MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol that is widely used in the Internet of Things (IoT). It is ideal for remote device connections due to its efficiency and simplicity. Some of its characteristics include:
- MQTT protocol headers are small. The minimal protocol overhead makes it well-suited for low-bandwidth, high-latency, and unreliable networks.
- The MQTT protocol uses a publish-subscribe model in which clients communicate indirectly through a broker. The decoupling of the sender and receiver allows for greater scalability and flexibility.
- MQTT protocol uses QoS (Quality of Service) levels to ensure the reliability of message delivery.
- MQTT protocol enables TLS/SSL-based security and various authentication mechanisms.
With the rapid increase in IoT adoption, the number of devices and systems relying on MQTT has grown significantly. MQTT testing, as an essential method of validating the functionality, performance, security, and reliability of MQTT implementations, become especially important in recent days.
Sufficient MQTT testing can guarantee the reliability, scalability, and security of the IoT system.
- MQTT testing ensures that communication between IoT devices is stable and reliable, preventing disruptions in critical applications. Conversely, a flawed system may experience unexpected breakdowns, resulting in downtime and loss of productivity. Additionally, defects in the system can lead to data loss or corruption.
- MQTT testing is essential for ensuring performance and scalability. By stress-testing MQTT implementations, we can make sure that the system can handle high volumes of messages and connections without any performance degradation. Inability to accommodate increasing numbers of devices and messages is a serious limitation in modern IoT applications.
