Take Note!
With the exception of issues and PRs regarding changes to
hosts/data/StevenBlack/hosts, all other issues regarding the content of the
produced hosts files should be made with the appropriate data source that
contributed the content in question. The contact information for all of the data
sources can be found in the hosts/data/ directory.
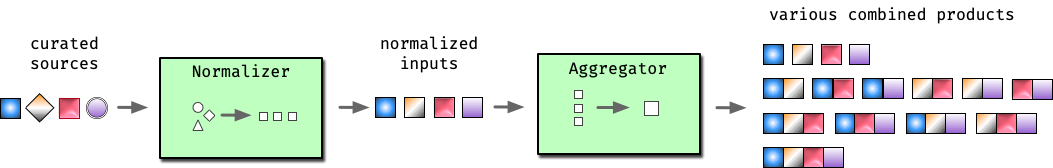
This repository consolidates several reputable hosts files, and merges them
into a unified hosts file with duplicates removed. A variety of tailored hosts
files are provided.
Therefore this repository is a hosts file aggregator.
- Last updated: @GEN_DATE@.
- Here's the raw hosts file @EXTENSIONS_HEADER@ containing @NUM_ENTRIES@ entries.
@SIZEHISTORY@
This repository offers 31 different host file variants, in addition to the base variant, with and without the unified hosts included.
The Non GitHub mirror is the link to use for some hosts file managers like Hostsman for Windows that don't work with GitHub download links.
| Host file recipe | Readme | Raw hosts | Unique domains | Non GitHub mirror |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| @TOCROWS@ |
Expectation: These unified hosts files should serve all devices, regardless of OS.
Updated hosts files from the following locations are always unified and
included:
| Host file source | Home page | Raw hosts | License | Issues | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @SOURCEROWS@ |
The unified hosts file is optionally extensible. Extensions are used to include
domains by category. Currently, we offer the following categories: fakenews,
social, gambling, and porn.
Extensions are optional, and can be combined in various ways with the base hosts
file. The combined products are stored in the
alternates
folder.
Data for extensions are stored in the
extensions
folder. You manage extensions by curating this folder tree, where you will find
the data for fakenews, social, gambling, and porn extension data that we
maintain and provide for you.
You have three options to generate your own hosts file. You can use our container image, build your own image, or do it in your own environment. Option #1 is easiest if you have Linux with Docker installed.
This will replace your
/etc/hosts.
We assume you have Docker available on your host. Just run the following command. Set extensions to your preference.
docker run --pull always --rm -it -v /etc/hosts:/etc/hosts \
ghcr.io/stevenblack/hosts:latest updateHostsFile.py --auto \
--replace --extensions gambling pornIf you want to add custom hosts or a whitelist, create either or both files as
per the instructions and add the
following arguments before ghcr.io/stevenblack/hosts:latest depending on
which you wish to use.
-v "path/to/myhosts:/hosts/myhosts" \
-v "path/to/whitelist:/hosts/whitelist" \You can rerun this exact command later to update based on the latest available hosts (for example, add it to a weekly cron job).
We provide the Dockerfile used by the previous step, which you can use to create a container image with everything you need. The container will contain Python 3 and all its dependency requirements, and a copy of the latest version of this repository.
Build the Docker container from the root of this repo like this:
docker build --no-cache . -t stevenblack-hostsThen run your command as such:
docker run --rm -it stevenblack-hosts updateHostsFile.pyThis will create the hosts file, and remove it with the container when done, so not very useful. You can use the example in option #1 to add volumes so files on your host are replaced.
To generate your own amalgamated hosts files you will need Python 3.6 or later.
First, install the dependencies with:
pip3 install --user -r requirements.txtNote we recommend the --user flag which installs the required dependencies
at the user level. More information about it can be found on pip
documentation.
Spin up a free remote Google Colab environment.
To run unit tests, in the top-level directory, run:
python3 testUpdateHostsFile.pyThe updateHostsFile.py script will generate a unified hosts file based on the
sources in the local data/ subfolder. The script will prompt you whether it
should fetch updated versions (from locations defined by the update.json text
file in each source's folder). Otherwise, it will use the hosts file that's
already there.
python3 updateHostsFile.py [--auto] [--replace] [--ip nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn] [--extensions ext1 ext2 ext3]--help, or -h: display help.
--auto, or -a: run the script without prompting. When --auto is invoked,
- Hosts data sources, including extensions, are updated.
- No extensions are included by default. Use the
--extensionsor-eflag to include any you want. - Your active hosts file is not replaced unless you include the
--replaceflag.
--backup, or -b: Make a backup of existing hosts file(s) as you generate
over them.
