IoT technology is continually improving and expanding its applications, reaching areas such as environmental monitoring, social networking, and instant messaging. These areas generate a lot of data from sensors, user behavior, and other sources, which can be sent to the cloud using the MQTT protocol and analyzed and aggregated there. This can enable user experience optimization, device monitoring, alerts, and more.
In this blog, we will show you how to use the EMQX MQTT broker to collect data from diverse sensors and device events. We will then integrate this data with the Redis database to achieve real-time statistics and analysis.
MQTT is a simple and efficient messaging protocol that uses the publish/subscribe pattern to communicate over the network. It is ideal for situations where the network is limited or unreliable. However, MQTT alone cannot handle some data-related tasks, such as storing messages, sorting and querying them, and performing real-time data analytics. By combining MQTT with Redis, a fast and versatile database, these limitations can be overcome.
Redis has the following features:
- Key-Value Data Store: Redis operates as a key-value database, facilitating rapid access to data. This model is ideal for storing simple data types like strings, lists, collections, and hash tables. Each data type supports flexible query operations, for example, you can query the length of a list, get all the elements of a set, find the maximum or minimum value in an ordered set, get the value of a field in a hash table, and so on.
- In-Memory Storage and Persistence: All data in Redis is stored in memory, ensuring swift read and write access. Additionally, Redis offers various data persistence mechanisms to safeguard data by saving it to the hard disk.
- Publish/Subscribe Mode: Redis supports a publish/subscribe mode for real-time message push and notification.
- Sort and Range Query: Ordered collections in Redis support sort and range query, simplifying the implementation of leaderboards and time-series data queries.
- Bitmap and HyperLogLog Query: Redis bitmap aids in implementing statistical functions like counting online users, while HyperLogLog efficiently estimates cardinalities.
- Counters: Redis strings can function as atomic counters, enabling real-time counting and statistics.
Despite being a memory-based key-value database, Redis is not suitable for storing vast amounts of telemetry data, limiting its support for long-term historical data queries. Nevertheless, Redis excels in querying and statistics, serving as a high-speed data storage system and meeting basic data query and analysis needs. When paired with the MQTT protocol, Redis becomes a valuable asset in IoT applications, facilitating real-time monitoring of device behavior, instant data analysis, and alarm functions.
- Git
- Docker Engine: v20.10+
- Docker Compose: v2.20+
This is a simple and effective architecture that avoids the need for complex components. It utilizes the following key components:
| Component Name | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EMQX Enterprise | 5.4.1+ | An MQTT broker used for message exchange between devices and Redis. |
| Node.js | 18.17 | A simulation tool is used to simulate an operational environment that generates environmental sensor data and various behavioral events. |
| Redis | 7.0.12 | A database that is used for temporary storage and analysis of sensor data, and storage and analysis of device events. |
| Grafana | 9.5.1+ | A visualization platform that is used to display and analyze the collected data. |
Clone the emqx/mqtt-to-redis repository locally using Git:
git clone https://github.com/emqx/mqtt-to-redis
cd mqtt-to-redisThe codebase consists of four parts:
- The
emqxfolder contains EMQX-Redis integration configurations to automatically create rules and actions when launching EMQX. - The
simulatefolder contains Node.js script that simulate devices connecting to the EMQX and generating data, and randomly trigger device events. - The
prometheusandgrafana-provisioningfolders include the statistical analysis visualization configurations. - The
docker-compose.ymlorchestrates all components to launch the project with one click.
Please make sure you have installed the Docker, and then run Docker Compose in the background to start the demo:
docker-compose up -dNow, the script will simulate 10 devices connecting to EMQX, and periodically publish simulated temperature and humidity data to specific topics. Below is an example of data published to the EMQX message-drop-test/${clientid} topic:
{
"message": "this is a stored message",
"clientId": "emqx_c",
"duration": "102s",
"temp": 44.37,
"hum": 32.52
}The simulation script also randomly generates different client exception events, such as:
- Message drop events: these occur when there is no subscriber, the message expires, or other reasons.
- Device disconnection events: these can be normal or abnormal, such as unsupported QoS, publish topic errors, etc.
- Publish and subscribe failures: these happen when the client lacks ACL permissions or other causes.
