Flitter is a powerful JavaScript rendering engine and framework inspired by Flutter, supporting both SVG and Canvas to create high-performance graphics and user interfaces. As a rendering engine, it provides fine-grained control over the rendering process, allowing developers to create complex, interactive visualizations with ease. It is designed to efficiently implement data visualizations, interactive charts, diagrams, and graphic editors in web applications.
-
Advanced Rendering Engine: At its core, Flitter is a sophisticated rendering engine that gives developers precise control over how elements are drawn and updated on the screen.
-
Render Object Tree: Flitter uses a render object tree for efficient rendering, allowing easy management and manipulation of complex layouts. This tree-based approach, central to Flitter's rendering engine, enables optimized updates and redraws.
-
Declarative Programming: Following a declarative paradigm, the screen automatically updates when values change, simplifying application state management and reducing the complexity of manual DOM manipulation.
-
Optimized Rendering Pipeline: Re-rendering, painting, and layout recalculations are managed by the renderer pipeline, with optimizations applied to update only necessary parts. This ensures high performance even with complex, data-heavy visualizations.
-
Dual Renderer Support: As a flexible rendering engine, Flitter supports both SVG and Canvas, meeting various graphic requirements. Developers can choose the appropriate renderer as needed, switching seamlessly between vector and bitmap graphics.
