ input_data = self.optData
+ return [
+ (
+ 0,
+ (
+ input_data,
+ {"show_progress_bar": False, "batch_size": self.getBatchSize()},
+ ),
+ )
+ ]
+
+ nav.optimize(model.encode, dataloader=_get_dataloader(), config=conf)
+
+ def _predict_batch_fn(self):
+ """
+ Create and return a function for batch prediction.
+ """
+ runtime = self.getRuntime()
+ if self.model == None:
+ global model
+ modelName = self.getModelName()
+
+ model = SentenceTransformer(
+ modelName, device="cpu" if runtime == "cpu" else "cuda"
+ ).eval()
+
+ if runtime in ("tensorrt"):
+ import tensorrt as trt
+ import model_navigator as nav
+
+ # this forces navigator to use specific runtime
+ nav.inplace_config.strategy = nav.SelectedRuntimeStrategy(
+ "trt-fp16", "TensorRT"
+ )
+
+ moduleName = modelName.split("/")[1]
+ model = nav.Module(model, name=moduleName, forward_func="forward")
+ try:
+ nav.load_optimized()
+ except Exception:
+ self._optimize(model)
+ nav.load_optimized()
+
+ self.model = model
+
+ def predict(inputs):
+ """
+ Predict method to encode inputs using the model.
+ """
+ with torch.no_grad():
+ output = model.encode(
+ inputs.tolist(), convert_to_tensor=False, show_progress_bar=False
+ )
+
+ return output
+
+ return predict
+
+ # Method to apply the transformation to the dataset
+ def _transform(self, dataset, spark):
+ """
+ Apply the transformation to the input dataset.
+ """
+ input_col = self.getInputCol()
+ output_col = self.getOutputCol()
+
+ size = dataset.count()
+ self.setRowCount(size)
+ if size >= self.NUM_OPT_ROWS:
+ df = dataset.take(self.NUM_OPT_ROWS)
+ self.optData = [row[input_col] for row in df]
+
+ encode = predict_batch_udf(
+ self._predict_batch_fn,
+ return_type=ArrayType(FloatType()),
+ batch_size=self.getBatchSize(),
+ )
+ return dataset.withColumn(output_col, encode(input_col))
+
+ def transform(self, dataset, spark=None):
+ """
+ Public method to transform the dataset.
+ """
+ return self._transform(dataset, spark)
diff --git a/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/__init__.py b/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e93fd6a140
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deep-learning/src/main/python/synapse/ml/hf/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+from synapse.ml.hf.HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder import *
diff --git a/deep-learning/src/test/python/synapsemltest/hf/test_HuggingFaceSentenceTransformer.py b/deep-learning/src/test/python/synapsemltest/hf/test_HuggingFaceSentenceTransformer.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..00208dae03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/deep-learning/src/test/python/synapsemltest/hf/test_HuggingFaceSentenceTransformer.py
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+# Copyright (C) NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
+# Licensed under the Apache License, See LICENSE in project root for information.
+
+import os, json, subprocess, unittest
+from synapse.ml.hf import HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder
+from synapse.ml.nn import KNN
+from synapse.ml.core.init_spark import *
+from pyspark.sql import DataFrame, SQLContext
+
+spark = init_spark()
+sc = SQLContext(spark.sparkContext)
+
+
+class HuggingFaceSentenceTransformerTest(unittest.TestCase):
+ def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ super(HuggingFaceSentenceTransformerTest, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
+
+ self.miniLMSize = 384
+ self.e5Size = 1024
+
+ self.e5Transformer = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(
+ modelName="intfloat/e5-large-v2",
+ inputCol="data",
+ outputCol="embeddings",
+ runtime="cpu",
+ )
+
+ self.miniLMTransformer = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(
+ modelName="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
+ inputCol="data",
+ outputCol="embeddings",
+ runtime="cpu",
+ )
+
+ # construction of test dataframe
+ self.sentenceDataFrame = sc.createDataFrame(
+ [
+ (1, "Happy"),
+ (2, "Good"),
+ (3, "Delicious"),
+ (4, "Like it"),
+ (5, "OK"),
+ (6, "Disgusting"),
+ (7, "Bad"),
+ (8, "Don't like it"),
+ (9, "Tastless"),
+ (10, "Poor quality"),
+ ],
+ ["id", "data"],
+ )
+ # self.sentenceDataFrame = (
+ # init_spark()
+ # .createDataFrame([(1, "desserts"), (2, "disgusting")], ["id", "data"])
+ # .cache()
+ # )
+
+ def test_e5_Embedding(self):
+ self._assert_input(self.sentenceDataFrame)
+ transformed = self.e5Transformer.transform(self.sentenceDataFrame).cache()
+ self._assert_input(transformed)
+ self._assert_embedding_df_size(self.sentenceDataFrame, transformed)
+ self._assert_embedding_embedding_size(transformed, self.e5Size)
+
+ def test_miniLM_Embedding(self):
+ self._assert_input(self.sentenceDataFrame)
+ transformed = self.miniLMTransformer.transform(self.sentenceDataFrame).cache()
+ self._assert_input(transformed)
+ self._assert_embedding_df_size(self.sentenceDataFrame, transformed)
+ self._assert_embedding_embedding_size(transformed, self.miniLMSize)
+
+ def _assert_input(self, input):
+ # Use assert to check if the result is a DataFrame
+ testDf = self.sentenceDataFrame
+ assert isinstance(testDf, DataFrame), "The input is not a DataFrame."
