Node-RED is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to create flows using a wide range of nodes. Flows can be deployed to their runtime with a single click.
Node-RED supports the MQTT protocol with mqtt-in nodes for data input and mqtt-out nodes for data output.
Key Features of Node-RED:
- Flow-Based Programming: Create applications by visually wiring nodes together.
- Wide Range of Nodes: Includes nodes for various input, output, and processing tasks.
- Message Passing: Nodes communicate by passing messages along wires.
- Browser-Based Editor: Accessible and easy-to-use interface for building and deploying flows.
- Extensibility: Custom nodes can be created to extend functionality.
- Social Development: JSON-based flows allow easy import, export, and sharing through an online flow library.
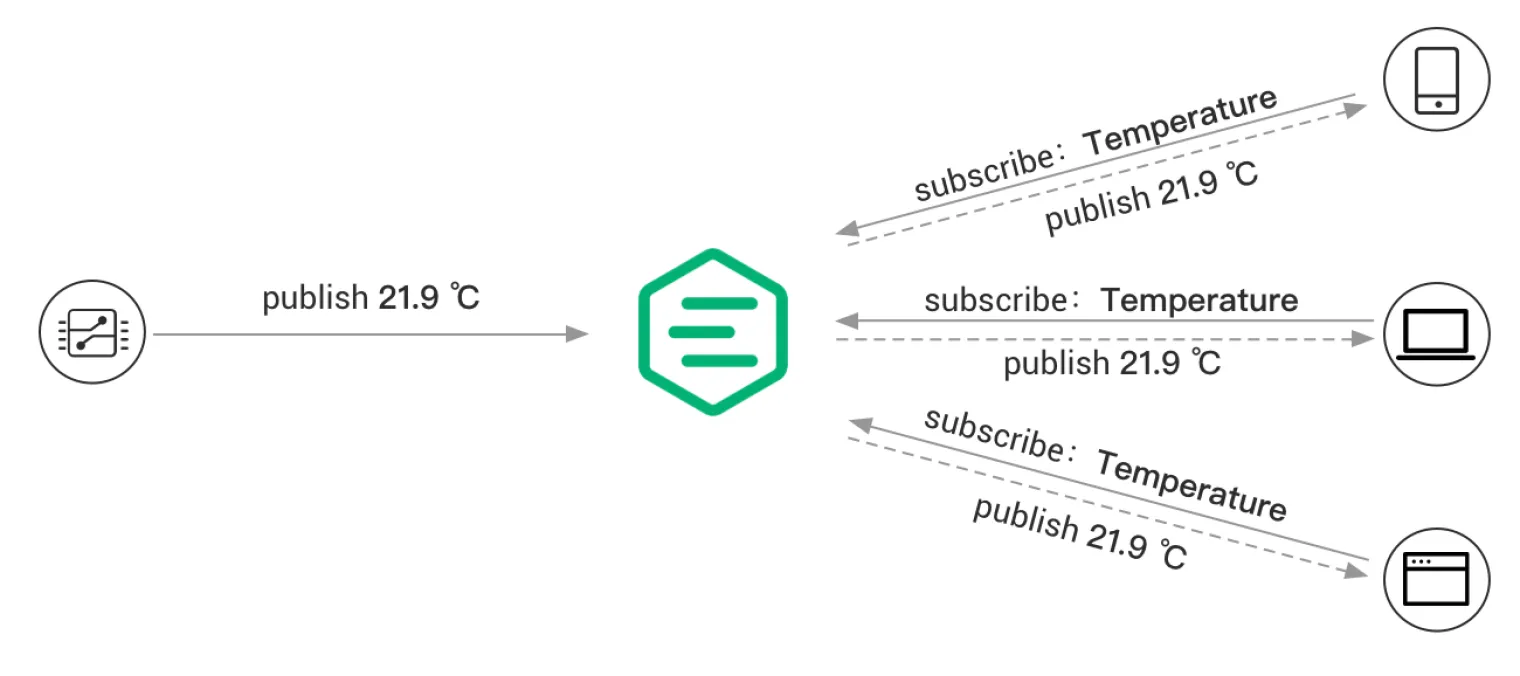
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight, publish-subscribe-based messaging protocol for resource-constrained devices and low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks. It is widely used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications, providing efficient communication between sensors, actuators, and other devices.
A central broker is required to use MQTT. EMQX, for example, is a broker that can be considered for its capabilities in ensuring reliable message delivery and scaling the system efficiently.
Combining MQTT with Node-RED provides a powerful solution for various applications, especially in IoT and real-time data processing. Here’s why:
- Efficient Data Handling: Node-RED processes MQTT messages in real-time, enabling immediate responses to sensor data and other inputs.
- Ease of Use: Node-RED's visual programming interface makes creating and deploying complex workflows easy without extensive coding knowledge.
- Optimized for IoT: Node-RED’s flexibility and extensive library of nodes enable seamless connection and data handling for various IoT devices. MQTT ensures efficient communication in low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks with features like Quality of Service (QoS) levels, retained messages, and last will (LWT).
- Versatility: Node-RED is not limited to IoT. It is useful for home automation, industrial automation, data visualization, and integration with cloud services.
- Scalability: Node-RED and MQTT support scalable solutions, handling numerous devices and large volumes of data efficiently.
You can quickly build scalable, reliable, and efficient applications across various domains by combining Node-RED’s visual flow-based development environment with MQTT’s robust features and lightweightness.
Node-RED, installed either on your PC or devices such as Raspberry Pi or cloud servers, can be quickly installed and used. Here are two common methods for installation:
Use npm for global installation:
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-redUse Docker for installation:
docker run -it -p 1880:1880 --name mynodered nodered/node-redIf you use npm for global installation, and after you are prompted that the installation is successful, you can start the Node-RED immediately by simply running the node-red command globally.