- MQTT testing plays a crucial role in safeguarding the security of IoT systems. Through thorough testing, potential security vulnerabilities can be uncovered and addressed, effectively shielding IoT systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber-attacks. Conversely, overlooking security flaws exposes IoT systems to the risk of compromising sensitive information and system integrity.
The main types of MQTT testing include functional testing, performance testing, and security testing:
- Functional testing validates that all MQTT features and functionalities work as designed. It involves verifying the correct connection handling and message delivery.
- Performance testing involves stress testing to assess system performance under heavy loads, endurance testing to evaluate stability over time, and scalability testing to measure the system's ability to scale efficiently.
- Security testing aims to uncover and fix vulnerabilities in the MQTT implementation to prevent unauthorized access, message interception, and data leakage.
There are also other types of MQTT testing like compatibility testing, interoperability testing, and usability testing.
To make MQTT testing process efficient and effective, some best practices can be adhered to.
Automation can streamline repetitive tests, boosting efficiency. Popular tools for MQTT testing and frameworks like JMeter can be utilized to meet custom requirements.
When designing test cases, it's important to consider all primary features of the protocol such as connect/disconnect, publish/subscribe, QoS, session persistence, topic wildcards, and security mechanisms. Additionally, different MQTT versions offer different functionalities which should also be taken into account.
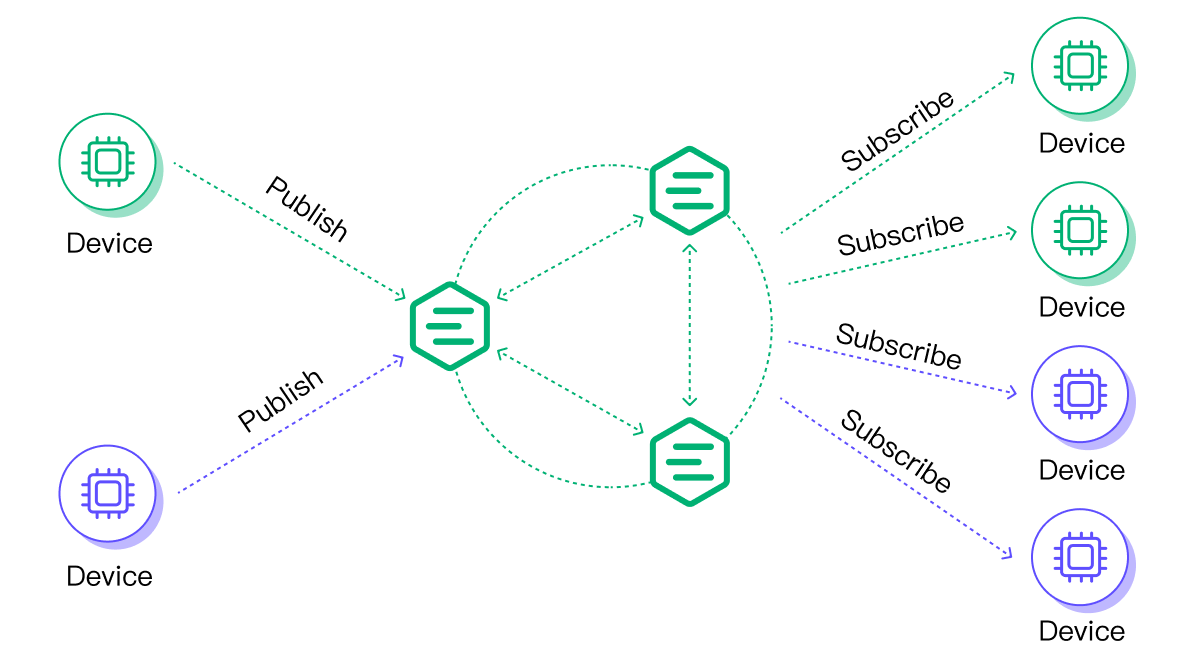
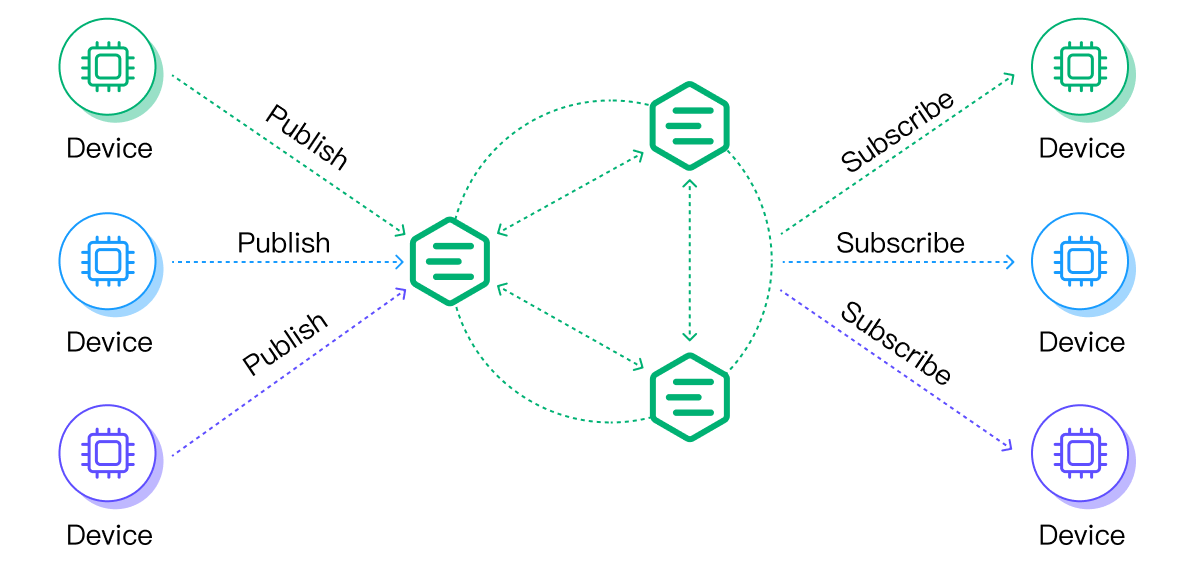
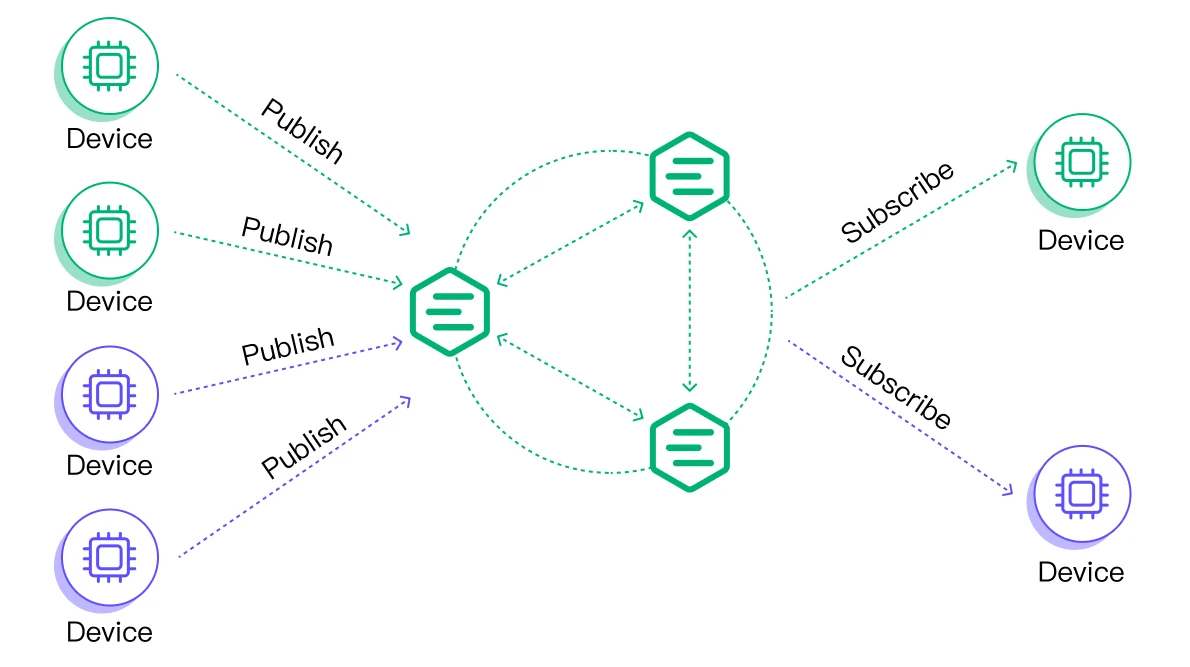