+
+ def _assert_embedding_embedding_size(self, transformed, expected_size):
+ # Debugging to check the type
+ collected_data = transformed.collect()
+ for row in collected_data:
+ embeddings_array = row["embeddings"]
+ size = len(embeddings_array)
+ assert (
+ size == expected_size
+ ), f"Embedding size mismatch: expected {expected_size}, got {size}"
+
+ def _assert_embedding_df_size(self, dataframe, transformed):
+ num_rows = transformed.count()
+ expected_num_rows = dataframe.count()
+ assert (
+ num_rows == expected_num_rows
+ ), f"DataFrame size mismatch after transformation: expected {expected_num_rows}, got {num_rows}"
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ result = unittest.main()
diff --git a/docs/Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - Custom Embeddings and Approximate KNN on GPU.ipynb b/docs/Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - Custom Embeddings and Approximate KNN on GPU.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e979110a30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - Custom Embeddings and Approximate KNN on GPU.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,583 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "6166efcb-b7f8-424b-8015-cb646a764271",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Embedding Text with local (per node) NVIDIA TensorRT accelerator and GPU based Aproximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN)\n",
+ "\n",
+ "The demo extending existing [Azure OpenAI based demo](https://github.com/microsoft/SynapseML/blob/master/docs/Explore%20Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart%20-%20OpenAI%20Embedding%20and%20GPU%20based%20KNN.ipynb) when encoding is processed by OpenAI requests and KNN was using GPU based brute force search. This tutorial shows how to perform fast local embeddings using [multilingual E5 text embeddings](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.05672) and fast aproximate Nearest Neighbor search using IVFFlat alcorithm. All tutorial stages accelerated by NVIDIA GPU using [NVIDIA TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) and [Spark Rapids ML](https://github.com/NVIDIA/spark-rapids-ml). The tutorial folder contains two benchmark notebooks to demonstrate advantages of the presented GPU based approach compare to [previos CPU based demo](https://github.com/microsoft/SynapseML/blob/master/docs/Explore%20Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart%20-%20OpenAI%20Embedding.ipynb)\n",
+ "\n",
+ "The key prerequisites for this quickstart include a working Azure OpenAI resource, and an Apache Spark cluster with SynapseML installed. We suggest creating a Synapse workspace, but currently the notebook was running on Databricks GPU based cluster using Standard_NC24ads_A100_v4 with 6 workers. Databricks Runtime was 13.3 LTS ML (includes Apache Spark 3.4.1, GPU, Scala 2.12) with related [init_script](https://github.com/microsoft/SynapseML/tree/master/tools/init_scripts) to install all required packages.\n"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "0444a03d-a701-4f59-b1a1-c4addb797d07",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 1: Prepare Environment\n",
+ "\n",
+ "It will imports required libraries and get initial settings"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "d188d8ee-8913-4170-8d35-8490f833ae95",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "import torch\n",