Whether Docker or npm is used, after successful startup, we only need to open the browser and enter the current address plus the 1880 port number to open the browser editor page of Node-RED. For example, if running locally, open the browser and enter http://127.0.0.1:1880. When you see the page shown in the following figure, it means that Node-RED has been successfully started:
In this guide, we will utilize the free public MQTT broker provided by EMQ, built on EMQX Platform. The server access details are as follows:
- Broker:
broker.emqx.io - TCP Port: 1883
- SSL/TLS Port: 8883
- WebSocket Port: 8083
- SSL/TLS Port: 8883
- Secure WebSocket Port: 8084
This article introduces MQTT in Node-RED in two parts. The basic part covers configuring MQTT nodes and connecting to an MQTT broker, while the advanced part focuses on data processing.
First, open http://host:1880 in your browser, creating a default Flow 1. Next, follow these steps:
1.1. Add MQTT-in Node: Drag an mqtt-in node from the palette onto the central canvas and double-click it to open the configuration page.
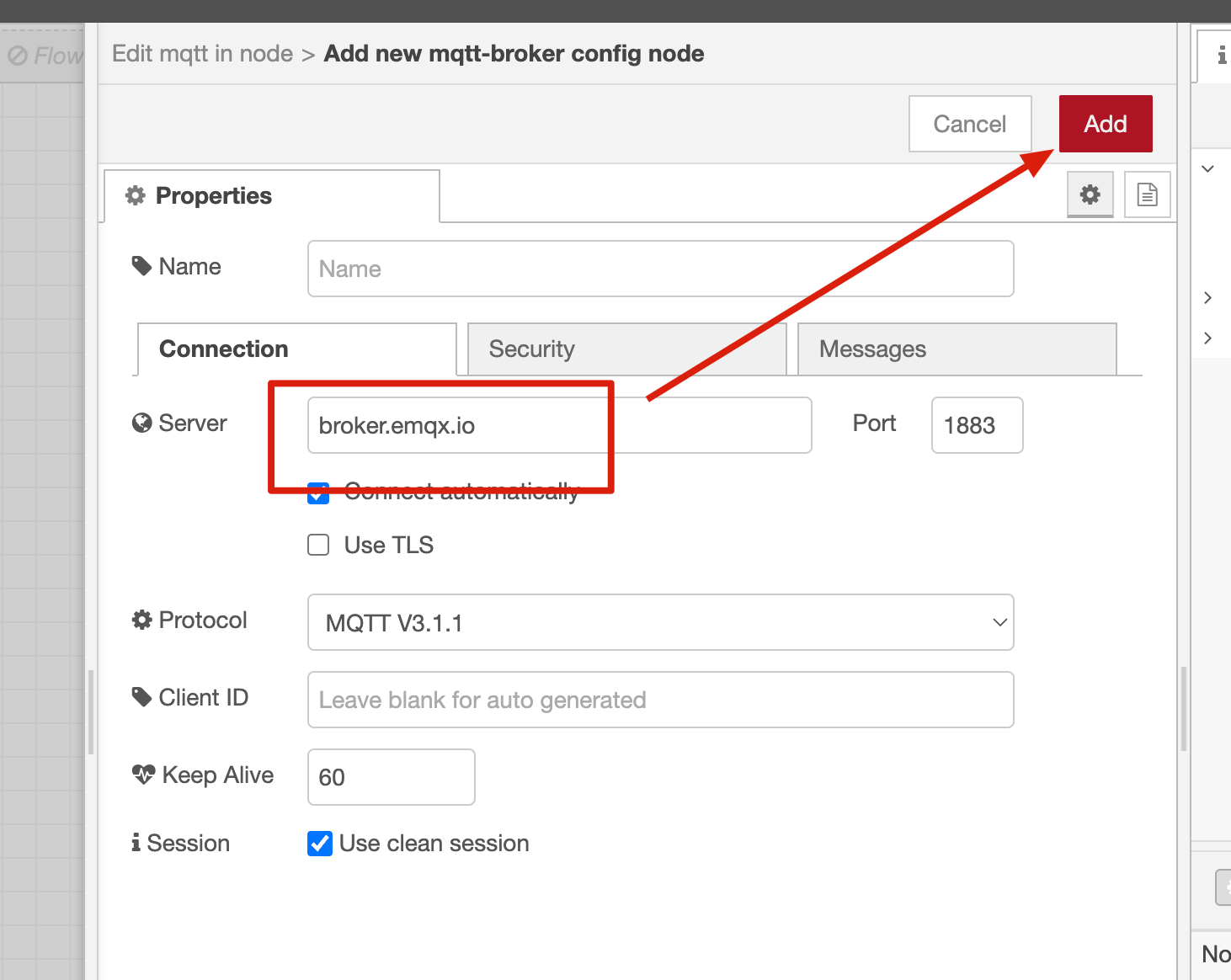
1.2. Configure MQTT Broker: Click the edit button next to the "Server" field to add a new MQTT broker, enter the broker address broker.emqx.io and other connection details, and click Add to save the broker configuration.
