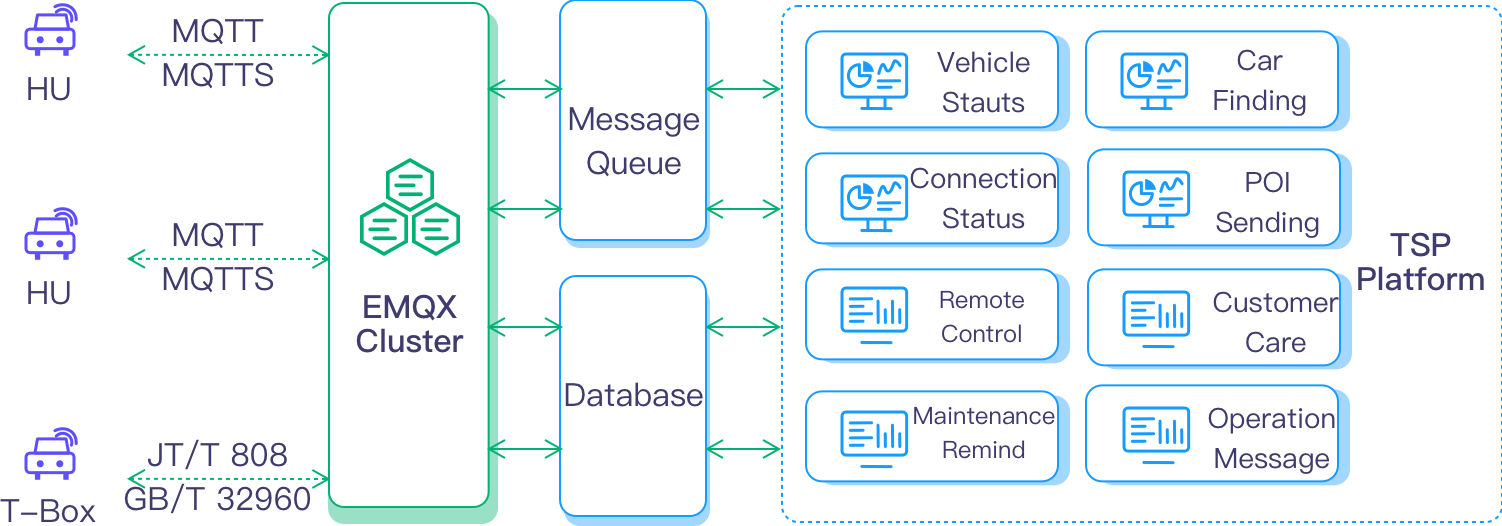
The current automotive industry is witnessing a surge in demand for a personalized driving experience. This has led to a wealth of TSP applications like smart navigation, remote control, car finding, and POI (Point-of-Interest) sending. In this evolving landscape, the Head Unit(HU) stands as the cornerstone of in-car intelligence by bridging people, cars, and the cloud. Its integration with TSP platforms empowers Original Equipment Manufacturers(OEMs) to deliver high-quality, tailored services to their customers.
The future of TSP platforms is to be "data-driven" and "service-oriented". To succeed, the TSP platform needs to ensure reliable connections with cars, efficient data transmission, and flexible data processing. This makes a robust, high-performance, and easy-to-maintain data infrastructure absolutely essential.
To ensure efficient vehicle management and offer all those cool services, OEMs need a TSP platform that can handle massive connections from the HU or T-Box. It must collect and process all the data from vehicles, and send the processed data back. However, this can be quite challenging in the following aspects:
-
Massive Connections & Throughput
As car sales surge, some major OEMs now oversee over a million cars. During peak times, like holidays, the platform must handle almost a million concurrent connections, each managing multiple data transfers in both directions. This requires the platform support millions of message throughput.
-
Multi-Protocols due to Policy or Application Requirements
In compliance with local regulations, vehicles must adhere to specific data transmission protocols. For instance, in China, the JT/T 808 protocol is used for vehicle location monitoring, and the GB/T 32960 protocol is applied for electric vehicle supervision. Meanwhile, OEMs may use varying data formats and transmit data through MQTT or TCP. Achieving unified access with these diverse protocols significantly adds to the platform's complexity.
-
Security & Privacy
Security threats also rise as vehicle connectivity deepens. The public network connection that HUs generally rely on makes it challenging to ensure communication security and user privacy. In addition, the varied authentication methods employed by different car models necessitate the establishment of unified authentication access.
-
Complex Network Environment
Obstacles like tunnels and base station switching can disrupt the vehicle-to-cloud connection, making it challenging to maintain reliable message delivery and prevent data loss. Moreover, ensuring the delivery of messages sent from the cloud during extended offline periods of the HU system, such as when the vehicle is parked, is a critical concern for downstream applications like customer care services.
-
Offline Message Delivery
In the context of sending data from the TSP platform to vehicles, such as POI updates, customer care, and operational messages, the platform typically uses batch delivery for all vehicles of a specific model. However, in real-world situations, many HUs may go offline after the engine is turned off. This poses a challenge in ensuring that service messages sent by the TSP platform can still reach the vehicle when it comes back online. Moreover, accommodating different business requirements for message delivery, like giving priority to user-initiated POI updates over other caring or operational messages, adds to the implementation complexity.
-
Diverse Requirements for Data Processing
Once data from the vehicle reaches the TSP platform, different backend application services demand diverse data processing and storage solutions, contingent on the data type and application context. Real-time vehicle monitoring services necessitate message queue storage, while data intended for historical analysis should be placed in a database. The challenge lies in implementing adaptable pre-processing, routing, and data bridging integration to effectively handle the influx of data from numerous vehicles.