+ "import sys\n",
+ "import pyspark.sql.functions as F\n",
+ "from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, IntegerType, StringType\n",
+ "from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors\n",
+ "from pyspark.ml.linalg import VectorUDT\n",
+ "from spark_rapids_ml.knn import (\n",
+ " ApproximateNearestNeighbors,\n",
+ " ApproximateNearestNeighborsModel,\n",
+ ")\n",
+ "from synapse.ml.hf import HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder\n",
+ "from synapse.ml.nn import KNN"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "42117315-a245-491a-b330-f8257d6fb35c",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 2: Load Input Data\n",
+ "\n",
+ "It will load public dataset and generate extra syntetic rows if set by size parameter\n",
+ "\n",
+ "The loaded dataset has 1000 rows. If you specify number_of_input_rows in [1..1000] it will cut extra rows if needed\n",
+ "\n",
+ "If number_of_input_rows in [1000..1000000] it will generate extra rows using cross join of original data"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "6b6bdb2c-d492-4114-a7e9-0ef2832ac05c",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "file_path = \"wasbs://publicwasb@mmlspark.blob.core.windows.net/fine_food_reviews_1k.csv\"\n",
+ "\n",
+ "df = spark.read.options(inferSchema=\"True\", delimiter=\",\", header=True).csv(file_path)\n",
+ "df = df.withColumn(\n",
+ " \"data\",\n",
+ " F.format_string(\"Title: %s; Content: %s\", F.trim(df.Summary), F.trim(df.Text)),\n",
+ ")\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# Size of DF\n",
+ "number_of_input_rows = 100\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# Check if the row count is less than 10\n",
+ "if number_of_input_rows <= 0 or number_of_input_rows >= 1000000:\n",
+ " raise ValueError(f\"Limit is {number_of_input_rows}, which should be less than 1M.\")\n",
+ "\n",
+ "if number_of_input_rows > 1000:\n",
+ "\n",
+ " # Cross-join the DataFrame with itself to create n x n pairs for string concatenation (synthetic data)\n",
+ " cross_joined_df = df.crossJoin(df.withColumnRenamed(\"data\", \"data_\"))\n",
+ "\n",
+ " # Create a new column 'result_vector' by concatenating the two source vectors\n",
+ " tmp_df = cross_joined_df.withColumn(\n",
+ " \"result_vector\",\n",
+ " F.concat(F.col(\"data\"), F.lit(\". \\n\"), F.col(\"data_\")),\n",
+ " )\n",
+ "\n",
+ " # Select only the necessary columns and show the result\n",
+ " tmp_df = tmp_df.select(\"result_vector\")\n",
+ "\n",
+ " # Shuffle the DataFrame with a fixed seed to have close strings spreaded\n",
+ " seed = 42\n",
+ "\n",
+ " df = (\n",
+ " tmp_df.withColumnRenamed(\"result_vector\", \"data\")\n",
+ " .withColumn(\"id\", F.monotonically_increasing_id())\n",
+ " .orderBy(F.rand(seed))\n",
+ " )\n",
+ "\n",
+ "df = df.limit(number_of_input_rows).repartition(10).cache()\n",
+ "\n",
+ "print(f\"Loaded: {number_of_input_rows} rows\")"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "0c69ee56-172f-413b-a335-d15482fda55e",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 3: Generate Embeddings\n",
+ "\n",
+ "We will first generate embeddings using NVIDIA TensorRT optimized SentenceTransformer. In the demo you can use two fifferent HF models: intfloat/e5-large-v2 or sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2\""
