diff --git a/docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/1.1-vector.md b/docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/vector.md
similarity index 74%
rename from docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/1.1-vector.md
rename to docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/vector.md
index f20aa0bdd..4362d75ef 100644
--- a/docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/1.1-vector.md
+++ b/docs/MatrixOne/Develop/schema-design/vector.md
@@ -105,19 +105,72 @@ CREATE TABLE t1 (
);
-- Insert some sample data
-INSERT INTO t1 (id,b) VALUES (1, '[1,2,3]'), (2, '[4,5,6]'), (3, '[2,1,1]'), (4, '[7,8,9]'), (5, '[0,0,0]'), (6, '[3,1,2]');
+INSERT INTO t1 (id,b) VALUES (1, '[1,2,3]'), (2, '[4,5,6]'), (3, '[2,1,1]'), (4, '[7,8,9]'), (5, '[2,2,2]'), (6, '[3,1,2]');
+
+mysql> select * from t1;
++------+-----------+
+| id | b |
++------+-----------+
+| 1 | [1, 2, 3] |
+| 2 | [4, 5, 6] |
+| 3 | [2, 1, 1] |
+| 4 | [7, 8, 9] |
+| 5 | [2, 2, 2] |
+| 6 | [3, 1, 2] |
++------+-----------+
+6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
-- Top K Queries using l1_distance
-SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY l1_norm(b - '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
+mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY l1_norm(b - '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
++------+-----------+
+| id | b |
++------+-----------+
+| 6 | [3, 1, 2] |
+| 5 | [2, 2, 2] |
+| 3 | [2, 1, 1] |
+| 1 | [1, 2, 3] |
+| 2 | [4, 5, 6] |
++------+-----------+
+5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- Top K Queries using l2_distance
-SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY l2_norm(b - '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
+mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY l2_distance(b,'[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
++------+-----------+
+| id | b |
++------+-----------+
+| 6 | [3, 1, 2] |
+| 5 | [2, 2, 2] |
+| 3 | [2, 1, 1] |
+| 1 | [1, 2, 3] |
+| 2 | [4, 5, 6] |
++------+-----------+
+5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- Top K Queries using cosine similarity
-SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY cosine_similarity(b, '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
+mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY cosine_similarity(b, '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
++------+-----------+
+| id | b |
++------+-----------+
+| 1 | [1, 2, 3] |
+| 2 | [4, 5, 6] |
+| 4 | [7, 8, 9] |
+| 5 | [2, 2, 2] |
+| 3 | [2, 1, 1] |
++------+-----------+
+5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- Top K Queries using cosine distance
-SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY 1 - cosine_similarity(b, '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
+mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY cosine_distance(b, '[3,1,2]') LIMIT 5;
++------+-----------+
+| id | b |
++------+-----------+
+| 6 | [3, 1, 2] |
+| 3 | [2, 1, 1] |
+| 5 | [2, 2, 2] |
+| 4 | [7, 8, 9] |
+| 2 | [4, 5, 6] |
++------+-----------+
+5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
```
These queries demonstrate retrieving the top 5 vectors most similar to the given vector `[3,1,2]` using different distance and similarity measures. With these queries, you can find the data that best matches your target vector based on different measurement criteria.
@@ -157,18 +210,19 @@ These queries demonstrate retrieving the top 5 vectors most similar to the given
- Currently, MatrixOne Vector type supports float32 and float64 types.
- Vector cannot be Primary Key or Unique Key.
-- Vector maximum dimension is 65536.
-
-Certainly, let's refine the original text in English:
+- Vector maximum dimension is 65535.
## Reference
For more documentation on vector functions, see:
-- [inner_product()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/inner_product.md)
-- [l1_norm()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/l1_norm.md)
-- [l2_norm()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/l2_norm.md)
-- [cosine_similarity()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/cosine_similarity.md)
-- [vector_dims()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/vector_dims.md)
-- [Arithemetic Operators](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/arithmetic.md)
-- [Misc Functions](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/misc.md)
+- [inner_product()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/inner_product.md)
+- [l1_norm()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/l1_norm.md)
+- [l2_norm()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/l2_norm.md)
+- [l2_distance()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/l2_distance.md)
+- [cosine_similarity()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/cosine_similarity.md)
+- [cosine_distance()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/cosine_distance.md)
+- [vector_dims()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/vector_dims.md)
+- [normalize_l2()](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/normalize_l2.md)
+- [Arithemetic Operators](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/arithmetic.md)
+- [Misc Functions](../../Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/misc.md)
diff --git a/docs/MatrixOne/Maintain/mo_ctl.md b/docs/MatrixOne/Maintain/mo_ctl.md
index 4502cc902..73ba400a8 100644
--- a/docs/MatrixOne/Maintain/mo_ctl.md
+++ b/docs/MatrixOne/Maintain/mo_ctl.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ The operating systems that `mo_ctl` has adapted so far are shown in the table be
The current function list of `mo_ctl` is shown in the table below.