EMQX rule engine can capture and process these messages and events, and then write or update them to Redis through data integration. To view the data in Redis, you can do the following:
$ docker exec -it redis bash
$ redis-cli
$ keys *
1) "emqx_message_dropped_count"
2) "emqx_messages"
3) "disconnected_reason"
4) "authz_result"
5) "message_dropped_reason"
6) "authz_source"The following section explains how EMQX writes data with rules.
EMQX creates a rule to handle MQTT messages with temperature and humidity data. You can also modify this rule later to add custom processing using EMQX's built-in SQL functions:
SELECT
*
FROM "store-last-message/+"The rule action updates the temperature and humidity data in Redis in real-time after the rule processes the message.
EMQX Redis integration can use the Redis template for data insertion, which leverages Redis's diverse data structures for flexible data manipulation and business development.
Create a named template for the action, and EMQX utilizes this Redis template to store the temperature data of the last message by client ID:
HSET emqx_messages ${clientid} ${payload.temp}EMQX also creates rules to log abnormal behavior of devices connected to EMQX for device management and analysis. The EMQX rule engine handles all MQTT device lifecycle events. You can monitor more events with the rule engine, for more information please refer to here.
This rule processes data from the EMQX $events/client_check_authz_complete topic, which shows the check authorization completion event. Rule SQL:
SELECT
*
FROM "$events/client_check_authz_complete"Create named templates corresponding to actions for counting by authorization source and authorization result, respectively:
HINCRBY authz_source ${authz_source} 1
HINCRBY authz_result ${result}:${action} 1This rule processes data from the EMQX $events/client_disconnected topic, which shows the client disconnected event. Rule SQL:
SELECT
*
FROM "$events/client_disconnected"Create a named template corresponding to the action for counting the disconnection reasons:
HINCRBY disconnected_reason ${reason} 1This rule processes data from EMQX $events/message_dropped and $events/delivery_dropped topics, which show the message dropped events. Rule SQL:
SELECT
*
FROM "$events/message_dropped", "$events/delivery_dropped"Create named templates corresponding to actions for counting based on the subject of the dropped messages and the reason for the dropped messages, respectively:
HINCRBY emqx_message_dropped_count ${topic} 1
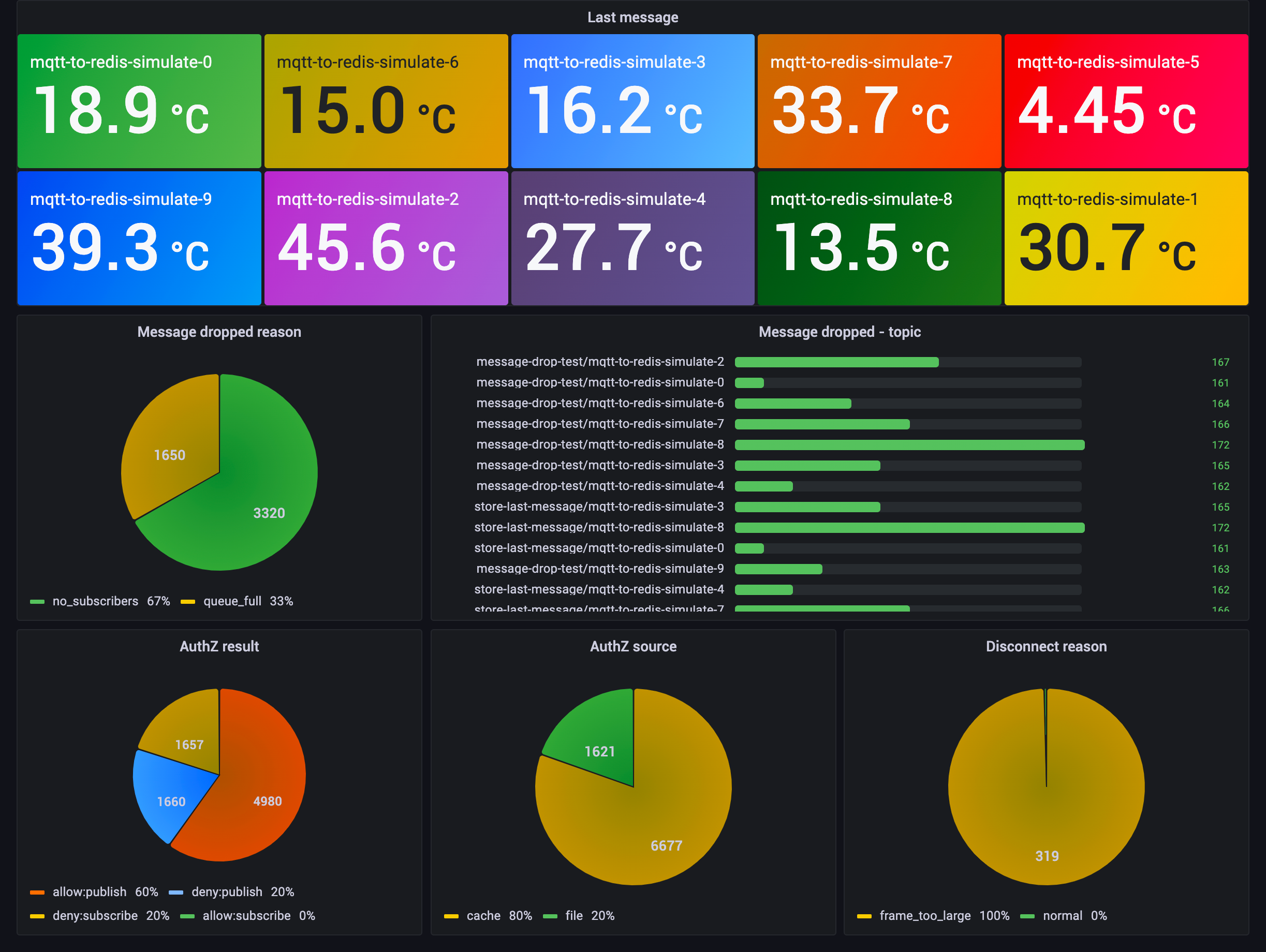