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "8d7bd9db-79a1-4d46-a849-ac49c3de7b49",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# To create embedder with different models, uncomment the following line\n",
+ "# embedder = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(modelName=\"intfloat/e5-large-v2\", inputCol=\"data\", outputCol=\"embeddings\", runtime=\"tensorrt\")\n",
+ "embedder = HuggingFaceSentenceEmbedder(\n",
+ " modelName=\"sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2\",\n",
+ " inputCol=\"data\",\n",
+ " outputCol=\"embeddings\",\n",
+ " runtime=\"tensorrt\",\n",
+ ")\n",
+ "\n",
+ "embeddings = embedder.transform(df).select(\"id\", \"embeddings\").cache()"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "6885033f-6eea-4338-a632-2837582d91a1",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 4: Build the query against embeddings\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Get query embeddings running standard SentenceTransformer just on the driver. Convert embedding results to a data frame"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "23b83621-3f42-42ff-847e-97a4af2d3276",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Sample query\n",
+ "queries = [\"desserts\", \"disgusting\"]\n",
+ "ids = [1, 2]\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# Create DataFrame directly from the data and schema\n",
+ "query_df = spark.createDataFrame(\n",
+ " list(zip(ids, queries)),\n",
+ " StructType(\n",
+ " [\n",
+ " StructField(\"id\", IntegerType(), nullable=False),\n",
+ " StructField(\"data\", StringType(), nullable=False),\n",
+ " ]\n",
+ " ),\n",
+ ")\n",
+ "\n",
+ "query_embeddings = embedder.transform(query_df).select(\"id\", \"embeddings\").cache()"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "0154ce06-5875-4236-8178-030d45091445",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 5: Build a fast vector index to over review embeddings\n",
+ "\n",
+ "We will use fast NVIDIA Rapids indexer. This KNN implementation will work only on GPU. If you want to use CPU then switch to synapse.ml.nn CPU based KNN implementation"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "c01d2c1e-837b-4525-a4d3-4938fd4221fb",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "RUN_ON_GPU = torch.cuda.is_available()"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "aa0e4178-75e4-412b-940e-25d55b7396ce",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "if RUN_ON_GPU:\n",
+ " rapids_knn_model = (\n",
+ " ApproximateNearestNeighbors(k=5)\n",
+ " .setInputCol(\"embeddings\")\n",
+ " .setIdCol(\"id\")\n",
+ " .fit(embeddings)\n",
+ " )\n",
+ "else:\n",
+ " array_to_vector_udf = udf(lambda array: Vectors.dense(array), VectorUDT())\n",
+ " df_with_vectors = embeddings.withColumn(\n",
+ " \"features\", array_to_vector_udf(embeddings[\"embeddings\"])\n",
+ " )\n",
+ " knn = (\n",
+ " KNN()\n",
+ " .setFeaturesCol(\"features\")\n",
+ " .setValuesCol(\"id\")\n",
+ " .setOutputCol(\"output\")\n",
+ " .setK(10)\n",
+ " )\n",
+ " knn_model = knn.fit(df_with_vectors)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "521c9c8e-6422-49c7-95f3-6bca44a90cbb",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 6: Find top k Nearest Neighbors ON GPU\n",
+ "\n",
+ "We will use fast ANN [IVFFlat algorithm](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/accelerated-vector-search-approximating-with-rapids-raft-ivf-flat/) from Rapids"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "0fb3f3d7-bbb6-4105-bb86-b08fabba4ca4",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "if RUN_ON_GPU:\n",
