Omron FINS (Factory Interface Network Service) is a network communication protocol developed by OMRON for industrial automation control. It enables seamless communication between Ethernet, control network Controller Link, and RS232C/485 serial communication through FINS commands. FINS protocol works on the application layer of the TCP/IP model, which ensures its good expandability, practicality, and real-time performance, thus connecting client applications, including HMI, SCADA, Historian, MES, ERP, and countless custom applications with controllers through Omron FINS Ethernet driver.
The FINS protocol has two variants: the FINS/UDP protocol uses UDP packets for communication, and the FINS/TCP protocol uses TCP connections.
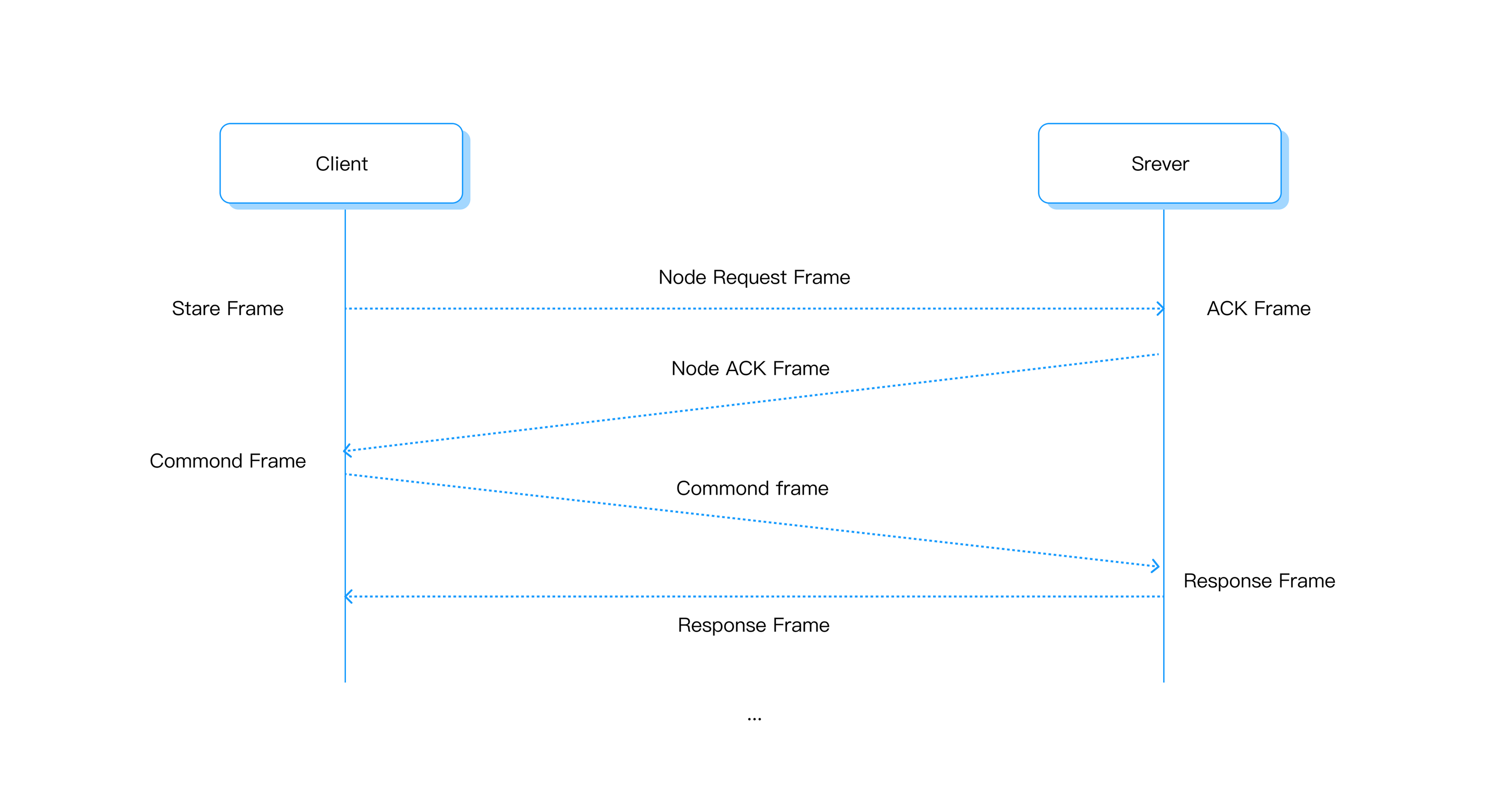
The FINS session process is based on the TCP/IP protocol. The following diagram describes the role of several data frames at the beginning of the FINS session. The session of the FINS protocol has a request frame, and the node parameters of the initiator are attached to the request frame. The Server side(e.g., PLCS) will confirm and return its node parameters to the requester. Only FINS over TCP needs session process.