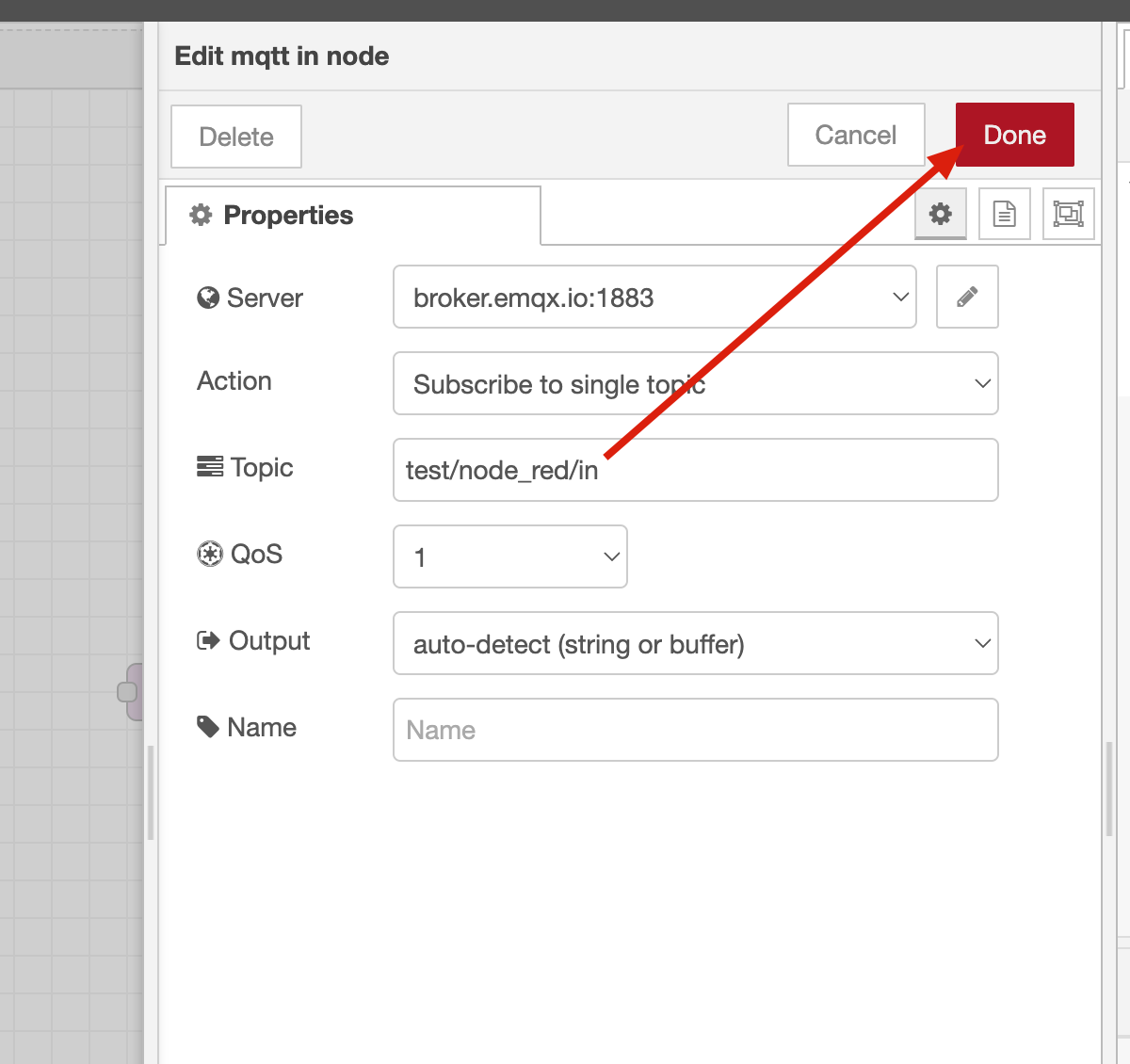
1.3. Subscribe to a Topic: Enter a topic to subscribe to, such as test/node_red/in, select the desired QoS level, and click Done to save the node configuration.
2.1. Add MQTT-out Node: Drag an mqtt-out node onto the central canvas and double-click the node to open the configuration page.
2.2. Configure MQTT Broker: Ensure the previously configured MQTT broker is selected.
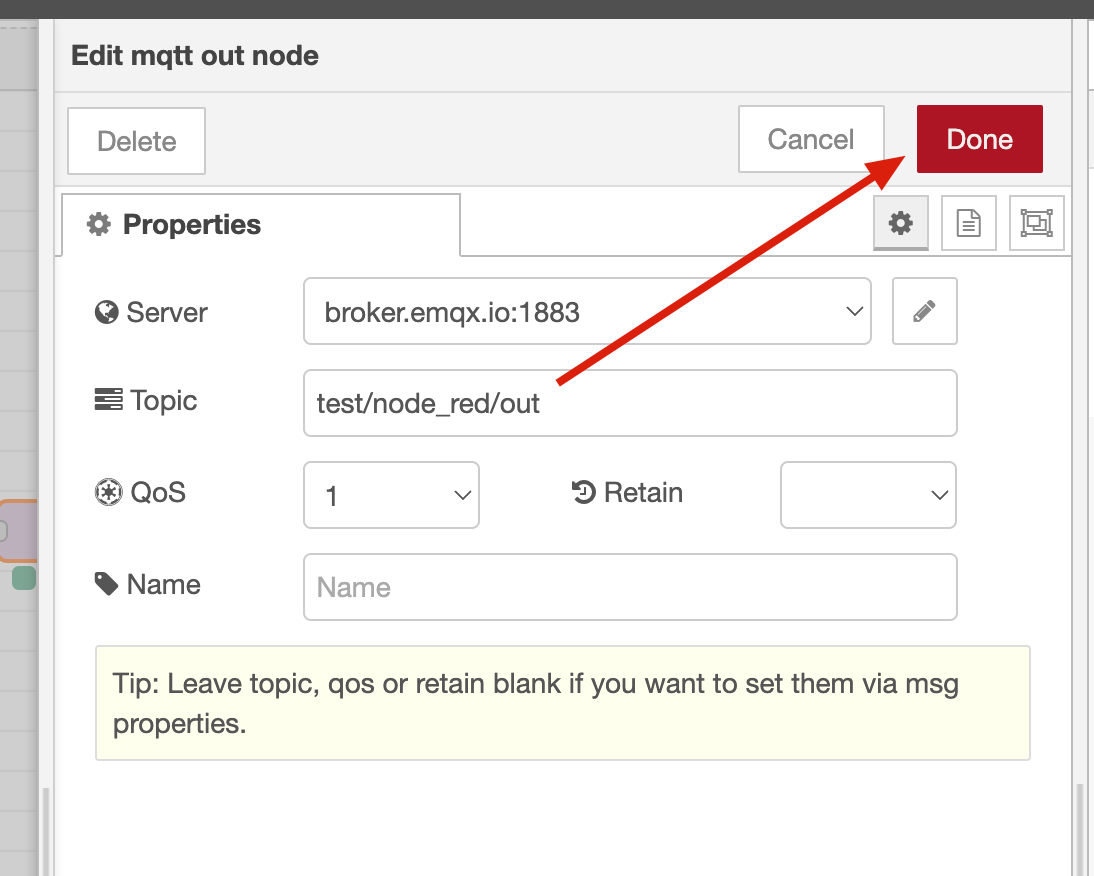
2.3. Publish to a Topic: Enter a topic to publish to, such as test/node_red/out, select the desired QoS level, configure if the message should be retained, and click Done to save the node configuration.