+ " (_, _, knn_df) = rapids_knn_model.kneighbors(query_embeddings)\n",
+ "else:\n",
+ " array_to_vector_udf = udf(lambda array: Vectors.dense(array), VectorUDT())\n",
+ " df_with_vectors = query_embeddings.withColumn(\n",
+ " \"features\", array_to_vector_udf(query_embeddings[\"embeddings\"])\n",
+ " )\n",
+ " knn_df = knn_model.transform(df_with_vectors)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "9f30473c-ff6e-438a-bbce-11f1b0080a48",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "## Step 7: Collect and display results"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 0,
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "2ec6847c-3592-4645-aca1-0fc6d9e3ed0f",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "if RUN_ON_GPU:\n",
+ " result_df = (\n",
+ " knn_df.withColumn(\n",
+ " \"zipped\", F.explode(F.arrays_zip(F.col(\"indices\"), F.col(\"distances\")))\n",
+ " )\n",
+ " .select(\n",
+ " F.col(\"query_id\"),\n",
+ " F.col(\"zipped.indices\").alias(\"id\"),\n",
+ " F.col(\"zipped.distances\").alias(\"distance\"),\n",
+ " )\n",
+ " .join(df, on=\"id\", how=\"inner\")\n",
+ " .select(\"query_id\", \"id\", \"data\", \"distance\")\n",
+ " )\n",
+ "else:\n",
+ " knn_df = knn_df.withColumnRenamed(\"data\", \"original_data\")\n",
+ " result_df = (\n",
+ " knn_df.withColumn(\"match\", F.explode(\"output\"))\n",
+ " .join(df, df[\"id\"] == F.col(\"match.value\"))\n",
+ " .select(\"original_data\", F.col(\"data\"), \"match.distance\")\n",
+ " )\n",
+ "\n",
+ "display(result_df)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+cell": {
+ "cellMetadata": {
+ "byteLimit": 2048000,
+ "rowLimit": 10000
+ },
+ "inputWidgets": {},
+ "nuid": "7b4c5a10-efd1-4d2d-b141-33e486943862",
+ "showTitle": false,
+ "title": ""
+ }
+ },
+ "source": [
+ "# Results\n",
+ "\n",
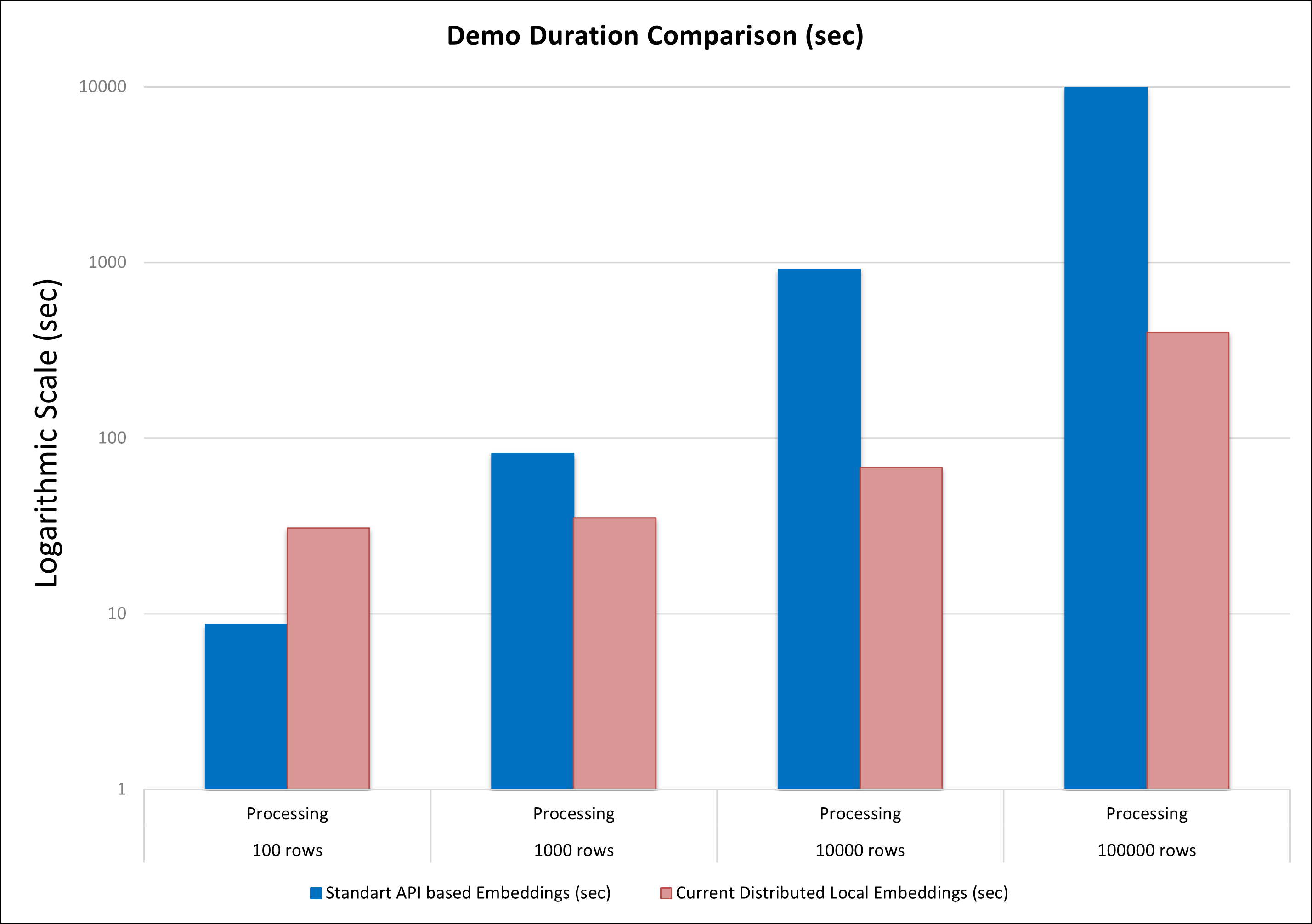
+ "The goal of this demo is to showcase two acceleration techniques: local (per node) embedding generation and approximate KNN. Compared to the original method, which relies on HTTP requests to the OpenAI model and CPU-based KNN. The new approach is significantly more scalable and provides substantial acceleration, especially for large input datasets.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "This is the comparison dureation results on 10 T4 GPU nodes for both approaches:\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "application/vnd.databricks.v1+notebook": {
+ "dashboards": [],
+ "environmentMetadata": null,
+ "language": "python",
+ "notebookMetadata": {
+ "mostRecentlyExecutedCommandWithImplicitDF": {
+ "commandId": -1,
+ "dataframes": [
+ "_sqldf"
+ ]
+ },
+ "pythonIndentUnit": 2,
+ "widgetLayout": []
+ },
+ "notebookName": "Quickstart - Custom Embeddings and Approximate KNN on GPU",
+ "widgets": {}
+ },
+ "kernel_info": {
+ "name": "synapse_pyspark"
+ },
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.8.8"
+ },
+ "save_output": true,
+ "synapse_widget": {
+ "state": {
+ "4bd0e60b-98ae-4bfe-98ee-6f0399ceb456": {
+ "persist_state": {
+ "view": {
+ "chartOptions": {
+ "aggregationType": "count",
+ "categoryFieldKeys": [
+ "0"
+ ],
+ "chartType": "bar",
+ "isStacked": false,
+ "seriesFieldKeys": [
+ "0"
+ ]
+ },
+ "tableOptions": {},
+ "type": "details"
+ }
+ },
+ "sync_state": {