-
Box Model Layout: Users can easily compose layouts using the familiar Box model, providing a intuitive way to structure complex UIs within the rendering engine.
-
Diverse Applications: Can be utilized in various fields such as charts, diagrams, data visualization, and graphic editors, leveraging the power of the underlying rendering engine.
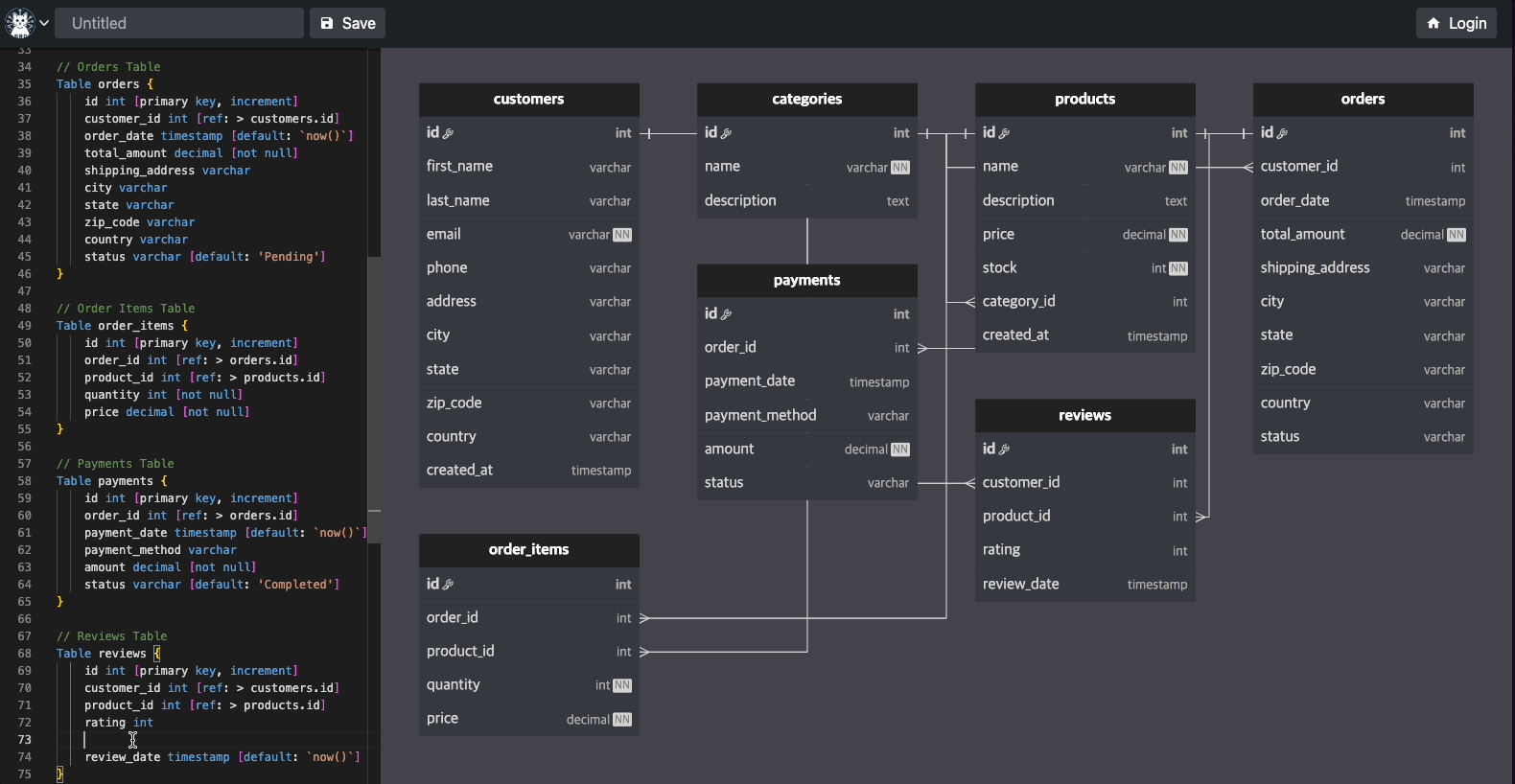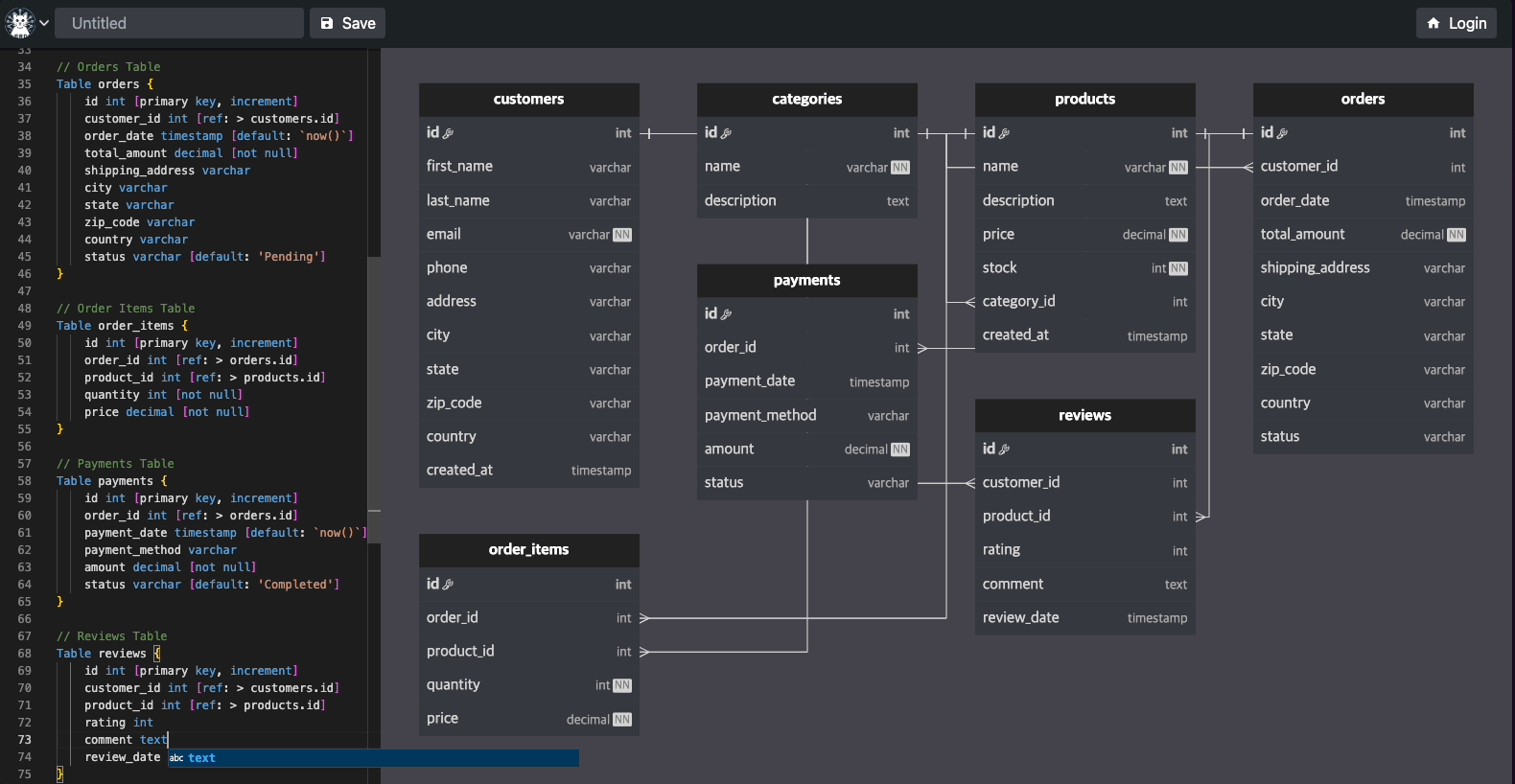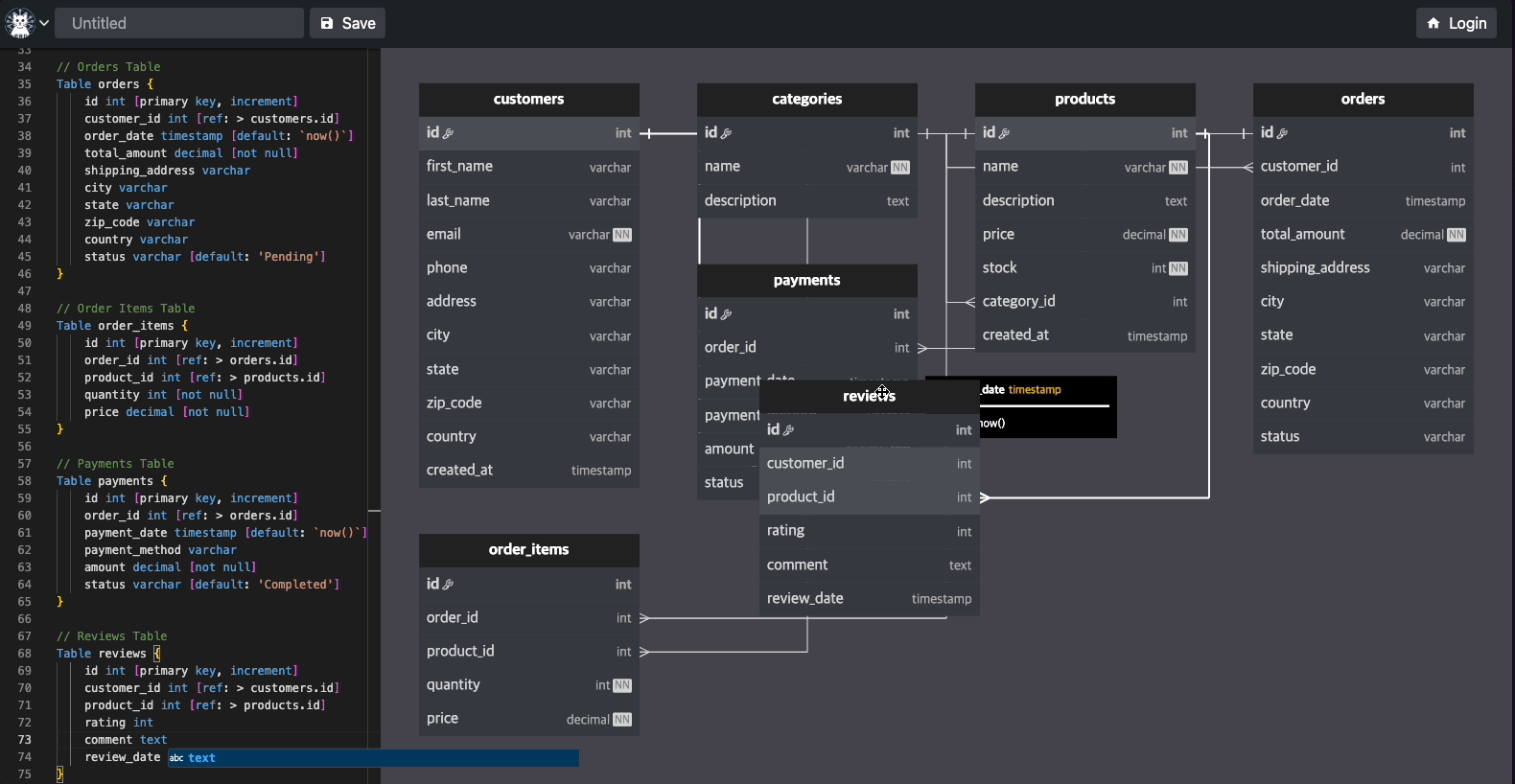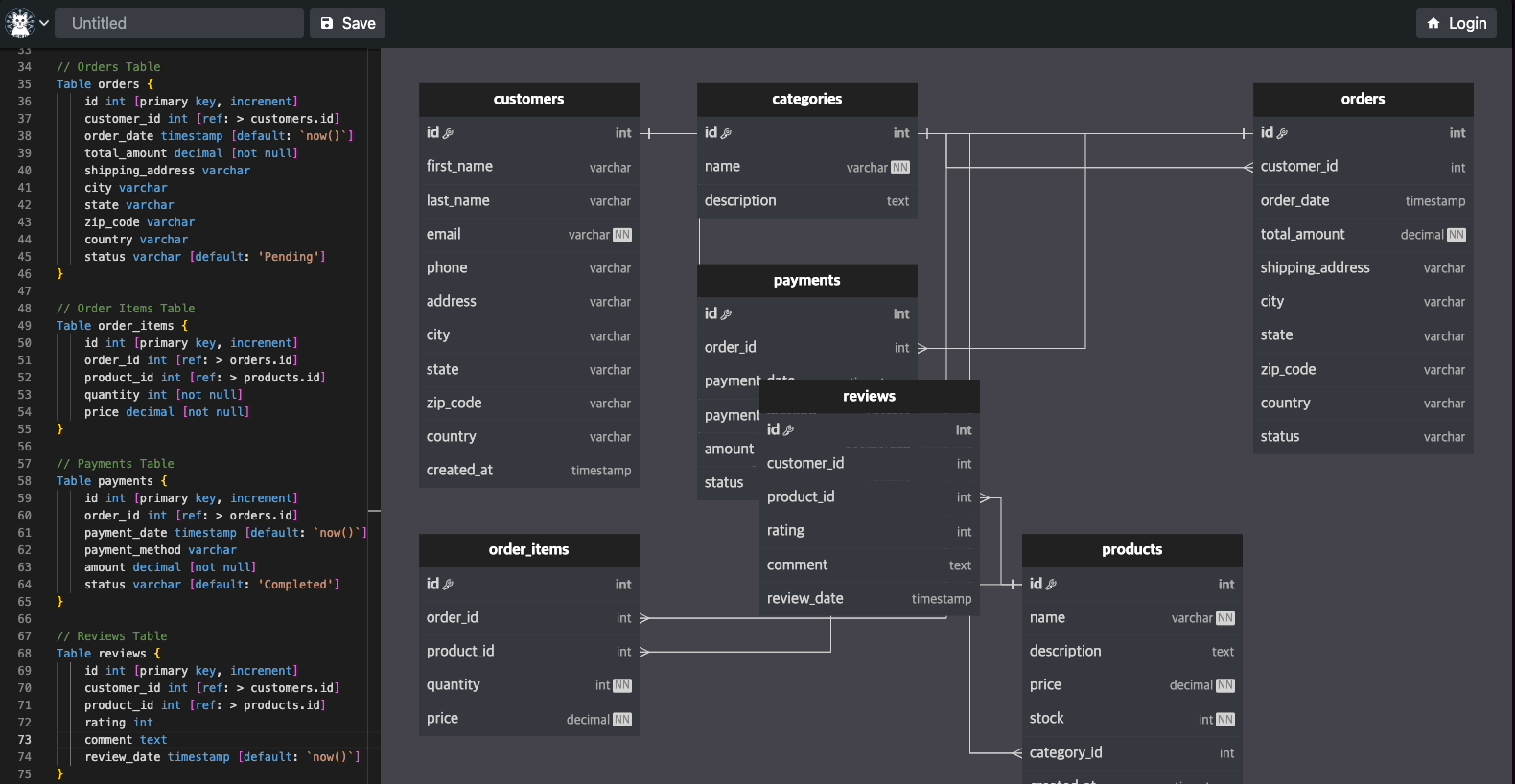
Here are some examples of what you can create with Flitter: Interactive ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagram)[https://easyrd.dev]
This interactive ERD demonstrates Flitter's capability to create complex, interactive diagrams. Users can manipulate entities, add relationships, and visualize database structures in real-time. This showcase highlights Flitter's strengths in:
Creating responsive, draggable elements Handling complex user interactions Rendering intricate diagrams with ease Real-time updates based on user input
Flitter can be used in various JavaScript environments. Here are installation and usage methods for major environments:
npm install @meursyphus/flitterimport { Container } from "@meursyphus/flitter";
/**
* canvas style must be set to 100%, 100%
* and you also must wrap div for canvas in order to calculate the size of the canvas
*/
document.querySelector<HTMLDivElement>("#app")!.innerHTML = `
<div style="width: 100vw; height: 100vh" id="container">
<canvas style="width: 100%; height: 100%;" id="view" />
</div>
`;
// Note: SVG is also supported