Realistic requirements may vary, but they are all based on common messaging test scenarios: fan-out, point-to-point, and fan-in.
- In a fan-out scenario, there are a large number of subscribers and only a few or a single publisher.
- A point-to-point scenario involves an equal number of subscribers and publishers.
- In a fan-in scenario, publishers greatly outnumber subscribers.
point-to-point
fan-in
More and more MQTT applications involve edge devices under limited network conditions with low bandwidth and high latency. A solid testing should also incorporate cases covering extreme or boundary conditions to ensure the availability and robustness of those systems.
Getting early feedback on code quality can increase the chances of reducing defects in production. Using automation tools and maximizing test coverage significantly improves the effectiveness of continuous testing. Integrating the testing process into CI/CD pipelines ensures that tests run automatically when there's a code change.
- MQTTX: A desktop and CLI MQTT client with cross-platform compatibility, providing a simplified way for developing and testing MQTT applications.
- Mosquitto: CLI MQTT client from Mosquitto project.
- MQTT.fx: A desktop MQTT client based on Eclipse Paho, providing the ability to debug and test MQTT communications.
- MQTT Explorer: An MQTT client to visualize, publish, subscribe, and plot topics.
For more detailed comparison of these tools, please refer to: 7 Best MQTT Client Tools Worth Trying in 2024
- XMeter: A public cloud service built on JMeter, providing easy and fast way for large-scale MQTT load testing.
- emqtt_bench: A lightweight MQTT benchmark tool for concurrent connections and message throughput.
To provide readers with a quick overview of MQTT testing tools, we will use MQTTX to demonstrate its capabilities in functional testing, and XMeter to showcase its suitability for performance testing.
