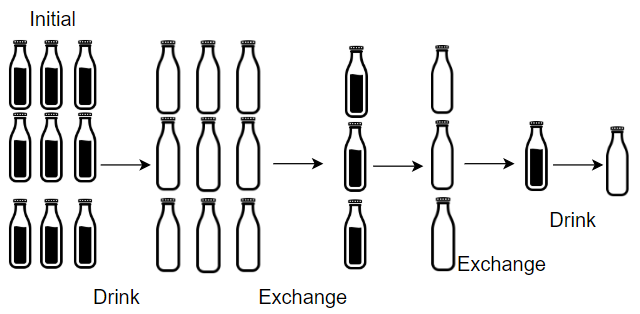
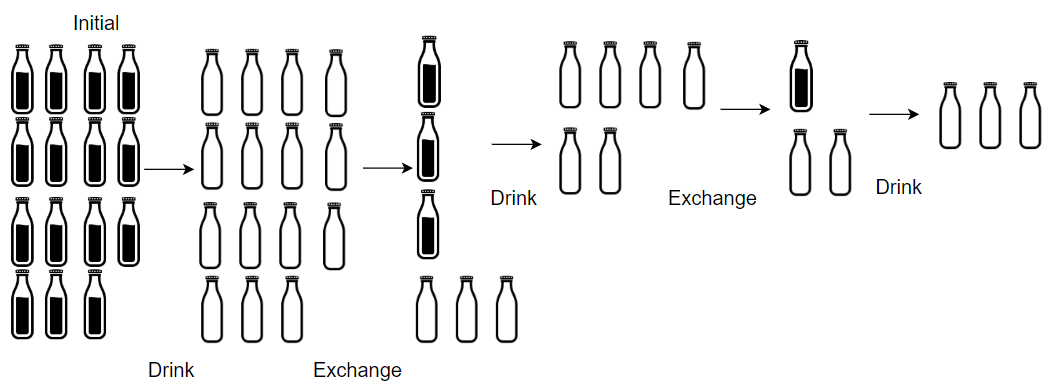
Given numBottles full water bottles, you can exchange numExchange empty water bottles for one full water bottle.
The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle.
Return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
Input: numBottles = 9, numExchange = 3 Output: 13 Explanation: You can exchange 3 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 9 + 3 + 1 = 13.
Input: numBottles = 15, numExchange = 4 Output: 19 Explanation: You can exchange 4 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 15 + 3 + 1 = 19.
Input: numBottles = 5, numExchange = 5 Output: 6
Input: numBottles = 2, numExchange = 3 Output: 2
1 <= numBottles <= 1002 <= numExchange <= 100
# @param {Integer} num_bottles
# @param {Integer} num_exchange
# @return {Integer}
def num_water_bottles(num_bottles, num_exchange)
ret = num_empty = num_bottles
while num_empty >= num_exchange
ret += num_empty / num_exchange
num_empty = num_empty % num_exchange + num_empty / num_exchange
end
return ret
endimpl Solution {
pub fn num_water_bottles(num_bottles: i32, num_exchange: i32) -> i32 {
let mut num_empty = num_bottles;
let mut ret = num_bottles;
while num_empty >= num_exchange {
ret += num_empty / num_exchange;
num_empty = num_empty % num_exchange + num_empty / num_exchange;
}
ret
}
}