// document.querySelector<HTMLDivElement>("#app")!.innerHTML = `
// <div style="width: 100vw; height: 100vh" id="container">
// <svg style="width: 100%; height: 100%;" id="view"></svg>
// </div>
// `;
const app = new AppRunner({
view: document.querySelector<HTMLCanvasElement>("#view")!,
});
/**
* you must set resizeTarget to calculate the size of the canvas
*/
app.onMount({
resizeTarget: document.querySelector<HTMLDivElement>("#container")!,
});
app.runApp(Container({ color: 'lightblue' }));npm install @meursyphus/flitter @meursyphus/flitter-reactimport { Container, Alignment, Text, TextStyle } from '@meursyphus/flitter';
import Widget from '@meursyphus/flitter-react';
const App = () => (
<>
<Widget
width="600px"
height="300px"
renderer="canvas" // or svg
widget={Container({
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: 'lightblue',
child: Text("Hello, Flitter SVG!", { style: TextStyle({ fontSize: 30, weight: 'bold' }) })
})}
/>
</>
);npm install @meursyphus/flitter @meursyphus/flitter-svelte<script>
import { Container, Alignment, Text, TextStyle } from '@meursyphus/flitter';
import Widget from '@meursyphus/flitter-svelte';
</script>
<Widget
width="600px"
height="300px"
renderer="canvas" <!-- or "svg" -->
widget={Container({
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: 'lightblue',
child: Text("Hello, Flitter SVG!", { style: TextStyle({ fontSize: 30, weight: 'bold' }) })
})}
/>Example of creating a simple chart using Flitter:
import {
Container,
Animation,
Text,
TextStyle,
StatefulWidget,
State,
Alignment,
SizedBox,
Column,
MainAxisSize,
MainAxisAlignment,
Row,