-
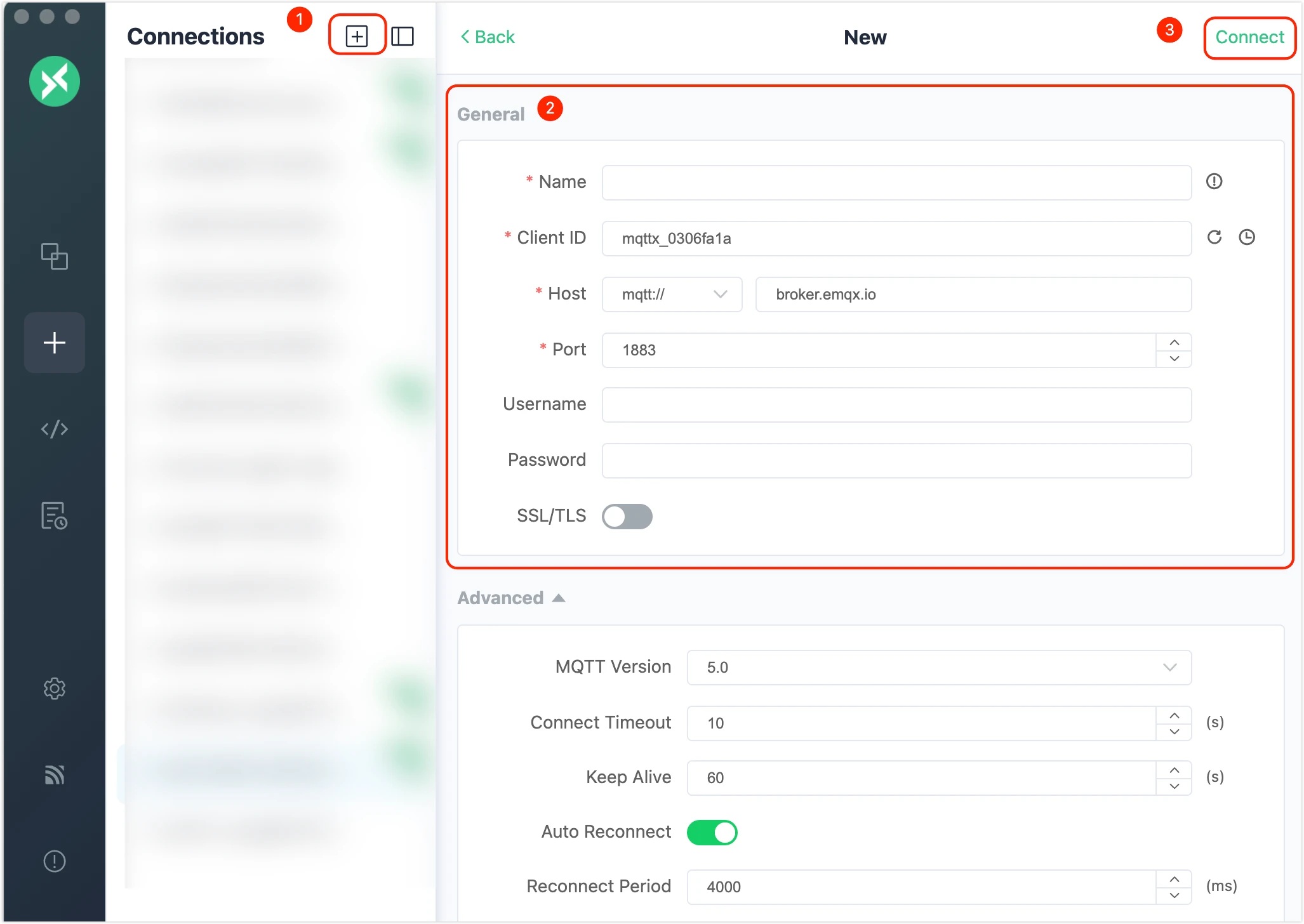
Configure and connect
Click the
+button from the left menu bar and fill in the general connection information. More sophisticated configuration can be set in 'Advanced' form. Then click theConnectbutton in the