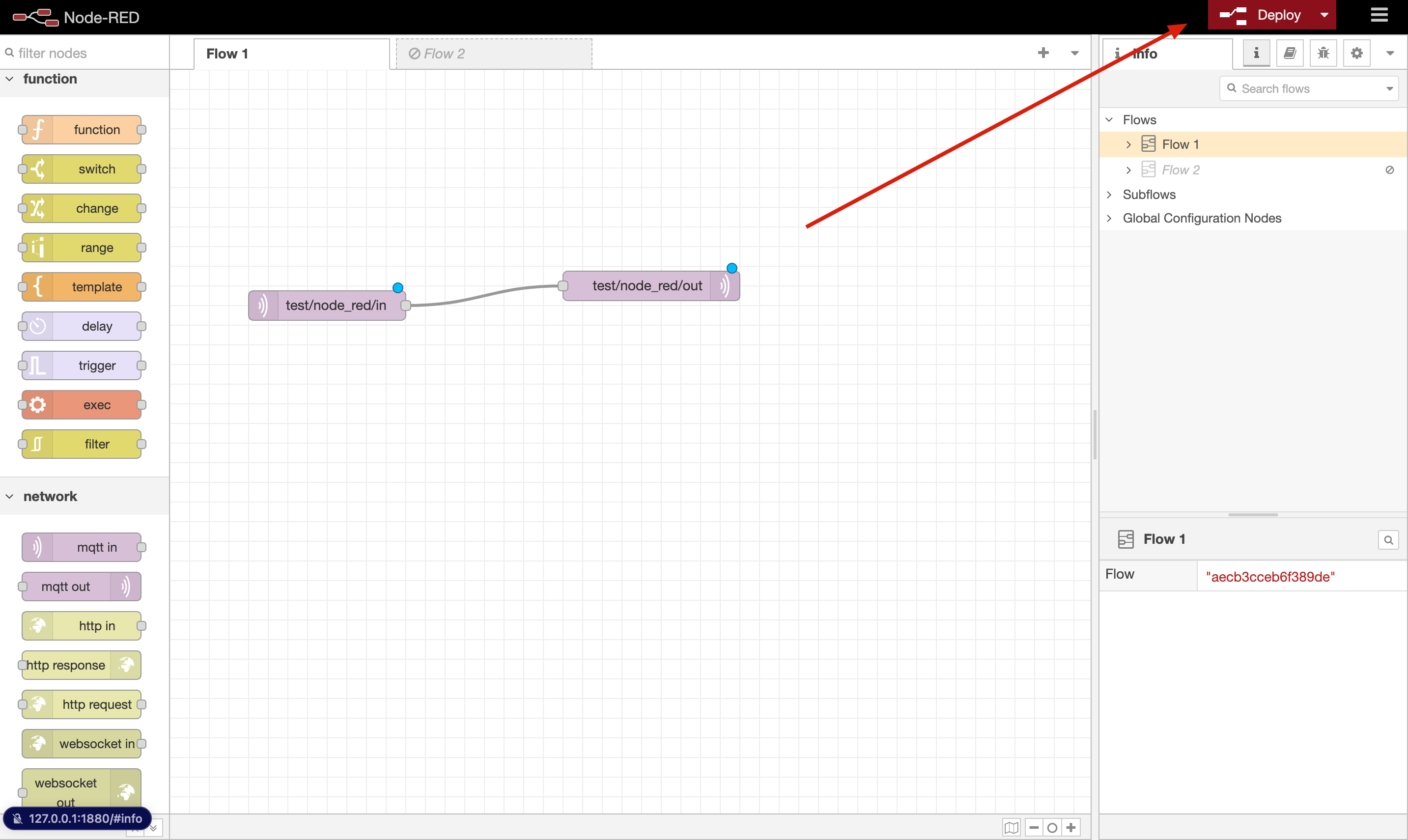
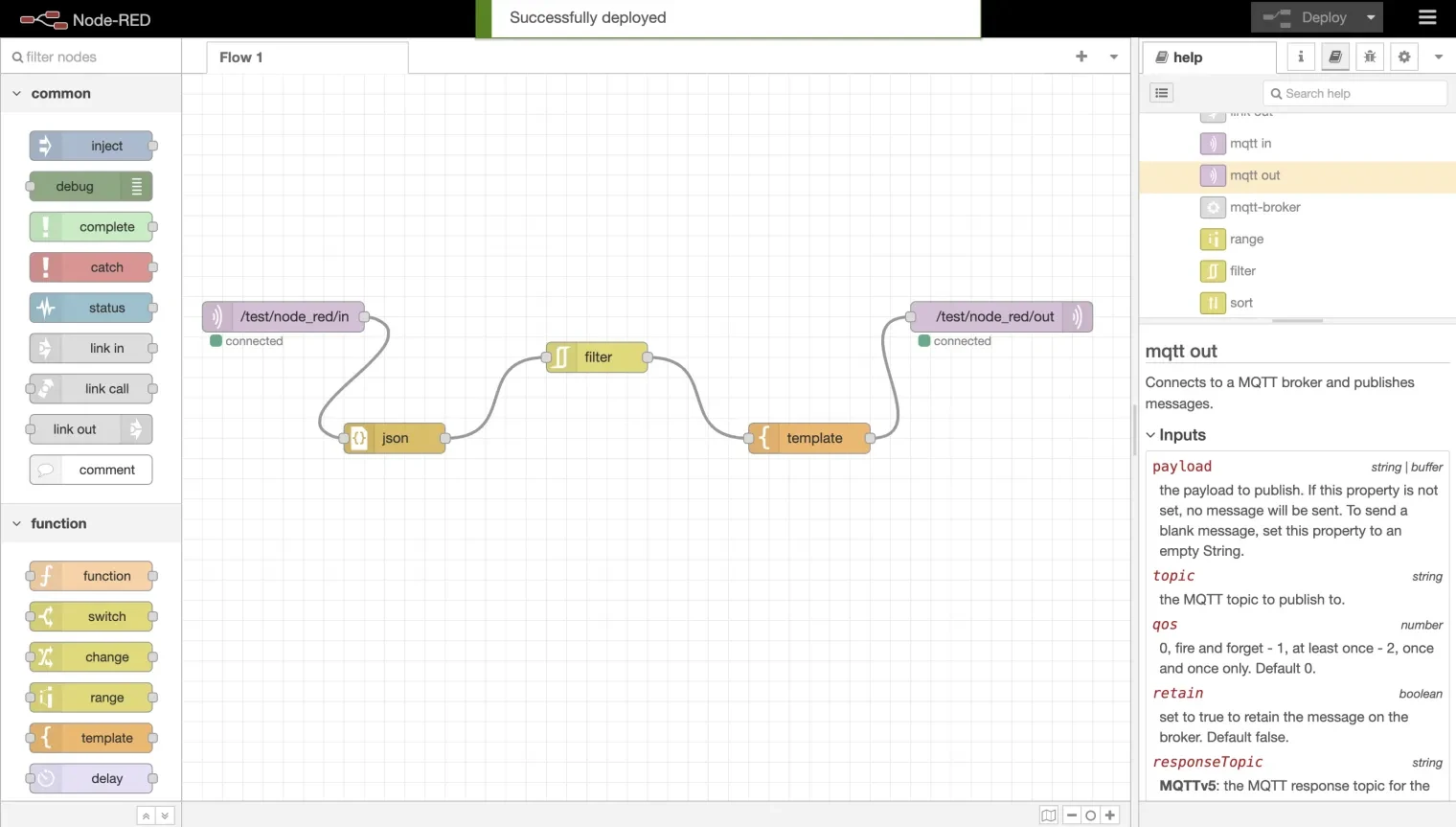
3.1. Connect Nodes: Connect the mqtt-in node to the mqtt-out node on the canvas and click the Deploy button in the upper-right corner to deploy the flow.
3.2. Verify Connection: After deploying, you should see a "connected" status