-
Reliability and Stability
Maintaining the stability of TSP service is crucial as it serves as the primary interface between people, cars, and OEMs. Any service interruptions can have a significant negative impact. The key to ensuring the stability of TSP services lies in maintaining a highly stable and reliable data infrastructure.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for scenarios with low bandwidth, high latency, and unreliable networks. Its publish/subscribe model, session persistence mechanism, and QoS message quality mechanism make it more suitable for vehicle networking scenarios than TCP and HTTP protocols in IoV scenario.
In the context of connected vehicles, the MQTT Broker serves as the core of the access layer in the entire TSP platform architecture. It decouples the direct connections between the platform and the numerous vehicles, acting as a proxy for message exchange between the two.
As a leading enterprise MQTT platform, EMQX provides powerful connection and data solutions for TSP platform infrastructure building. Its high performance, reliability, and scalability designs allow for reliable vehicle connection, data collection, and data delivery. This can help OEMs address the aforementioned challenges and enable them to concentrate on application development.
-
High Performance Supports Growing Business
EMQX adopts a distributed and highly available architecture that can easily support millions of concurrent connections. This ensures concurrent access and stable operation even during peak periods of online connections. The cluster's scalability enables it to expand flexibly with the growth of future vehicle numbers.
-
Multi-Protocol Support for Different Requirements
EMQX's multi-protocol gateway supports connections between vehicles and TSP platforms through multiple protocols, such as MQTT, JT/T 808, GB/T 32960, or their variants. This ensures that the TSP platform can collect vehicle location tracking, safety monitoring, and other data in compliance with relevant standard regulations.
-
Data Security Guarantee
EMQX supports TLS/DTLS security protocols, which enable TSPs and vehicles to establish secure connections through one-way and two-way authentication using TLS. EMQX can also interact with PKI/CA system to enable a One-Vehicle-One-Secret authentication. Additionally, EMQX can enable multiple listening ports with different security authentication policies, allowing different vehicle models to access the TSP platform using various authentication methods. The identity authentication and access control functions provided by EMQX can further ensure secure data access.
-
Messaging Enhancement in Mobile Networks
With multiple mechanisms such as keep alive, session persistence, and QoS levels based on the MQTT protocol, message transmission can be re-established after vehicle disconnection caused by intricate network problems. This ensures the achievement of real-time and reliable message communication between moving vehicles and the cloud.
Furthermore, starting from version 5.0, EMQX became the first MQTT broker to support MQTT over QUIC, which further improves the robustness of MQTT Protocol for complex mobile networks in terms of faster connection establishment, reconnection, and connection migration for moving vehicles.
-
High Throughput Capacity Enables Diverse Applications
EMQX supports MQTT based subscribe/publish interactions, with the ability to handle massive MQTT topics, and a million TPS level throughput capacity. It allows for multiple logically isolated MQTT topics in each vehicle-platform connection to support the upstream and downstream transmission of different application data. For instance, TSP can monitor and manage vehicles by receiving real-time information such as location and battery status, and provide services such as POI sending and customer care delivery.
-
Flexible Offline Message Delivery
The challenge of delivering messages while the HU is offline can be addressed with the offline delivery function of EMQX. It can be combined with databases like Redis to cache data during HU offline period, ensuring that it can promptly receive the messages sent by the TSP platform once the HU is online. EMQX also supports customizing different offline delivery strategies like priority and expiration time for different businesses.
-
Convenient Operation and Maintenance
EMQX provides a dashborad for monitoring and configuration. It can monitor the real-time connection status and message traffic of the vehicles, and push monitoring data to TSP or third-party monitoring systems through APIs. The hot configuration and hot upgrade allows customers to make configuration adjustments without stopping the service, ensuring the continuity of TSP service to the maximum extent. Functions such as Slow subscribers statistics and Log Trace can help TSP operation and maintenance team quickly troubleshoot abnormal connections, message reception delays, and other issues.
EMQX has extensive experience in the connected car market. As of 2023, more than 20 global OEMs and 30 Tier 1 TSP providers have chosen EMQX as their preferred TSP infrastructure solution, with over 20 million vehicles worldwide accessing EMQX.
In connected vehicle scenarios, EMQX offers several key advantages:
- High Reliability and Scalability: EMQX Enterprise adopts a distributed architecture, with high availability and scalability, capable of supporting millions of concurrent connections and message throughput. It supports flexible scaling to accommodate the growing number of vehicles and business data, ensuring the stable operation of the TSP platform.
- Secure Connection and Data access: EMQX supports multiple authentication methods such as username/password, TLS authentication, JWT authentication, and ACL. It can also be integrated with TSP’s authentication services to achieve unified security authentication.
- Unified Access on Multiple Listening Ports: Different car models may have inconsistent MQTT protocol versions, connection authentication methods. EMQX supports custom multiple listening ports with different protocols and authentication methods to achieve unified connection for different car models.
- Powerful Data Integration: By using simple SQL statements, data processing can be performed quickly and flexibly according to business needs, including data filtering, transformation, aggregation, and persistence. Then, with easy configurations on dashboard of EMQX, the processed data can be bridged and integrated into various message queues and SQL/NoSQL/time-series databases with high performance.
See customer stories: SAIC Volkswagen and EMQ create a new generation of intelligent Internet of Vehicles systems