--extensions <ext1> <ext2> <ext3>, or -e <ext1> <ext2> <ext3>: the names of
subfolders below the extensions folder containing additional category-specific
hosts files to include in the amalgamation. Example: --extensions porn or
-e social porn.
--flush-dns-cache, or -f: skip the prompt for flushing the DNS cache. Only
active when --replace is also active.
--ip nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, or -i nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn: the IP address to use as the
target. Default is 0.0.0.0.
--keepdomaincomments, or -k: true (default) or false, keep the comments
that appear on the same line as domains. The default is true.
--noupdate, or -n: skip fetching updates from hosts data sources.
--output <subfolder>, or -o <subfolder>: place the generated source file in
a subfolder. If the subfolder does not exist, it will be created.
--replace, or -r: trigger replacing your active hosts
--skipstatichosts, or -s: false (default) or true, omit the standard
section at the top, containing lines like 127.0.0.1 localhost. This is useful
for configuring proximate DNS services on the local network.
--nogendata, or -g: false (default) or true, skip the generation of the
readmeData.json file used for generating readme.md files. This is useful if you
are generating host files with additional whitelists or blacklists and want to
keep your local checkout of this repo unmodified.
--nounifiedhosts: false (default) or true, do not include the unified hosts
file in the final hosts file. Usually used together with --extensions.
--compress, or -c: false (default) or true, Compress the hosts file
ignoring non-necessary lines (empty lines and comments) and putting multiple
domains in each line. Reducing the number of lines of the hosts file improves
the performances under Windows (with DNS Client service enabled).
--minimise, or -m: false (default) or true, like --compress, but puts
each domain on a separate line. This is necessary because many implementations
of URL blockers that rely on hosts files do not conform to the standard which
allows multiple hosts on a single line.
--blacklist <blacklistfile>, or -x <blacklistfile>: Append the given
blacklist file in hosts format to the generated hosts file.
--whitelist <whitelistfile>, or -w <whitelistfile>: Use the given whitelist
file to remove hosts from the generated hosts file.
Add one or more additional sources, each in a subfolder of the data/ folder,
and specify the url key in its update.json file.
Add one or more optional extensions, which originate from subfolders of the
extensions/ folder. Again the url in update.json controls where this
extension finds its updates.
Create an optional blacklist file. The contents of this file (containing a
listing of additional domains in hosts file format) are appended to the
unified hosts file during the update process. A sample blacklist is included,
and may be modified as you need.
- NOTE: The
blacklistis not tracked by git, so any changes you make won't be overridden when yougit pullthis repo fromoriginin the future.
If you have custom hosts records, place them in file myhosts. The contents of
this file are prepended to the unified hosts file during the update process.
The myhosts file is not tracked by git, so any changes you make won't be
overridden when you git pull this repo from origin in the future.
The domains you list in the whitelist file are excluded from the final hosts
file.
The whitelist uses partial matching. Therefore if you whitelist
google-analytics.com, that domain and all its subdomains won't be merged into
the final hosts file.
The whitelist is not tracked by git, so any changes you make won't be
overridden when you git pull this repo from origin in the future.
If you discover sketchy domains you feel should be included here, here are some ways to contribute them.
The best way to get new domains included is to submit an issue to any of the data providers whose home pages are listed here. This is best because once you submit new domains, they will be curated and updated by the dedicated folks who maintain these sources.
Option 2: Fork this repository, add your domains to Steven Black's personal data file, and submit a pull request
Fork this hosts this repo and add your links to https://github.com/StevenBlack/hosts/blob/master/data/StevenBlack/hosts.
Then, submit a pull request.
WARNING: this is less desirable than Option 1 because the ongoing curation falls on us. So this creates more work for us.
If you're able to curate your own collection of sketchy domains, then curate your own hosts list. Then signal the existence of your repo as a new issue and we may include your new repo into the collection of sources we pull whenever we create new versions.
A hosts file, named hosts (with no file extension), is a plain-text file used
by all operating systems to map hostnames to IP addresses.
In most operating systems, the hosts file is preferential to DNS. Therefore
if a domain name is resolved by the hosts file, the request never leaves your
computer.
Having a smart hosts file goes a long way towards blocking malware, adware,
and other irritants.
For example, to nullify requests to some doubleclick.net servers, adding these lines to your hosts file will do it:
# block doubleClick's servers
0.0.0.0 ad.ae.doubleclick.net
0.0.0.0 ad.ar.doubleclick.net
0.0.0.0 ad.at.doubleclick.net
0.0.0.0 ad.au.doubleclick.net
0.0.0.0 ad.be.doubleclick.net
# etc...
Traditionally most host files use 127.0.0.1, the loopback address, to
establish an IP connection to the local machine.