under each node, indicating a successful connection to the MQTT broker.
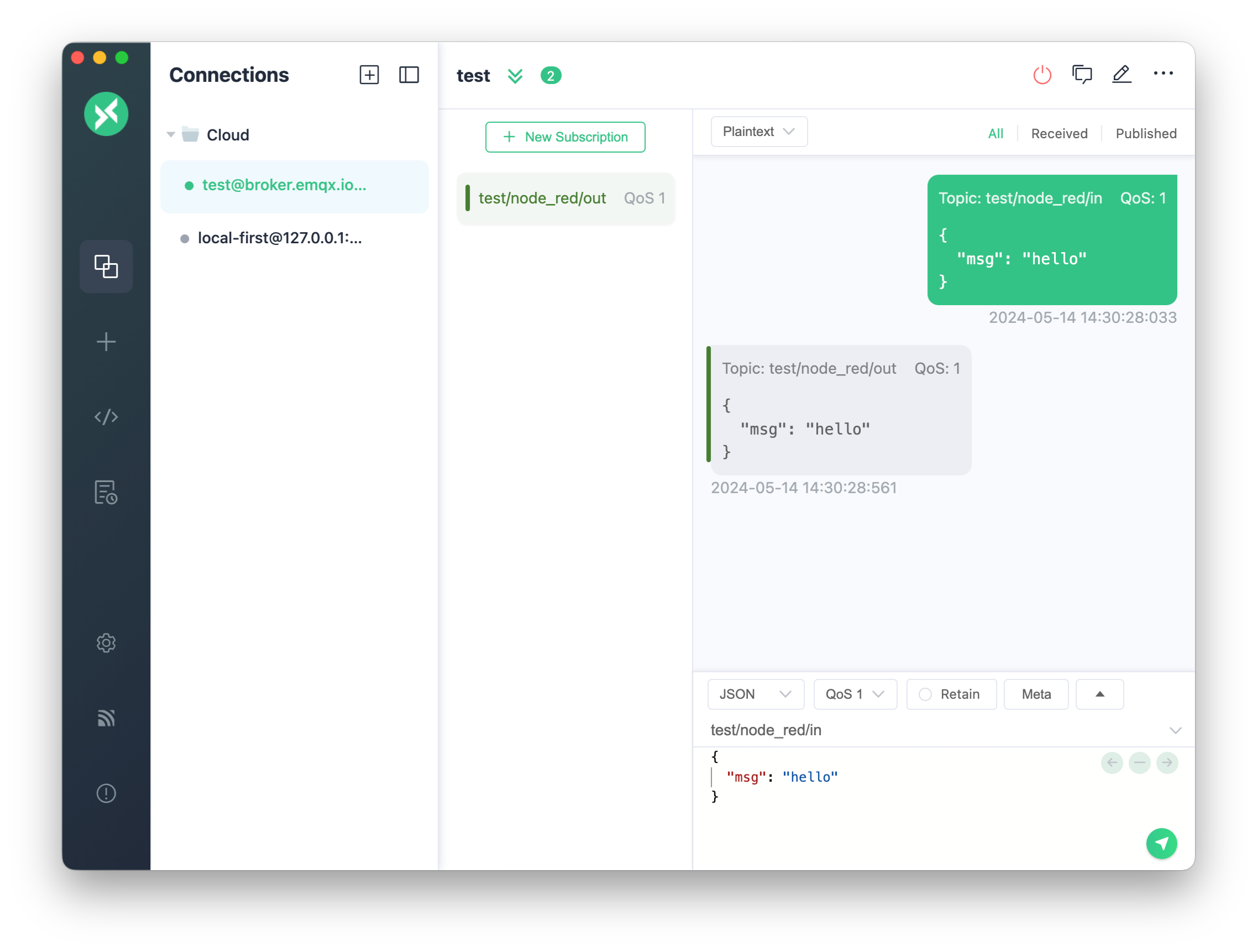
3.3. Test with MQTTX Client: Use MQTTX as an MQTT client to test the setup. Publish a message to the test/node_red/in topic and subscribe to the test/node_red/out topic to verify the message is received.