| Command | Function |
-| ------- | -------- ||
+| ------- | -------- |
| `mo_ctl help` | See a list of statements and functions for the `mo_ctl` tool itself |
| `mo_ctl precheck` | Check dependencies required for MatrixOne source code installation, namely golang, gcc, git, MySQL Client |
| `mo_ctl deploy` | Download and install and compile the corresponding version of MatrixOne; the default is to install the latest stable version |
diff --git a/docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/arithmetic.md b/docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/arithmetic.md
similarity index 100%
rename from docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/1.1-Vector/arithmetic.md
rename to docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/arithmetic.md
diff --git a/docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/cosine_distance.md b/docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/cosine_distance.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..101c58d88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/MatrixOne/Reference/Functions-and-Operators/Vector/cosine_distance.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+# COSINE_DISTANCE()
+
+## Description
+
+The `COSINE_DISTANCE()` function is used to calculate the cosine distance between two vectors.
+
+Cosine Distance is a measure of the directional difference between two vectors, typically defined as 1 minus the cosine similarity ([Cosine Similarity](cosine_similarity.md)). The value of cosine distance ranges from 0 to 2. A value of 0 indicates that the directions of the two vectors are exactly the same (minimum distance). A value of 2 indicates that the directions of the two vectors are exactly opposite (maximum distance). In text analysis, cosine distance can be used to measure the similarity between documents. Since it only considers the direction of the vectors and not their magnitude, it is fair for comparisons between long and short texts.
+
+
+
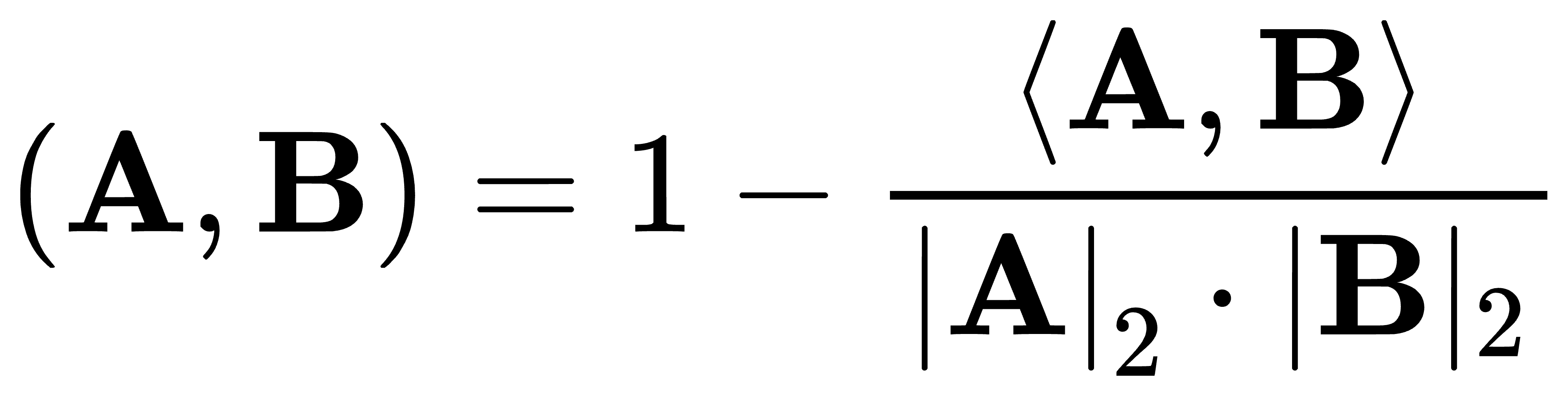
+
+
+
+
+
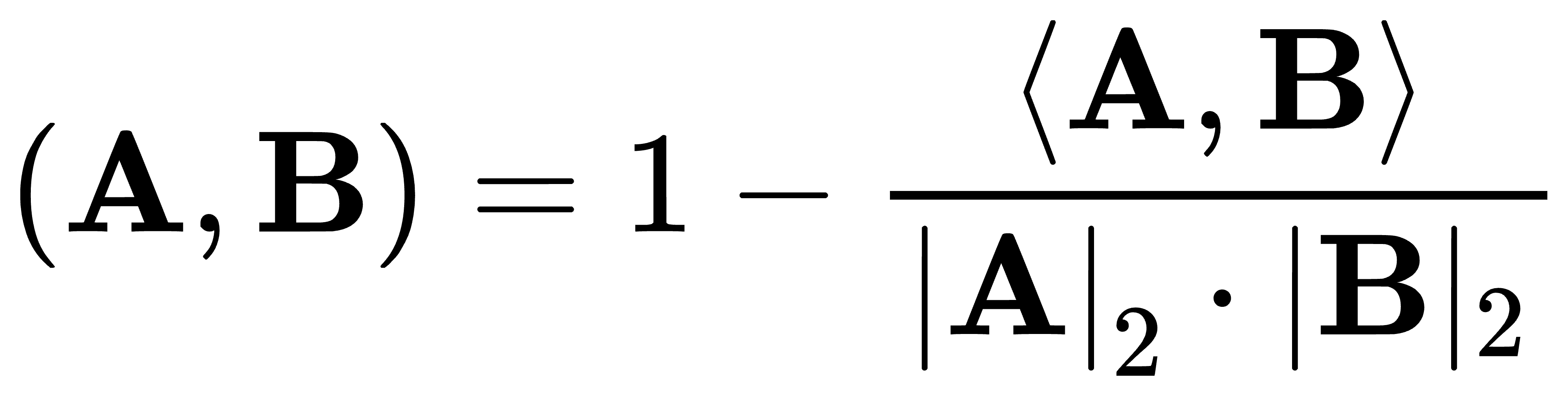 +
+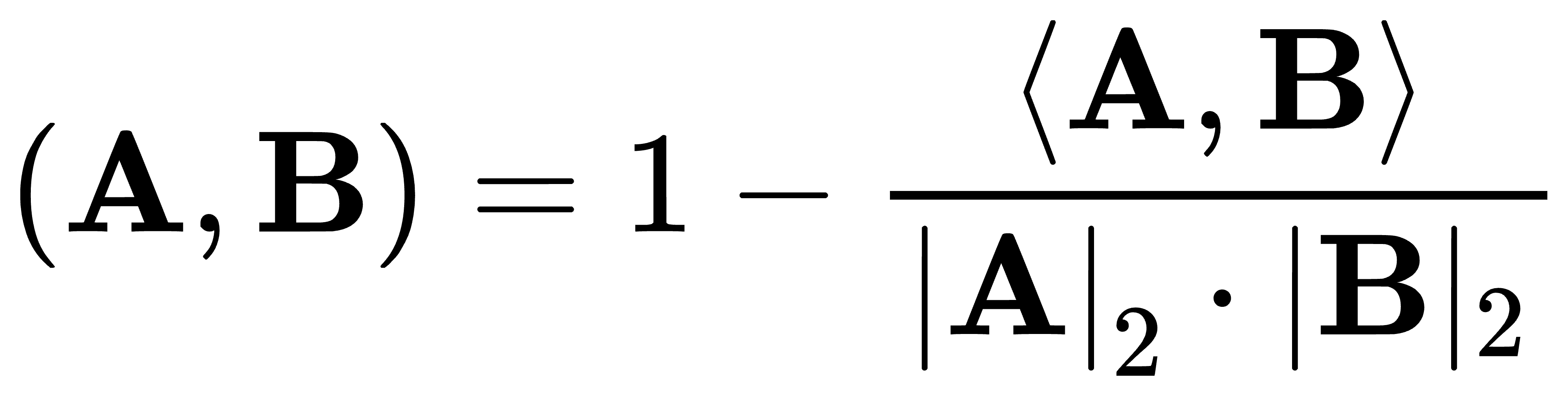 +
+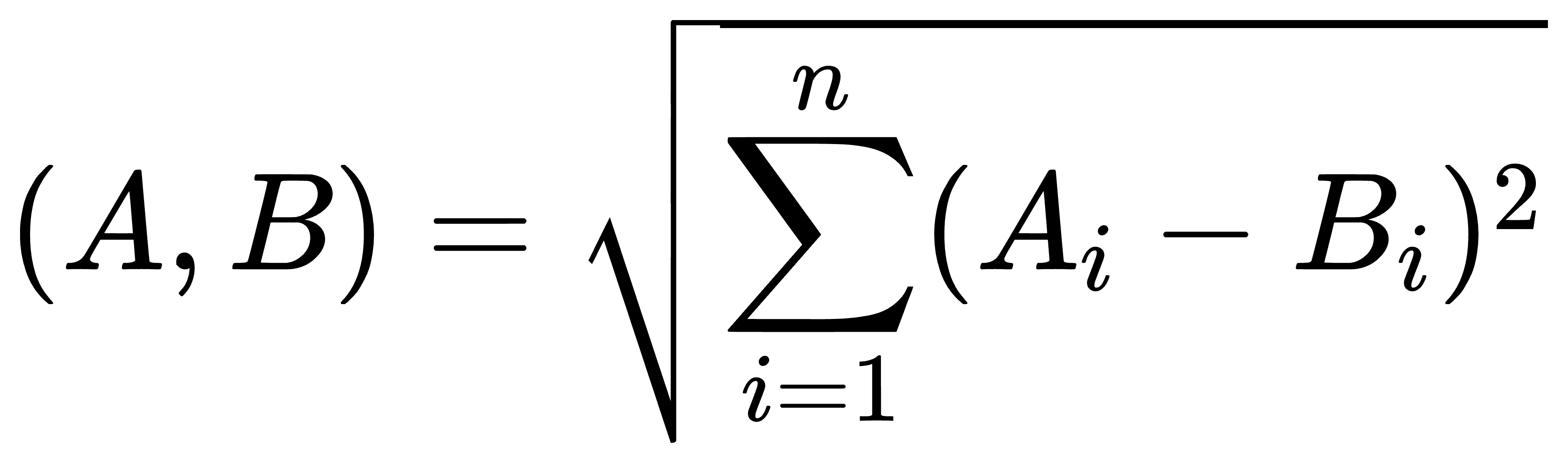 +
+ +
+