upper right corner to connect to the desired MQTT Broker. -
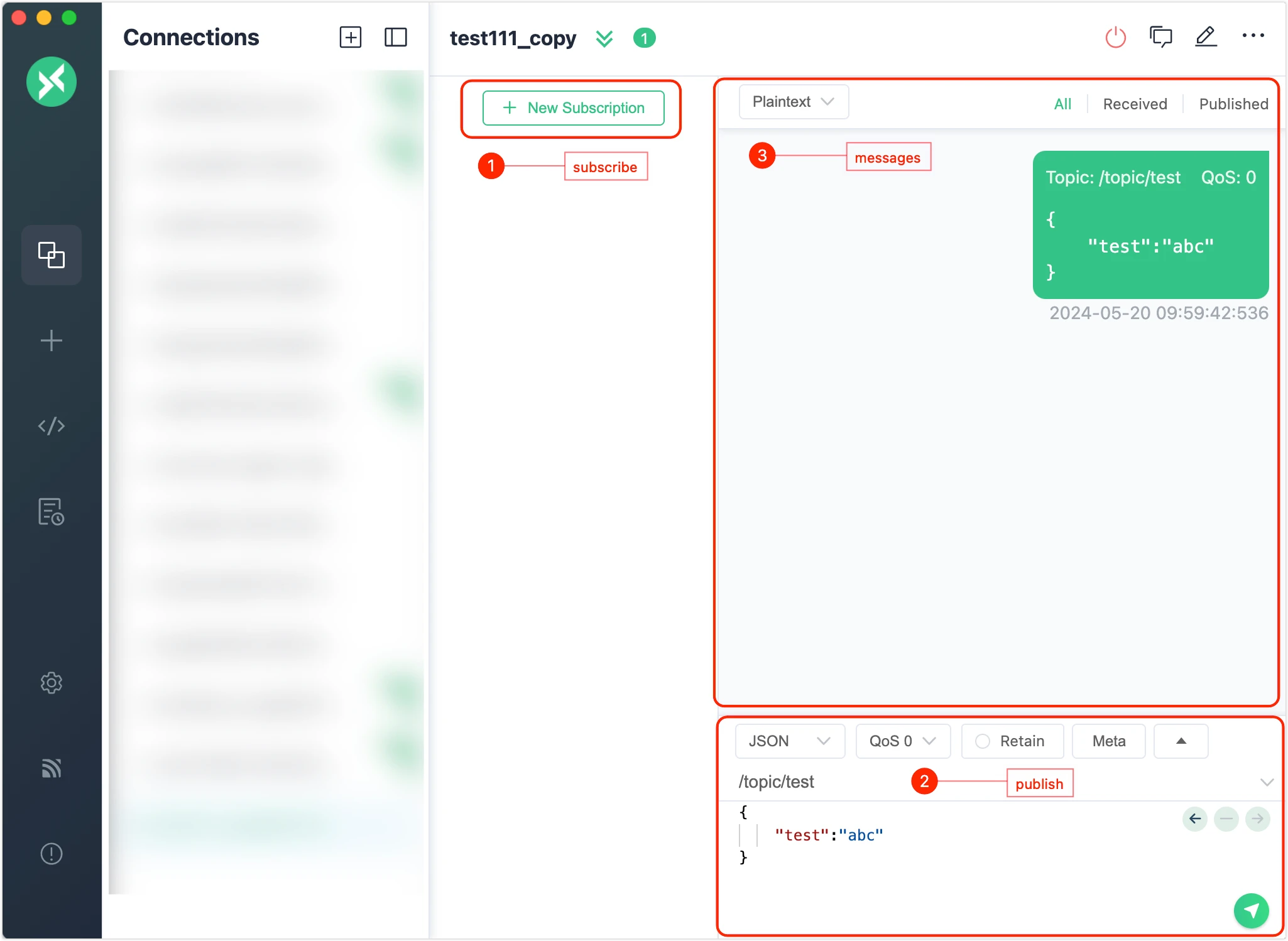
Subscribe and publish
Add a subscription by clicking the
New Subscriptionbutton on the left.Publish messages to a topic from the lower right corner.