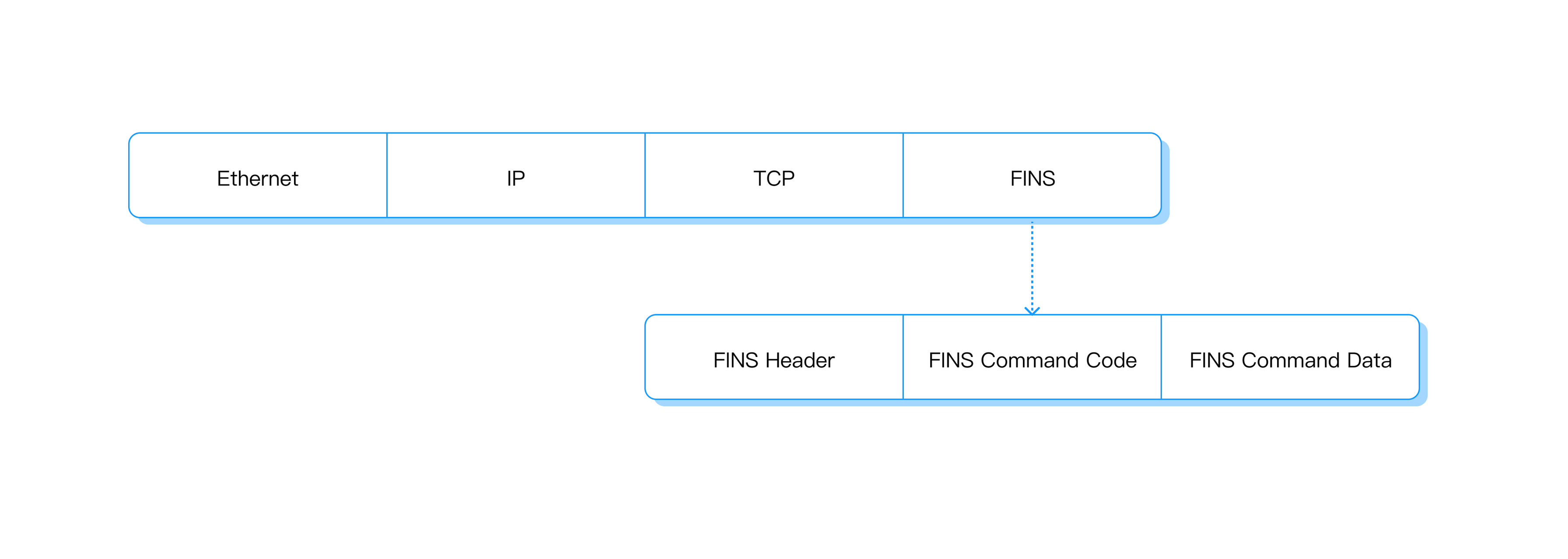
The FINS frame structure consists of three parts, namely FIN Header, FINS Command Code, and FINS Command Data.