+ "isSummary": false,
+ "language": "scala",
+ "table": {
+ "rows": [
+ {
+ "0": "Once upon a time",
+ "1": [
+ " there was a girl who had a dream of becoming a writer.\n\nShe started writing short stories"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "0": "Hello my name is",
+ "1": [
+ "***** and I have a question about my cat\n\nHello, thank you for bringing your question to"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "0": "The best code is code thats",
+ "1": [
+ " not there\n\nCommenting your code is important. Not only does it help you remember what you"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "schema": [
+ {
+ "key": "0",
+ "name": "prompt",
+ "type": "string"
+ },
+ {
+ "key": "1",
+ "name": "text",
+ "type": "ArrayType(StringType,true)"
+ }
+ ],
+ "truncated": false
+ }
+ },
+ "type": "Synapse.DataFrame"
+ }
+ },
+ "version": "0.1"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 0
+}
diff --git a/environment.yml b/environment.yml
index 5302760212..477edb9c84 100644
--- a/environment.yml
+++ b/environment.yml
@@ -51,3 +51,4 @@ dependencies:
- markdownify
- traitlets
- opencv-python
+ - sentence_transformers~=2.2.2
diff --git a/tools/init_scripts/init-rapidsml-cuda-11.8.sh b/tools/init_scripts/init-rapidsml-cuda-11.8.sh
index dd702d3e4b..bcb8fdc93e 100644
--- a/tools/init_scripts/init-rapidsml-cuda-11.8.sh
+++ b/tools/init_scripts/init-rapidsml-cuda-11.8.sh
@@ -1,11 +1,24 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2024, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
#!/bin/bash
-# set portion of path below after /dbfs/ to dbfs zip file location
-SPARK_RAPIDS_ML_ZIP=/dbfs/path/to/zip/file
# IMPORTANT: specify RAPIDS_VERSION fully 23.10.0 and not 23.10
# also in general, RAPIDS_VERSION (python) fields should omit any leading 0 in month/minor field (i.e. 23.8.0 and not 23.08.0)
# while SPARK_RAPIDS_VERSION (jar) should have leading 0 in month/minor (e.g. 23.08.2 and not 23.8.2)
-RAPIDS_VERSION=23.10.0
+RAPIDS_VERSION=24.4.0
SPARK_RAPIDS_VERSION=23.10.0
+SPARK_RAPIDSML_VERSION=24.6.0
curl -L https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/nvidia/rapids-4-spark_2.12/${SPARK_RAPIDS_VERSION}/rapids-4-spark_2.12-${SPARK_RAPIDS_VERSION}-cuda11.jar -o /databricks/jars/rapids-4-spark_2.12-${SPARK_RAPIDS_VERSION}.jar
@@ -28,6 +41,8 @@ ln -s /usr/local/cuda-11.8 /usr/local/cuda
rmm-cu11~=${RAPIDS_VERSION} \
--extra-index-url=https://pypi.nvidia.com
-# install spark-rapids-ml
-/databricks/python/bin/pip install spark-rapids-ml
+# install model navigator
+/databricks/python/bin/pip install --extra-index-url https://pypi.nvidia.com onnxruntime-gpu "tensorrt" "triton-model-navigator==0.10.1" "sentence_transformers~=2.2.2" "urllib3<2"
+# install spark-rapids-ml
+/databricks/python/bin/pip install spark-rapids-ml~=${SPARK_RAPIDSML_VERSION}
diff --git a/website/sidebars.js b/website/sidebars.js
index 0ab11ee7ed..5ef56a0f78 100644
--- a/website/sidebars.js
+++ b/website/sidebars.js
@@ -52,6 +52,7 @@ module.exports = {
"Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/OpenAI",
"Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - OpenAI Embedding",
"Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - OpenAI Embedding and GPU based KNN",
+ "Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - Custom Embeddings and Approximate KNN on GPU",
"Explore Algorithms/OpenAI/Quickstart - Understand and Search Forms",
],
},