Received and published messages can be seen from the message panel.
-
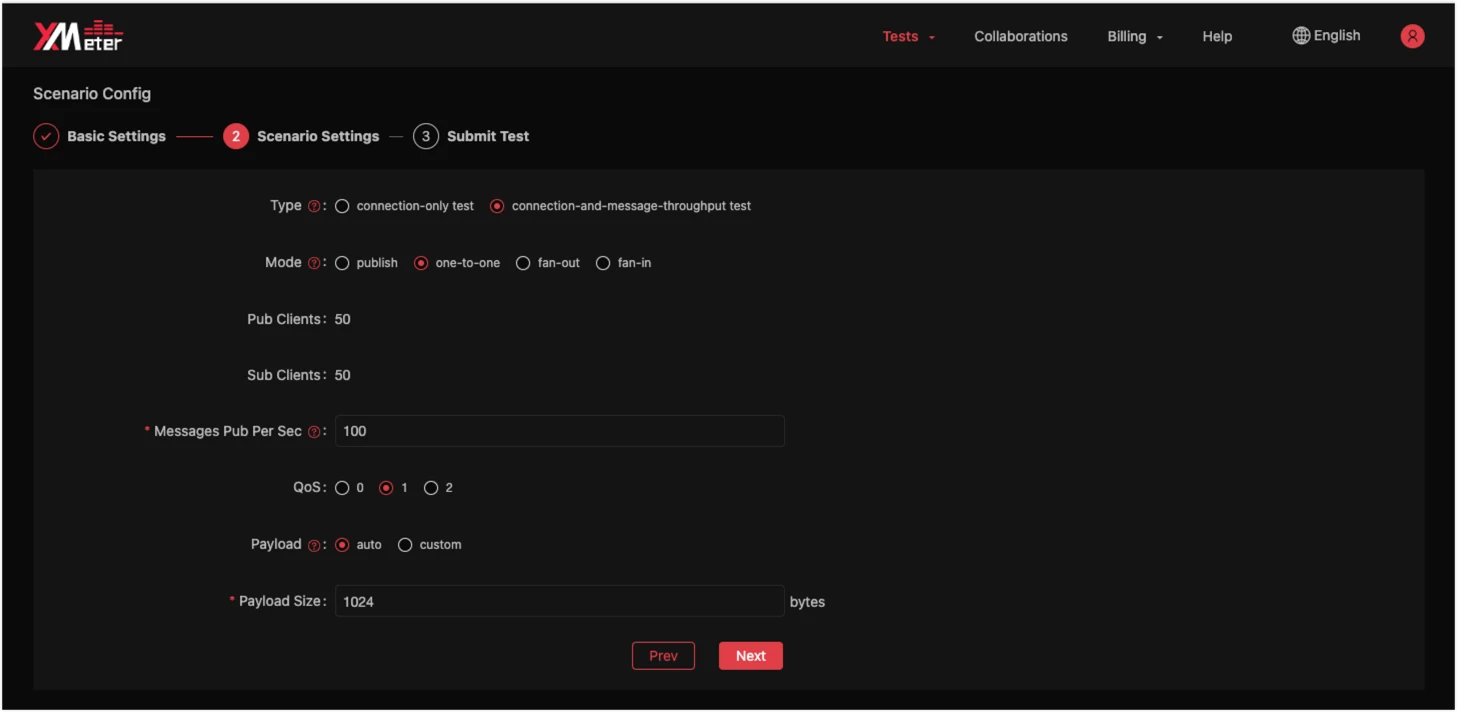
Create a test
Configure MQTT Broker information, select a built-in test scenario, and fill in load test specifications.