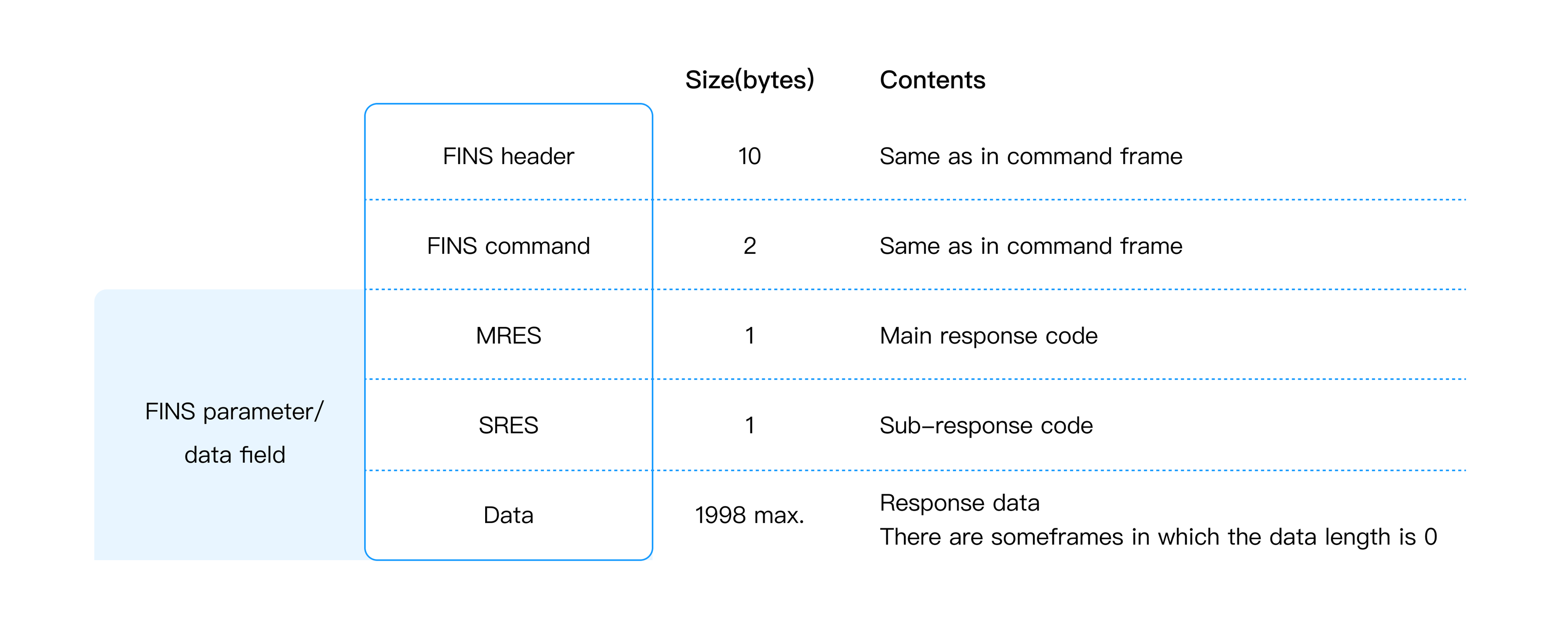
Both command frames and response frames are comprised of a FINS header for storing transfer control information, a FINS command field for storing a command, and a FINS parameter/data field for storing command parameters and transmission/response data.
