Wireless link planning, or more specifically assessing the viability of a wireless link such as a Wi-Fi or UHF/VHF radio link between two locations can be a complex task. Designing these links, particularly long links or links greater than 10 Km, can be challenging, as there are many factors that must be accounted for to ensure high quality transmission. Specifically, it can be difficult to assess concerns such as the existence of intrusions into the line of sight path between two points.
This JavaScript library is an effort to streamline and simplify the wireless link planning process. It focuses on two key areas of wireless link planning. It provides 1) Fresnel Zone intrusion analsysis of a point-to-point wireless link, and 2) a 360° viewshed analysis around a single point.
This project uses Google's Elevation API. Note that while Google maintains a free public facing API, Google enforces daily usage limits – currently 2,500 calls per day. If you have a Google Maps API for Business account, the daily call limit is significantly higher. See below on how to configure the library with your key.
In addition, note Google's terms of service state that the Elevation API may only be used in conjunction when displaying results on a Google map. Using elevation data without displaying the results on a map for which elevation data was requested is prohibited.
Note, this library is only able to factor in intrusions of terrain (the surface of the earth) into the Fresnel Zone. The underlying data does not account for buildings, trees, or other potential obstructions.
Using this library to perform point-point link analysis is relatively lightweight in terms of calls to Google's API. The library will make one call each time the page is loaded or refreshed.
Using this library to perform Viewshed analysis is considerably more expensive in terms of the number of calls to Google's API. The library performs a series of calls based on the precision variable. To perform a quick viewshed analysis of lesser quality, set the resolution variable to something such as 30 (or 30°). The library will then make 12 calls to Google's API (360/30=12). To perform a high quality viewshed analysis, set the resolution variable to something like 1. The library will then make 360 calls to Google's API (360/1=360). Note that at high precision, you may quickly exhaust Google's daily API limit of 2,500 calls.
This project requires:
- Raphael.js, v2.1.2, http://raphaeljs.com/
- gRaphael with g.line.js, v0.5.1
- D3.js, v3 (3.3.4+), http://d3js.org/
- jQuery
- Google Maps Javascript API v3 with Geometry Library,
While not a dependency to use RFAnalysisJS, CoffeeScript is required to recompile the JavaScript for the viewshed analysis.
See reference code in elevation-analysis.html.
Usage:
- Enter the coordinates (decimal format) of two locations
- Enter the radio frequency (GHz)
- Select the number of points you wish to calculate along the path - note Google's Elevation API allows for a maximum of 512 points
- Adjust the height (meters) of each location
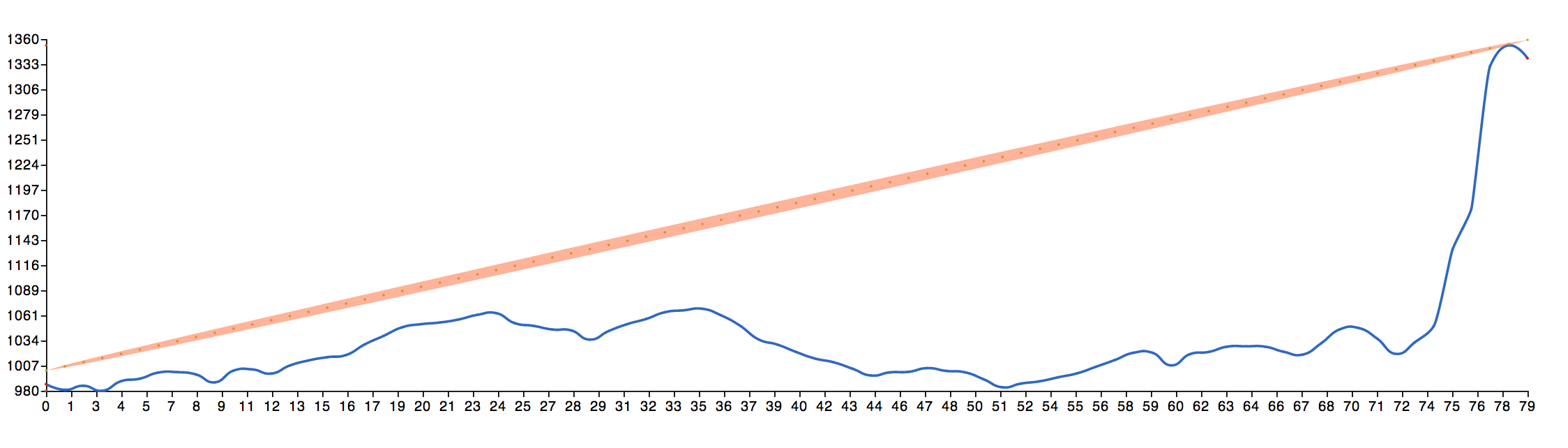
The resulting image shows the path between the two points with the first Fresnel zone.
