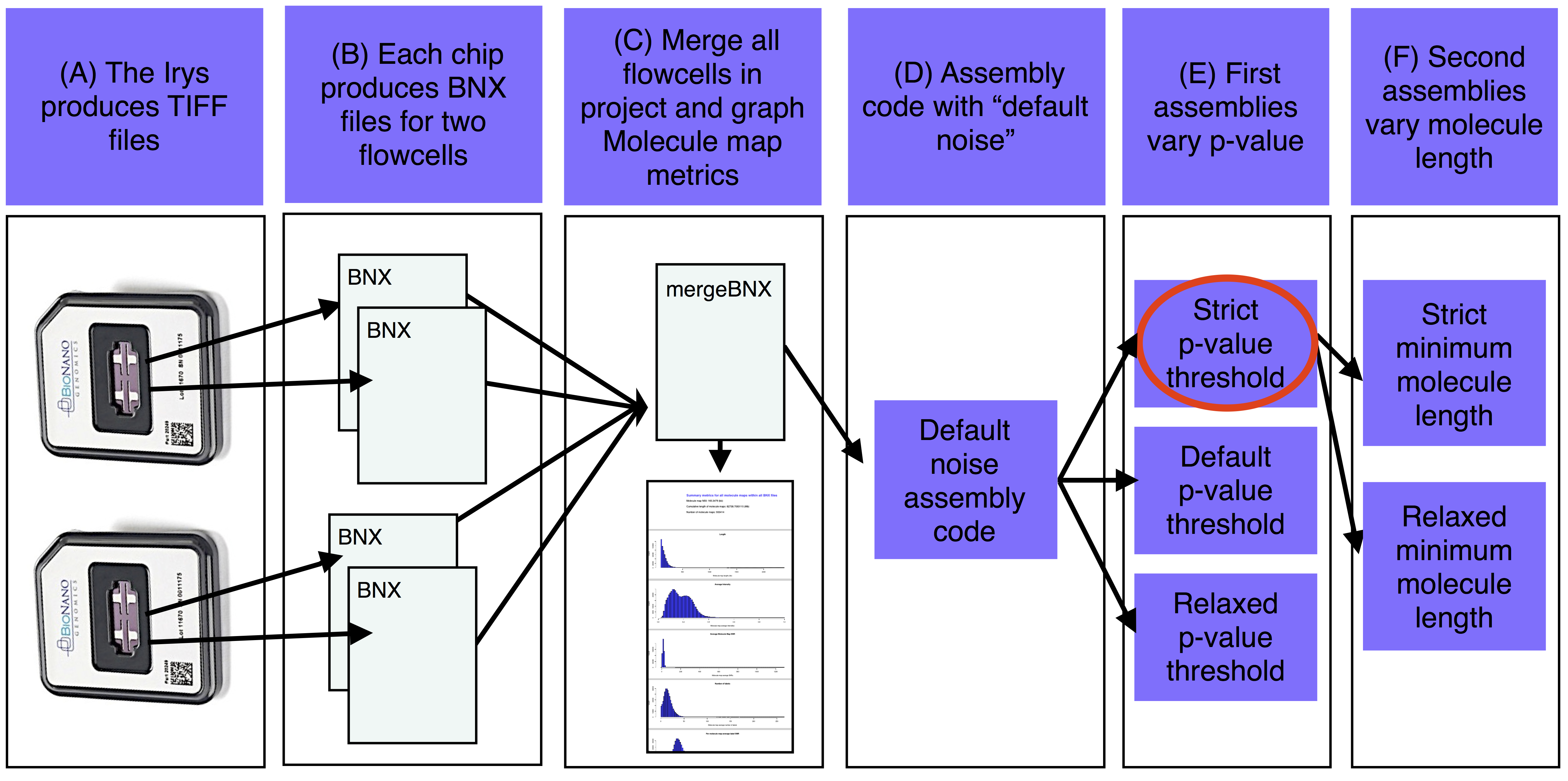
##"Raw data-to-finished de novo assembly and assembly analysis" pipeline for BioNano molecule maps
All of the scripts you will need to complete this lab as well as the sample datasets will be copied to your computer as you follow the instructions below. You should type or paste the text in the beige code block into your terminal as you follow along with the instructions below. If you are not used to commandline, practice with real data is one of the best ways to learn.
If you would like a quick primer on basic linux commands try these 10 minute lessons from Software Carpentry http://software-carpentry.org/v4/shell/index.html.
Note: This pipeline was designed to run on a Xeon Phi server with 576 cores (48x12-core Intel Xeon CPUs), 256GB of RAM, and Linux CentOS 7 operating system. Customization of the "Customize RefAligner Settings" section of Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/rescale_stretch.pl may be required to run the BioNano Assembler on a different machine. Customization of Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/clusterArguments.xml may also be required for assembly to run successfully on a different cluster.
We will be using a BNX file of single molecule maps generated on the BioNano Irys genome mapping system from Escherichia coli genomic DNA. We will write and run a series of assemblies for them. We will then find the best assembly and summarize our final assembly metrics.
The basic steps of the assemble_XeonPhi pipeline for de novo projects are A) The Irys produces TIFF files that are converted into BNX text files of molecule maps. B) Each IrysChip produces one BNX file for each of two flowcells. C) Each BNX file in the bnx/ subdirectory of the -a assembly working directory is merged and molecule map quality metrics are summarized and plotted. D) Base assembly code is determined based on estimated genome size with Default Noise parameters. E) The first assemblies are run with a variety of p-value thresholds (at least one assembly is also run with defult noise parameters). F) The best of the first assemblies (red oval) is chosen and a version of this assembly is produced with a variety of minimum molecule length filters.