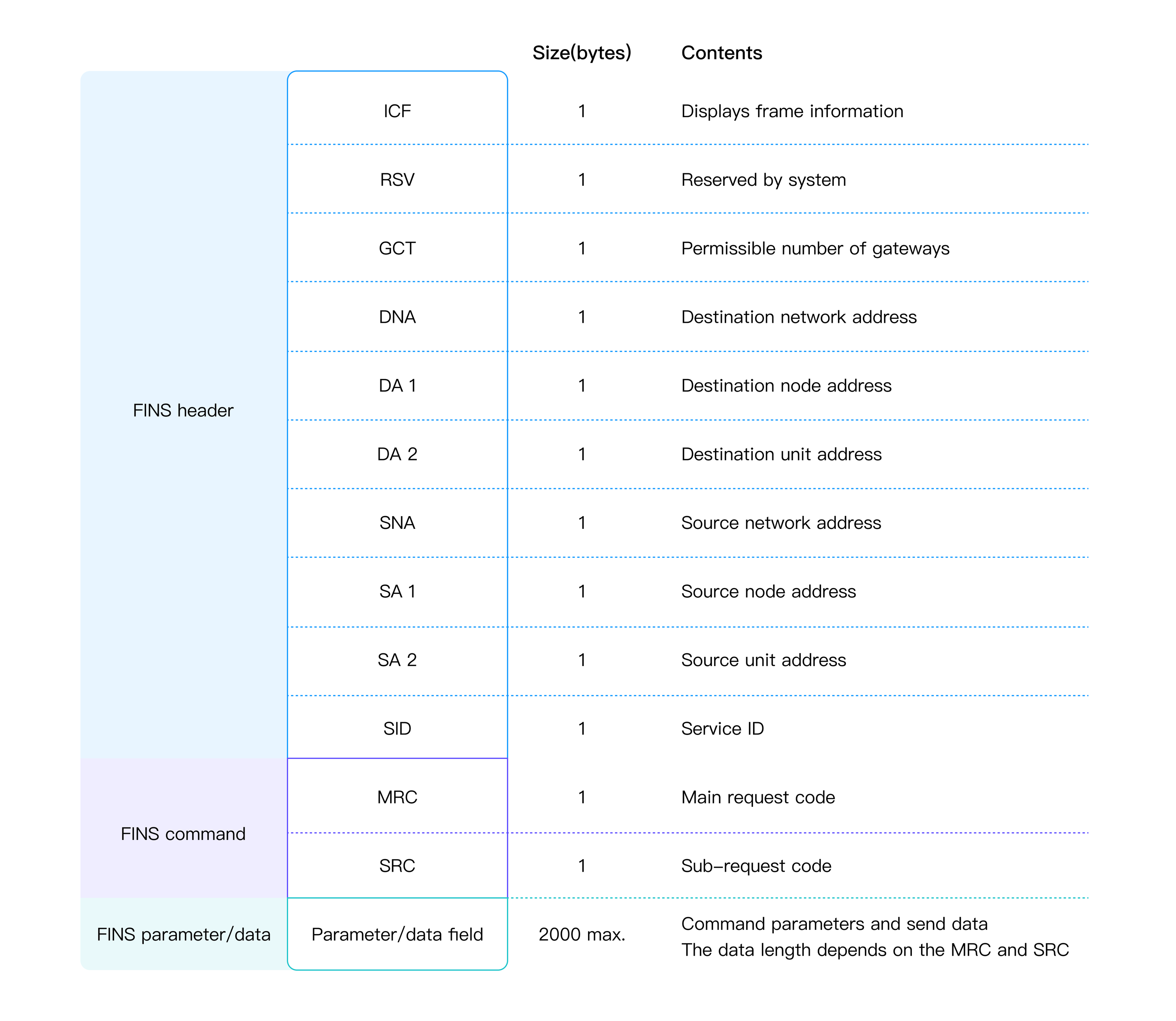
FINS over UDP consists of two parts: FINS Command Code and FINS Command Data.