We prefer to use 0.0.0.0, which is defined as a non-routable meta-address used
to designate an invalid, unknown, or non-applicable target.
Using 0.0.0.0 is empirically faster, possibly because there's no wait for a
timeout resolution. It also does not interfere with a web server that may be
running on the local PC.
We tried that. Using 0 doesn't work universally.
To modify your current hosts file, look for it in the following places and
modify it with a text editor.
- macOS (until 10.14.x macOS Mojave), iOS, Android, Linux:
/etc/hostsfile. - macOS Catalina:
/private/etc/hostsfile. - Windows:
%SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\hostsfile.
Gentoo users may find
sb-hosts
in ::pf4public Gentoo overlay
To install hosts file on your machine add the following into your
configuration.nix:
{
networking.extraHosts = let
hostsPath = https://raw.githubusercontent.com/StevenBlack/hosts/master/hosts;
hostsFile = builtins.fetchurl hostsPath;
in builtins.readFile "${hostsFile}";
}- NOTE: Change
hostsPathif you need other versions of hosts file. - NOTE: The call to
fetchurlis impure. UsefetchFromGitHubwith the exact commit if you want to always get the same result.
NixOS installations which are managed through flakes can use the hosts file like this:
{
inputs.hosts.url = "github:StevenBlack/hosts";
outputs = { self, nixpkgs, hosts }: {
nixosConfigurations.my-hostname = {
system = "<architecture>";
modules = [
hosts.nixosModule {
networking.stevenBlackHosts.enable = true;
}
];
};
};
}The hosts extensions are also available with the following options:
{
networking.stevenBlackHosts = {
blockFakenews = true;
blockGambling = true;
blockPorn = true;
blockSocial = true;
};
}(NOTE: See also some third-party Hosts managers, listed below.)
On Linux and macOS, run the Python script. On Windows more work is required due to compatibility issues so it's preferable to run the batch file as follows:
updateHostsWindows.batThis file MUST be run in command prompt with administrator privileges in the repository directory. In addition to updating the hosts file, it can also replace the existing hosts file, and reload the DNS cache. It goes without saying that for this to work, you must be connected to the internet.
To open a command prompt as administrator in the repository's directory, do the following:
- Windows XP: Start → Run →
cmd - Windows Vista, 7: Start Button → type
cmd→ right-click Command Prompt → "Run as Administrator" - Windows 8: Start → Swipe Up → All Apps → Windows System → right-click Command Prompt → "Run as Administrator"
- Windows 10: Start Button → type
cmd→ right-click Command Prompt → "Run as Administrator"
You can also refer to the "Third-Party Hosts Managers" section for further recommended solutions from third parties.
Windows has issues with larger hosts files. Recent changes in security within
Windows 10 denies access to changing services via other tools except registry
hacks. Use the disable-dnscache-service-win.cmd file to make proper changes to
the Windows registry. You will need to reboot your device once that's done. See
the
the comments within the cmd file
for more details.
Disabling the DNS Cache Service can cause issues with services and applications like WSL and it's possible to compress the hosts file and negate the need to disable the DNS caching service. You can try the C++ Windows command line tool at Hosts Compress - Windows (the recommended method) or the PowerShell compression script and check out the guide located at the Hosts Compression Scripts repository.
Your operating system will cache DNS lookups. You can either reboot or run the following commands to manually flush your DNS cache once the new hosts file is in place.
The Google Chrome browser may require manually cleaning up its DNS Cache on
chrome://net-internals/#dns page to thereafter see the changes in your hosts
file. See: https://superuser.com/questions/723703
Open a command prompt with administrator privileges and run this command:
ipconfig /flushdnsOpen a Terminal and run with root privileges:
-
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo service network-manager restart -
Linux Mint
sudo /etc/init.d/dns-clean start -
Linux with systemd:
sudo systemctl restart network.service -
Fedora Linux:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service -
Arch Linux/Manjaro with Network Manager:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service -
Arch Linux/Manjaro with Wicd:
sudo systemctl restart wicd.service -
RHEL/Centos:
sudo /etc/init.d/network restart -
FreeBSD:
sudo service nscd restartTo enable the
nscddaemon initially, it is recommended that you run the following commands:sudo sysrc nscd_enable="YES" sudo service nscd startThen modify the
hostsline in your/etc/nsswitch.conffile to the following:hosts: cache files dns -
NixOS: The
nscd.serviceis automatically restarted when the optionnetworking.extraHostswas changed. -
Others: Consult this Wikipedia article.