Following these steps, you will successfully configure MQTT nodes in Node-RED to handle message reception and transmission. Next, we will move on to more advanced tutorials on processing the received data.
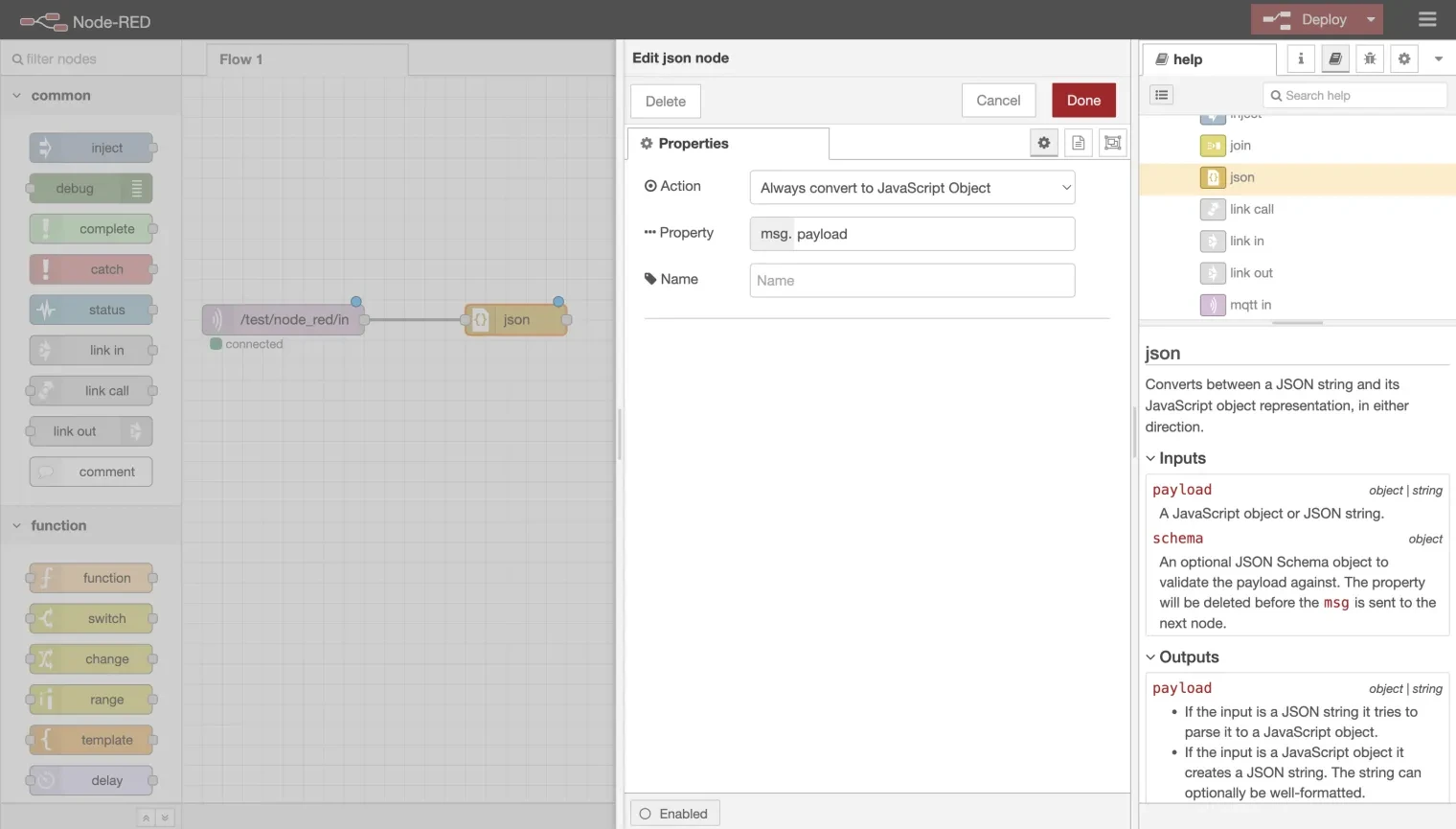
1.1. Add JSON Node: Drag and drop a JSON node onto the canvas and double-click it to open its configuration page.
1.2. Configure JSON Conversion: Set the action to "Always Convert to JavaScript Object" to ensure received messages are converted to JSON format.