CrossAxisAlignment,
FractionallySizedBox,
BoxDecoration,
BorderRadius,
Radius,
AnimationController,
Tween,
CurvedAnimation,
Curves
} from '@meursyphus/flitter';
export default function BarChart() {
return Container({
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: 'lightgrey',
child: Column({
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('BarChart', { style: new TextStyle({ fontFamily: 'Intent', fontWeight: '600' }) }),
SizedBox({
width: 200,
height: 150,
child: Row({
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
{ label: 'S', value: 60 },
{ label: 'M', value: 20 },
{ label: 'T', value: 30 },
{ label: 'W', value: 90 },
{ label: 'T', value: 70 },
{ label: 'F', value: 50 },
{ label: 'S', value: 40 }
].map(({ label, value }) => new Bar(label, value))
})
})
]
})
});
}
class Bar extends StatefulWidget {
constructor(public label: string, public value: number) {
super();
}
createState(): State<StatefulWidget> {
return new BarState();
}
}
class BarState extends State<Bar> {
animationController!: AnimationController;
tweenAnimation!: Animation<number>;
override initState(): void {
this.animationController = new AnimationController({
duration: 10000
});
this.animationController.addListener(() => {
this.setState();
});
const tween = new Tween({ begin: 0, end: this.widget.value });
this.tweenAnimation = tween.animated(
new CurvedAnimation({
parent: this.animationController,
curve: Curves.easeInOut
})
);
this.animationController.forward();
}
override build() {
return Column({
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
FractionallySizedBox({