As you work through this lab your should read about the software are using by generating and reading the help menus.
Try the -man flag instead of the -help flag for a more detailed description of the program (you type q and enter to exit from a manual screen).
###Step 1: Clone the Git repositories
The following workflow requires that you install BioNano scripts and executables in ~/scripts and ~/tools directories respectively. Follow the Linux installation instructions in the "2.5.1 IrysSolve server RefAligner and Assembler" section of http://www.bnxinstall.com/training/docs/IrysViewSoftwareInstallationGuide.pdf.
When this is done install the KSU custom software using the code below:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/i5K-KINBRE-script-share/Irys-scaffolding.git
git clone https://github.com/i5K-KINBRE-script-share/BNGCompare.git
###Step 2: Create project directory with sample input data in it
Make a working directory by making a copy of the sample_assembly_working_directory. This directory has a fragmented copy of the Escherichia coli str. K-12 substr. DH10B complete genome in it. While only the Molecules.bnx files have any content the file names listed are the same as the filenames one would see in an IrsyView workspace "Datasets" directory.
cp -r ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/sample_assembly_working_directory ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory
###Step 3: Get Molecules.bnx files from the IrysView Dataset subdirectories
Read about the software in this section:
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/prep_bnxXeonPhi.pl -help
In a real workflow you will move the Datasets directory from IrysView to the assembly working directory and run prep_bnxXeonPhi.pl. In this case the Datasets directory is already in our assembly working directory.
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/prep_bnxXeonPhi.pl -a ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory
Check that this worked by looking for the Molecule BNX files in the new bnx subdirectory. The next scripts you call will assume any BNX file in the bnx sub directory of your assembly directory should be used in the assembly.
ls ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/bnx
#####Note, if you need to create a new Datasets directory for data directly from the Irys:
To create a new Datasets directory like this, run "AutoDetect" on your data. Next import the needed flowcells into a new IrsyView workspace. After importing you need to click on each flowcell listed in the workspace to generate a Molecules.bnx file from the RawMolecules.bnx file. After each click wait until the RunReport is displayed in IyrsView before moving to the next flowcell. Finally, move the entire Datasets directory to your linux machine and the same workflow as in this lab to analyze your own data.
###Step 4: Summarize molecule map stats (i.e. for maps in Molecules.bnx files) and write assembly scripts
Read about the software in this section:
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/AssembleIrysXeonPhi.pl -help
Run AssembleIrysXeonPhi.pl to generate summary metrics for your molecule maps , MapStatsHistograms.pdf. Running AssembleIrysXeonPhi.pl will also output an assembly script named assembly_commands.sh that includes commands for assemblies with a variety of parameters. Each set of parameters has its own output sub directory created by the script. For de novo projects add the --de_novo flag to the AssembleIrysXeonPhi.pl command.
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/AssembleIrysXeonPhi.pl -a ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory -g 5 -p Esch_coli_1_2015_000 -r ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/fasta_and_cmap/cmaps/NC_010473_mock_scaffolds_BspQI.cmap --de_novo
Explore the output of this script in the ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/ directory.
The ~/sample_assembly_working_directory/Esch_coli_1_2015_000/MapStatsHistograms.pdf file contains information about the molecule maps > 100 kb. This information includes molecule map N50 and cumulative length, number of maps, molecule map signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), molecule map intensity, average label SNR per molecule map and average label intensity per molecule map.
The assembly script ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/assembly_commands.sh is written with all but three assembly commands commented out. If after running this command no satisfactory assemblies were created, uncomment assemblies with higher and/or lower minimum molecule map length and the best assembly p-value threshold. Also comment out the assemblies that have already run and save your script. Rerun the altered script to see if the new parameters improve the assembly.
###Step 5: Run assembly scripts
Read about the software in this section:
python2 ~/scripts/pipelineCL.py -help
Start your first four assemblies with the command below:
nohup bash ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/assembly_commands.sh &> ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/assembly_commands_out.txt
###Step 6: Evaluate your assemblies
Read about the software in this section:
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/assembly_qcXeonPhi.pl -help
Check the quality of your assemblies with assembly_qcXeonPhi.pl. For de novo projects add the --de_novo flag to the assembly_qcXeonPhi.pl command.
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/assembly_qcXeonPhi.pl -a ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory -g 5 -p Esch_coli_1_2015_000 --de_novo
The ultimate goal is often to produce consensus genome maps that can be used to guide sequence-based haploid reference genome assembly. While single molecule maps can be used to reconstruct haplotypes, genome assembly involves collapsing polymorphisms arbitrarily into a consensus reference genome. Therefore the cumulative length of ideal consensus genome maps should equal the estimated haploid genome length.
Take a look at the ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/Assembly_quality_metrics.csv file to see the results for this assembly. The file Assembly_parameter_tests.csv has details about each assembly that can be used find the best assembly.
###Step 7: Summarize the results for your best assembly
Read about the software in this section:
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/write_report.pl -help
For de novo projects add the --de_novo flag to the write_report.pl command.
perl ~/Irys-scaffolding/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/write_report.pl -b ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/strict_t_150 -p Esch_coli_1_2015_000 -e BspQI --alignment_parameters default_alignment --de_novo
Read your ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/report.txt file or explore files in your ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/Esch_coli_1_2015_000 output directory. The contents of the ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/Esch_coli_1_2015_000 directory are also compressed in the ~/de_novo_sample_assembly_working_directory/Esch_coli_1_2015_000.tar.gz file. Review https://github.com/i5K-KINBRE-script-share/Irys-scaffolding/blob/master/KSU_bioinfo_lab/assemble_XeonPhi/README.pdf file to find out more about this output.