1.3. Connect Nodes: Connect the JSON node to the mqtt-in node.
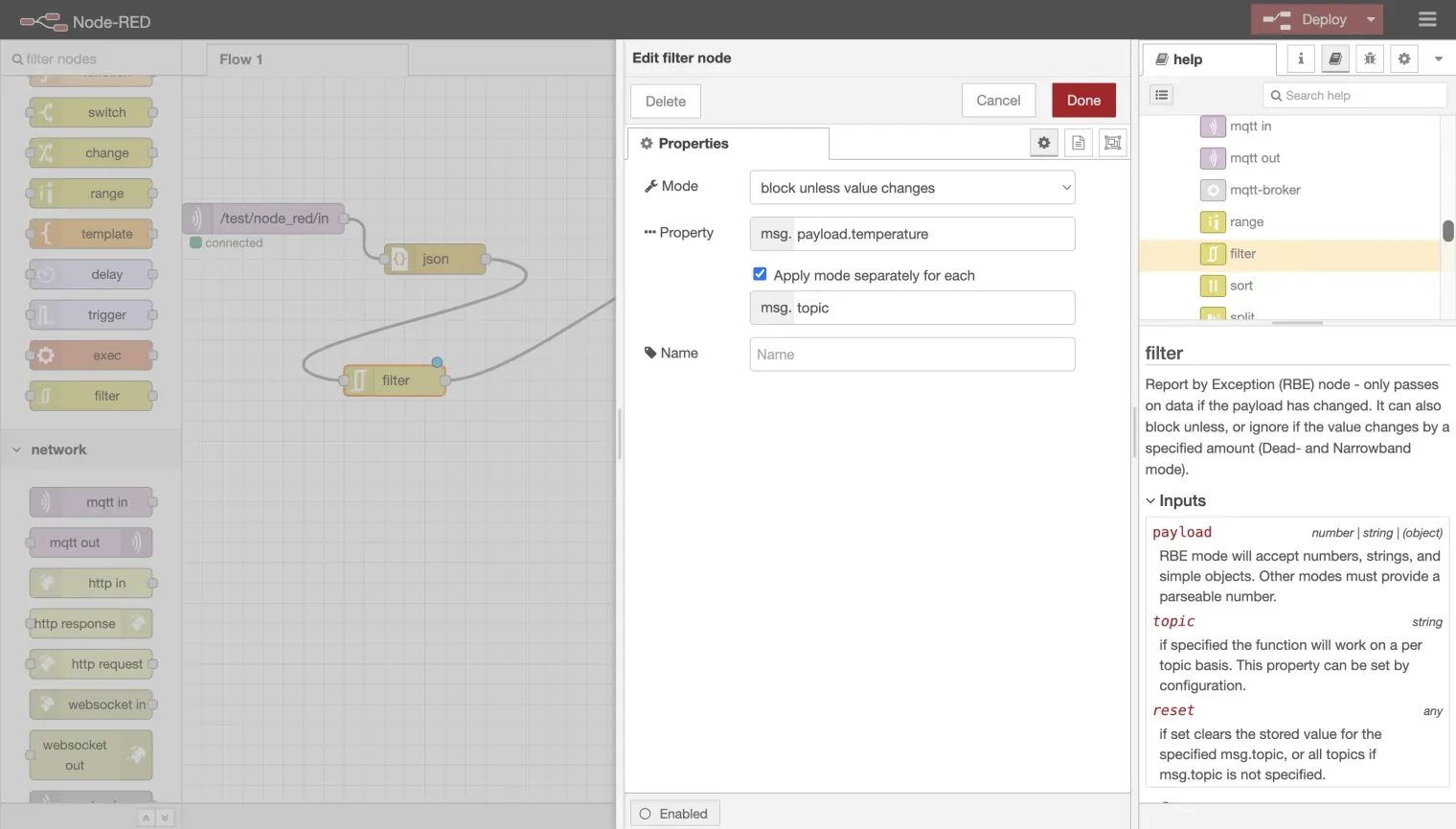
2.1. Add Filter Node: Drag and drop a filter node onto the canvas and double-click it to open the configuration page.
2.2. Configure Filter Rules: Set the mode to "block unless value changes" and configure the property to msg.payload.temperature to filter messages based on the temperature value.
2.3. Connect Nodes: Connect the filter node to the JSON node.
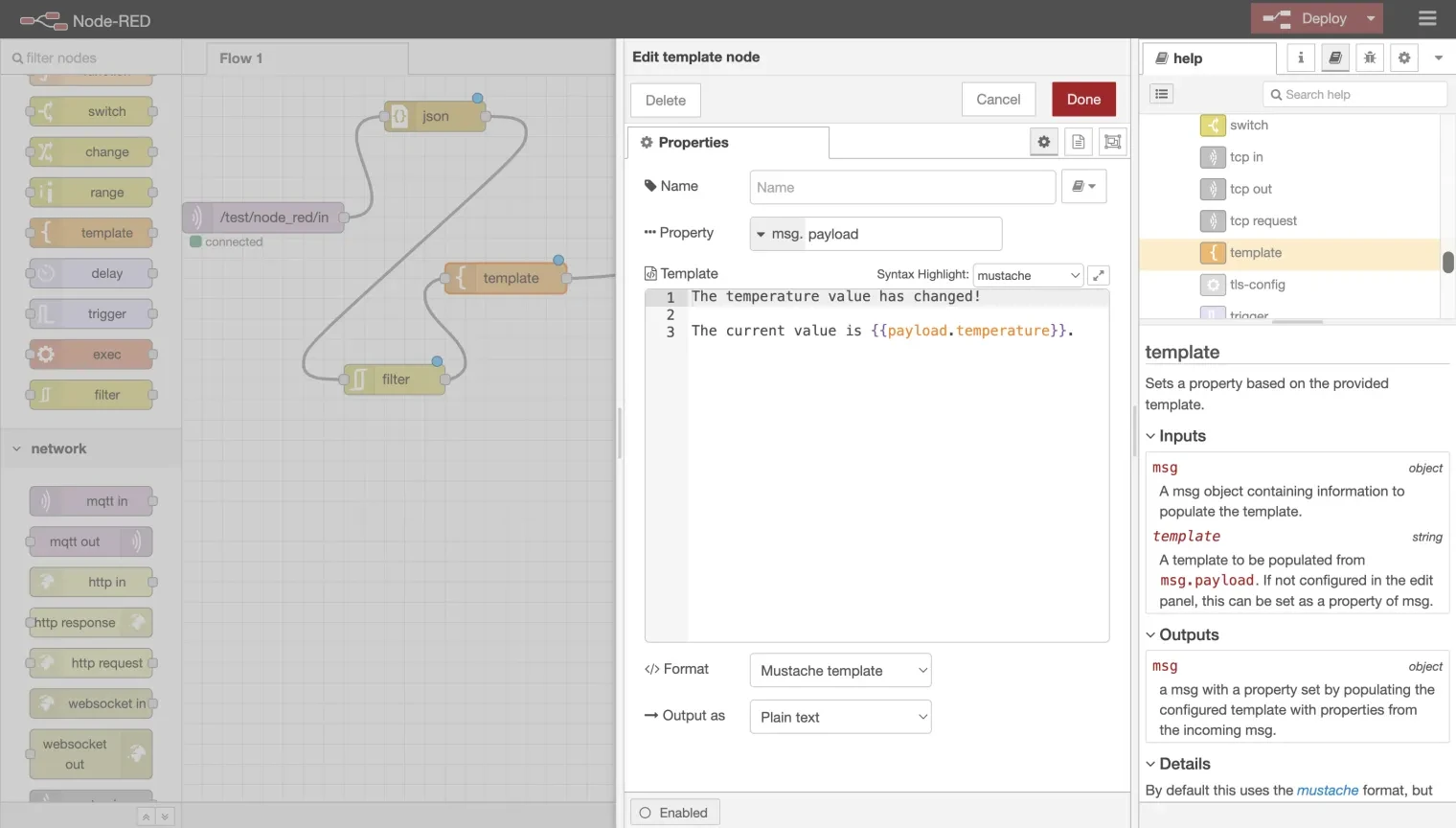
3.1. Add Template Node: Drag and drop a template node onto the canvas and double-click it to open the configuration page.