As described in this article, open a Terminal and run:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponderThis repository uses release-it, an excellent CLI release tool for GitHub repos and npm packages, to automate creating releases. This is why the package.json and .release-it.json files are bundled.
The goals of this repo are to:
- automatically combine high-quality lists of hosts,
- provide situation-appropriate extensions,
- de-dupe the resultant combined list,
- and keep the resultant file reasonably sized.
A high-quality source is defined here as one that is actively curated. A hosts source should be frequently updated by its maintainers with both additions and removals. The larger the hosts file, the higher the level of curation is expected.
It is expected that this unified hosts file will serve both desktop and mobile devices under a variety of operating systems.
- Unified Hosts AutoUpdate (for Windows): The Unified Hosts AutoUpdate package is purpose-built for this unified hosts project as well as in active development by community members. You can install and uninstall any blacklist and keep it automatically up to date, and can be placed in a shared network location and deployed across an organization via group policies. And since it is in active development by community members, your bug reports, feature requests, and other feedback are most welcome.
- ViHoMa is a Visual Hosts file Manager, written in Java, by Christian Martínez. Check it out!
- Hosts-BL is a simple tool to handle hosts file black lists. It can remove comments, remove duplicates, compress to 9 domains per line, add IPv6 entries. In addition, it can also convert black lists to multiple other black list formats compatible with other software, such as dnsmasq, DualServer, RPZ, Privoxy, and Unbound, to name a few.
- Host Minder is a simple GUI that allows you to easily update your /etc/hosts file to one of four consolidated hosts files from StevenBlack/hosts. It is provided as a deb package and comes pre-installed on UbuntuCE.
- Maza ad blocking is a bash script that automatically updates host file. You can also update a fresh copy. And each time it generates a dnsmasq-compatible configuration file. Fast installation, compatible with MacOS, Linux and BSD.
- Hostile is a nifty command line utility
to easily add or remove domains from your hosts file. If our hosts files are
too aggressive for you, you can use
hostileto remove domains, or you can usehostilein a bash script to automate a post process each time you download fresh versions of hosts. - macOS Scripting for Configuration, Backup and Restore helps customizing, re-installing and using macOS. It also provides a script to install and update the hosts file using this project on macOS. In combination with a launchd it updates the hosts file every x days (default is 4). To install both, download the GitHub repo and run the install script from the directory one level up.
- Pi-hole is a network-wide DHCP server and ad blocker that runs on Raspberry Pi. Pi-hole uses this repository as one of its sources.
- Block ads and malware via local BIND9 DNS server
(for Debian, Raspbian & Ubuntu): Set up a local DNS server with a
/etc/bind/named.conf.blockedfile, sourced from here. - Block ads, malware, and deploy parental controls via local DualServer DNS/DHCP server (for BSD, Windows & Linux): Set up a blacklist for everyone on your network using the power of the unified hosts reformatted for DualServer. And if you're on Windows, this project also maintains an update script to make updating DualServer's blacklist even easier.
- Blocking ads and malwares with unbound – Unbound is a validating, recursive, and caching DNS resolver.
- dnsmasq conversion script
This GitHub gist has a short shell script (bash, will work on any 'nix) and
uses
wget&awkpresent in most distros, to fetch a specified hosts file and convert it to the format required by dnsmasq. Supports IPv4 and IPv6. Designed to be used as either a shell script, or can be dropped into/etc/cron.weekly(or wherever suits). The script is short and easily edited, also has a short document attached with notes on dnsmasq setup. - BlackHosts - Command Line Installer/Updater This is a cross-platform command line utility to help install/update hosts files found at this repository.
- Hosts Compression Scripts These are various scripts to help compress hosts files (by the author of BlackHosts).
- Hosts Compress - Windows This is a C++ Windows command line tool to help compress hosts files (by the author of BlackHosts and Hosts Compression Scripts). This is highly recommended over the scripts as it is exponentially faster.
- dnscrypt-proxy provides a tool to build block lists from local and remote lists in common formats.
- Control D
offers a public anycast network hosted mirror of the Unified (Adware + Malware) blocklist:
- Legacy DNS:
76.76.2.35,76.76.10.35,2606:1a40::35,2606:1a40:1::35 - DNS-over-HTTPS/TLS/DOQ:
https://freedns.controld.com/x-stevenblack,x-stevenblack.freedns.controld.com
- Legacy DNS:
Please read our Contributing Guide. Among other things, this explains how we organize files and folders in this repository.
We are always interested in discovering well-curated sources of hosts. If you find one, please open an issue to draw our attention.
Before you create or respond to any issue, please read our code of conduct.
Logo by @Tobaloidee Thank you!.