-
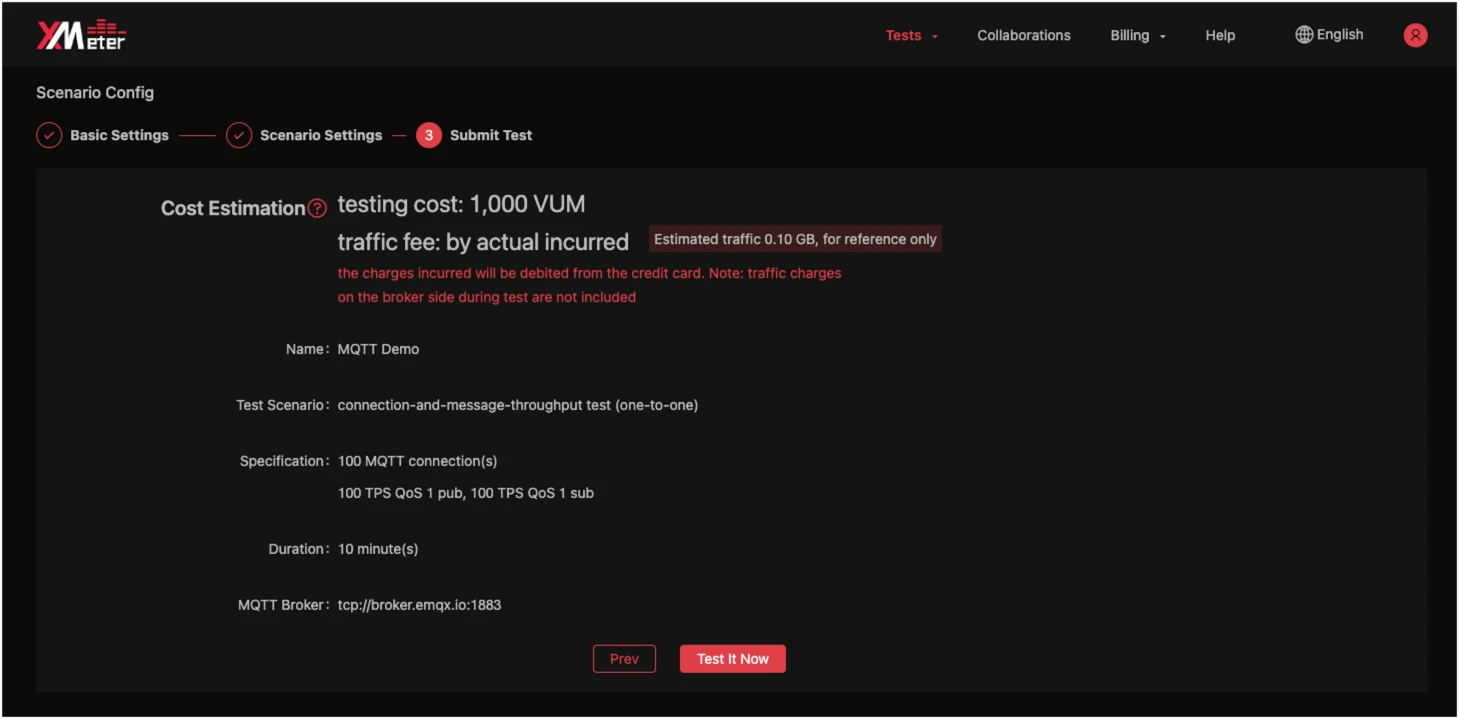
Execute the load test
Click
Test it Nowbutton to submit the MQTT load test. Test resources will be created automatically. -
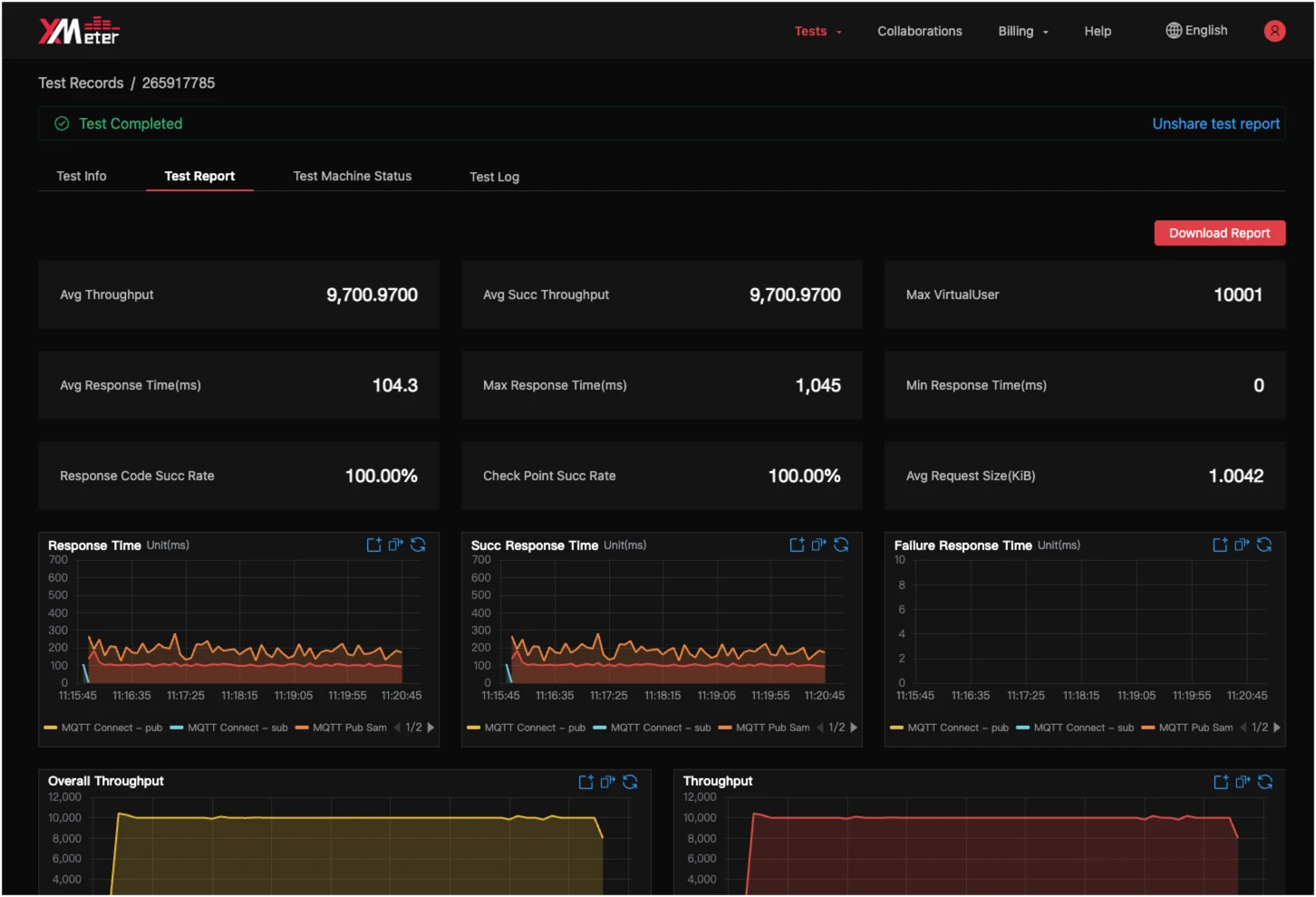
View test report
Check test progress and analysis results from a graphic report in real time.
In conclusion, MQTT testing is a critical component in the development and maintenance of reliable and secure IoT solutions. By rigorously testing MQTT implementations, we can ensure that data transmission between devices is both efficient and resilient to potential failures. Moreover, thorough testing helps identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities, safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of IoT ecosystems. As the reliance on interconnected devices continues to grow, the importance of robust MQTT testing cannot be overstated—it is essential for delivering dependable and secure communication in an increasingly connected world.