HINCRBY message_dropped_reason ${reason} 1To view data in the Grafana dashboard, open http://localhost:3000 in your browser and log in with username admin and password public.
After successfully logging in, navigate to the Home → Dashboards page, and choose the Redis dashboard. This dashboard presents real-time temperature data temporarily stored and provides insights into client anomalous behavior events. These crucial metrics offer a visual monitoring experience for environmental data and client behavior on EMQX, thereby mitigating potential security risks.
Beyond the real-time data analysis features explored in this blog, the EMQX and Redis combination offers a diverse range of application scenarios, including:
- Real-Time Data Streaming: EMQX excels in managing real-time data streaming, ensuring efficient and reliable data transfer from devices to Redis. Redis, with its rapid data processing capabilities, proves to be an ideal storage component for the temporary storage of real-time data, enhancing the overall functionality of EMQX.
- User Behavior Tracking: Leveraging Redis's robust time-window capabilities, such as bitmap data for tracking user behavior over time, enables the attainment of real-time statistical outputs with lightweight data.
- Geolocation Analysis: Redis provides specialized data structures and commands for storing and querying geolocation information. When integrated with EMQX's potent device access capabilities, this combination finds applications in diverse IoT scenarios like logistics, Internet of Vehicles, and smart cities.
It's noteworthy that the seamless scalability of the application can be ensured through the support of EMQX's distributed architecture and Redis's cluster mode. This scalability accommodates the growing data volume, guaranteeing consistent performance and responsiveness even with substantial datasets.
In this blog, we explored how to integrate EMQX and Redis to build an IoT real-time data statistics application. By using EMQX as a real-time MQTT Broker and importing data into Redis, we achieved an end-to-end solution for IoT data and EMQX client event analysis.
EMQX + Redis are powerful tools for IoT applications in various sectors. They can collect, transmit, and analyze data, and support complex data storage and analysis tasks. With their high performance, real-time, scalability, and flexibility, they can manage many device connections and data streams, and enable quick and precise data-driven decisions.
In essence, the synergy between EMQX and Redis introduces a powerful solution to the IoT landscape, empowering enterprises to effectively harness data, foster innovation, and enhance operational efficiency.