3.2. Configure Template: Enter the template content to format the filtered data.
3.3. Optional Step: If direct output is preferred, you can skip adding the template node.
4.1. Add MQTT-out Node: Drag and drop an mqtt-out node onto the canvas and double-click it to open the configuration page.
4.2. Configure MQTT Broker: Ensure the previously configured MQTT broker is selected.
4.3. Configure Topic: Enter a topic for publishing the processed data, such as test/node_red/out, and select the desired QoS level.
4.4. Connect Nodes: Connect the MQTT-out node to the template node.
5.1. Deploy the Flow: Click the Deploy button in the upper-right corner to deploy the flow.
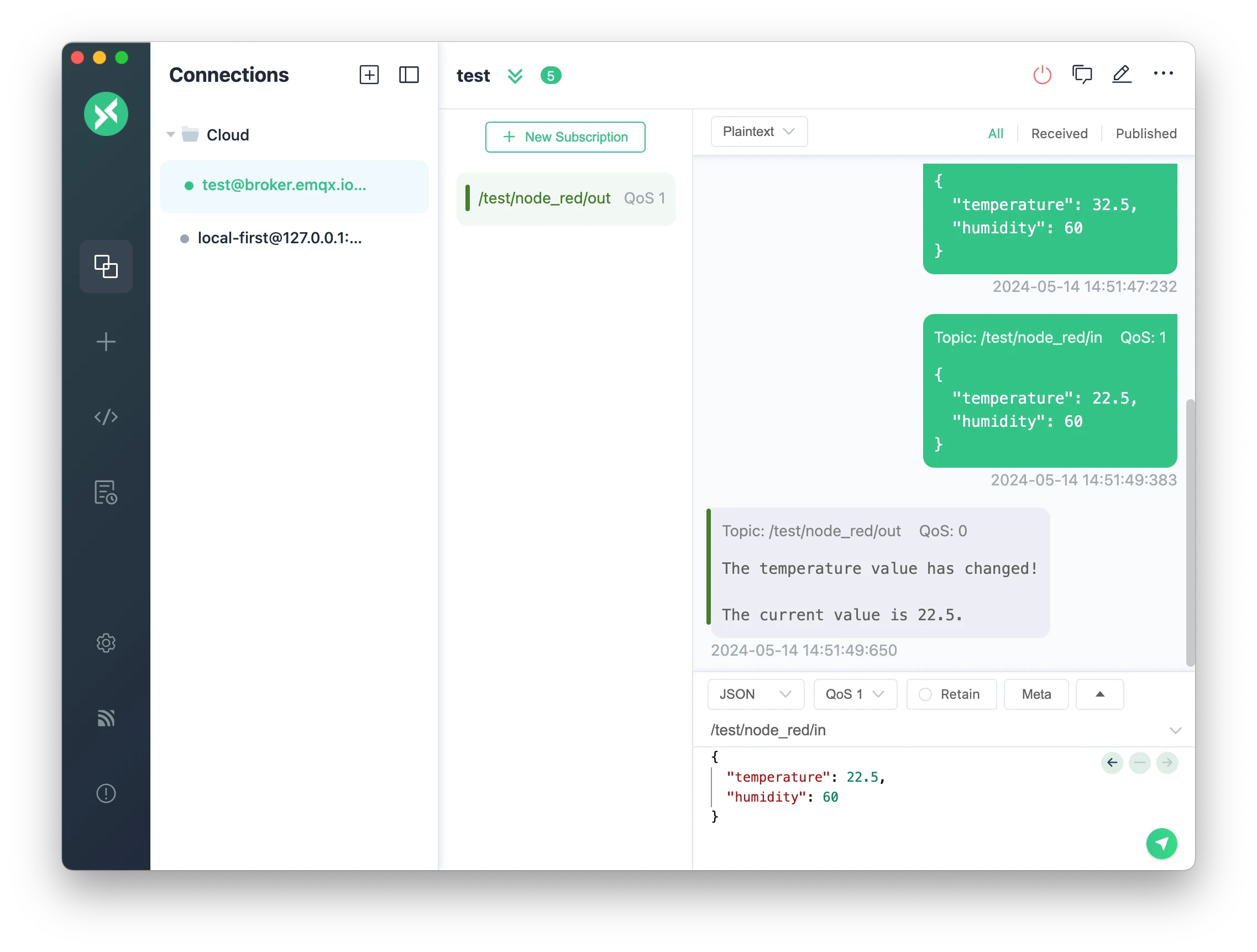
5.2. Test with MQTTX Client:
- Publish a message to the
test/node_red/intopic to allow Node-RED to receive the data. - Subscribe to the
test/node_red/outtopic to verify the processed message is received according to the set template. - Validate the filtering logic in Node-RED to ensure the same message is not received again if sent multiple times. If the temperature value changes, you should receive a new message indicating the change.
Following these steps, you will have successfully configured Node-RED to process and filter MQTT data, then send the processed data through MQTT.
We have now finished the entire process of installing and connecting with MQTT cloud service using Node-RED, as well as filtering and processing MQTT message data, and ultimately sending the processed data message. The use of Node-RED's UI to describe general business logic allows for a lower threshold for non-professional developers to get started. Users can create complex execution tasks quickly using a visual tool, by connecting simple nodes. This is particularly helpful for IoT application scenarios.
Next, you can check out The Easy-to-understand Guide to MQTT Protocol series of articles provided by EMQ to learn about MQTT protocol features, explore more advanced applications of MQTT, and get started with MQTT application and service development.