See the sample code in elevation-analysis.html. Note the JavaScript for viewshed analysis is compiled from CoffeeScript.
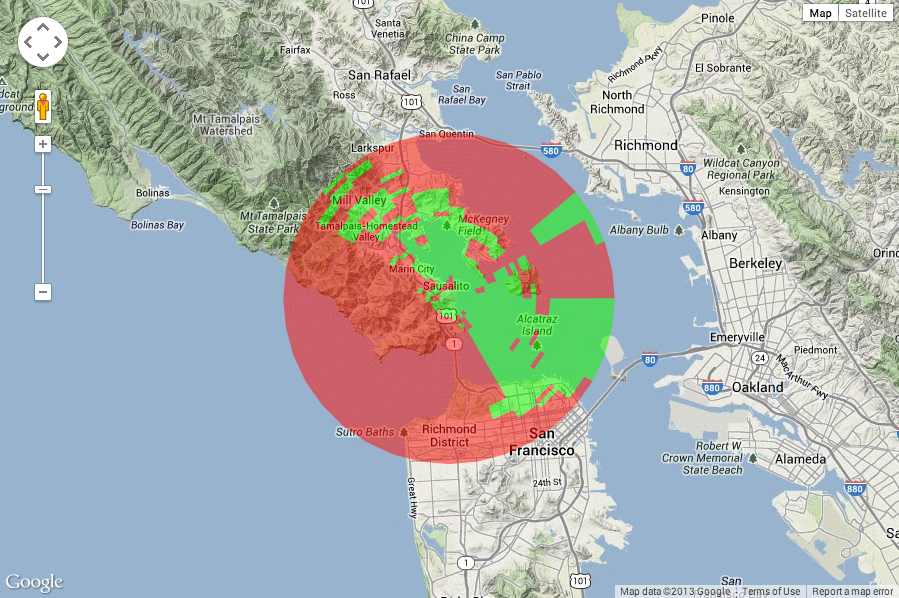
Green indicates clear line of sight from the center point, red indicates no clear line of sight.
The call to the Google Maps API should look like this:
<script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?v=3.exp&sensor=false&libraries=geometry"></script>Variables to set in the HTML file:
var lat = 37.852357; // latitude of center point
var lng = -122.483139; // longitude of center point
var frequency = 5800; // frequency of radio
var aboveGroundHeight = 5; // meters above ground
var distance = 10000; // radius of viewshed in meters
var precision = 30; // resolution (degrees)To get a higher usage limit to perform more higher resolution analysis or more analysis per day with the viewshed.js file, this library supports the use of Google Maps API for Business. Instead of calling createViewshed on a site, you would call createViewshedBusiness(<GOOGLE_MAPS_BUSINESS_CLIENT_ID>, <URL_TO_SIGN_CALLS_FUNCTION>). Note that the second parameter is a function that would be stored server-side and will sign the url to authorize your Google Maps for Business account. For more information, visit (https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/business/webservices/auth). You may want to view the viewshed.html demo in order to utilize this feature.
- Redo the Point-Point Link Analysis to use D3 instead of Raphael.js
- Merge the Point-Point Link Analysis with the Viewshed Analysis
- Cache Google's elevation data on the Viewshed Analysis so when you zoom in, we can grab the elevation values and redraw without another API call
- Put this in some kind of package management system and break up the files in a more modular way to develop with
- Highlight intrusions into the Fresnel zone in Point-Point Link Analysis
- Allow for a variable tolerance (intrusion) level in the Viewshed Analysis -- e.g. a slider might permit the user to adjust for intrusions ranging from 0 to 100%, which would then alter the resulting viewshed. Typically one might allow for intrusions of up to 40% (or 60% unobstructed) in the first Fresnel zone.
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
4Gon Solutions maintains a good introduction and overview to Fresnel Zones. Mike Bostock and his plentiful d3 examples! http://bl.ocks.org/mbostock