heightFactor: this.tweenAnimation.value / 100,
child: Column({
children: [
Container({
width: 20,
decoration: new BoxDecoration({
color: '#1a1a1a',
borderRadius: BorderRadius.only({
topLeft: Radius.circular(4),
topRight: Radius.circular(4)
})
})
}),
SizedBox({ height: 5 }),
Text(this.widget.label, { style: new TextStyle({ fontFamily: 'Intent' }) })
]
})
})
]
});
}
}-
Powerful Rendering Engine: Flitter's core strength lies in its advanced rendering capabilities, allowing for smooth handling of complex graphics and animations.
-
Easy Learning Curve: Uses syntax similar to Flutter, allowing mobile developers to easily adapt to the web environment while leveraging a powerful web-based rendering engine.
-
High Performance: The optimized rendering pipeline ensures smooth performance even with complex, data-intensive visualizations.
-
Flexibility: Abstracts SVG and Canvas manipulation, allowing developers to focus on business logic while the rendering engine handles the low-level drawing operations.
-
Renderer Selection: Can choose between SVG and Canvas renderers as needed, meeting various graphic requirements and allowing for the best performance in different scenarios.
-
Reusability: Increases code reusability through a component-based approach, enabled by the underlying rendering engine's architecture.
Flitter is an open-source project. We welcome all forms of contributions including bug reports, feature suggestions, and pull requests. For more details, please visit Discord
Flitter is provided under the MIT license.
For detailed documentation and examples, visit the Flitter Official Documentation.