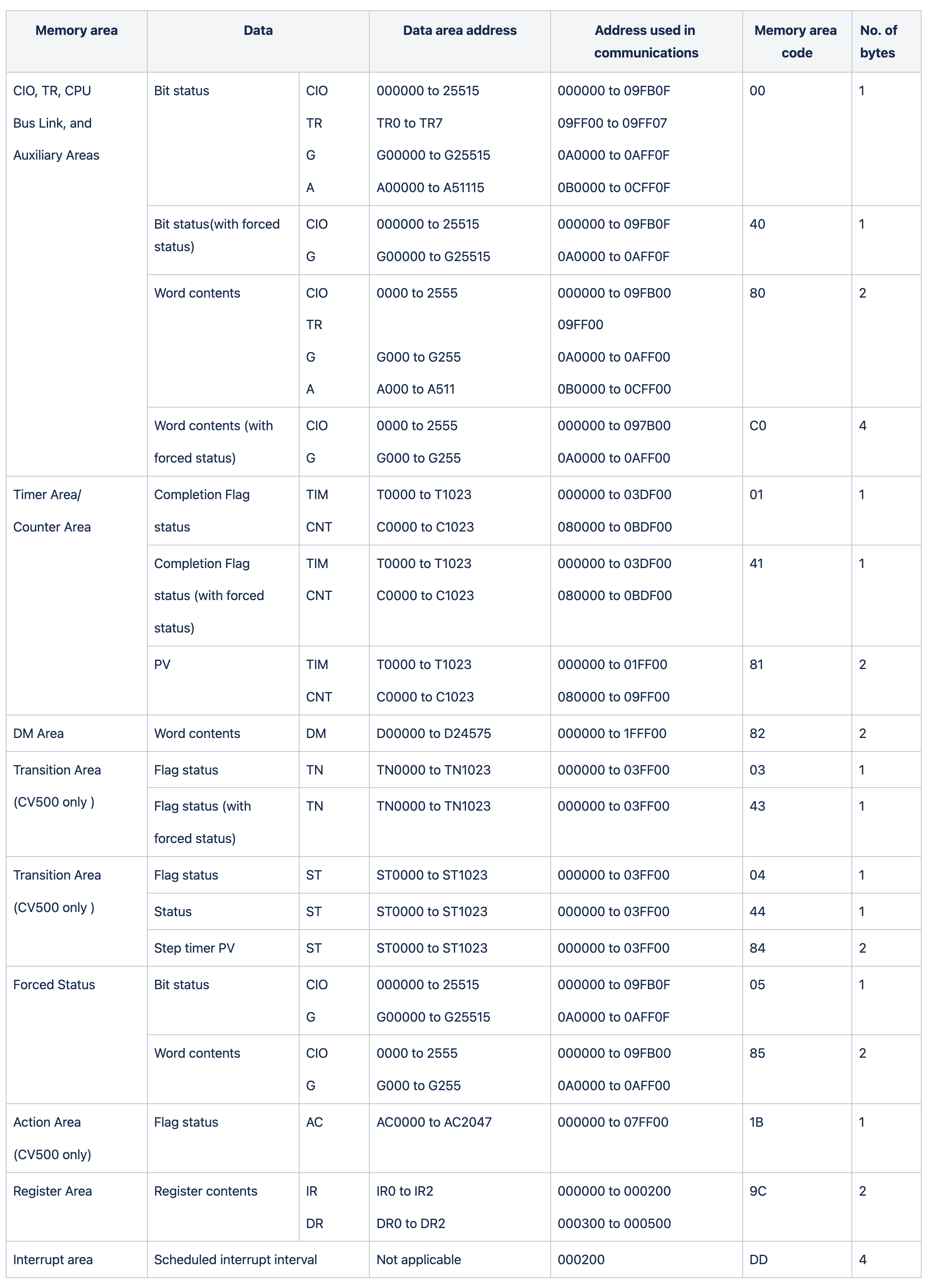
The following table gives the addresses to use when reading or writing PC data.
- The Data area address column gives the normal addresses used in the PC program.
- The Address used in the communications column is the addresses used in CV-mode commands and responses(CV-mode command is an alias for FINS command). These addresses are combined with the memory area codes to specify PC memory locations. They are not the same as the actual memory addresses of the data.
- The No. of bytes column specifies the number of bytes to read or write data for that area. The number of bytes varies for the same area depending on the memory area code.
Different PLC CPU models have different memory areas. Take CV500 or CVM1-CPU01-E as an example.
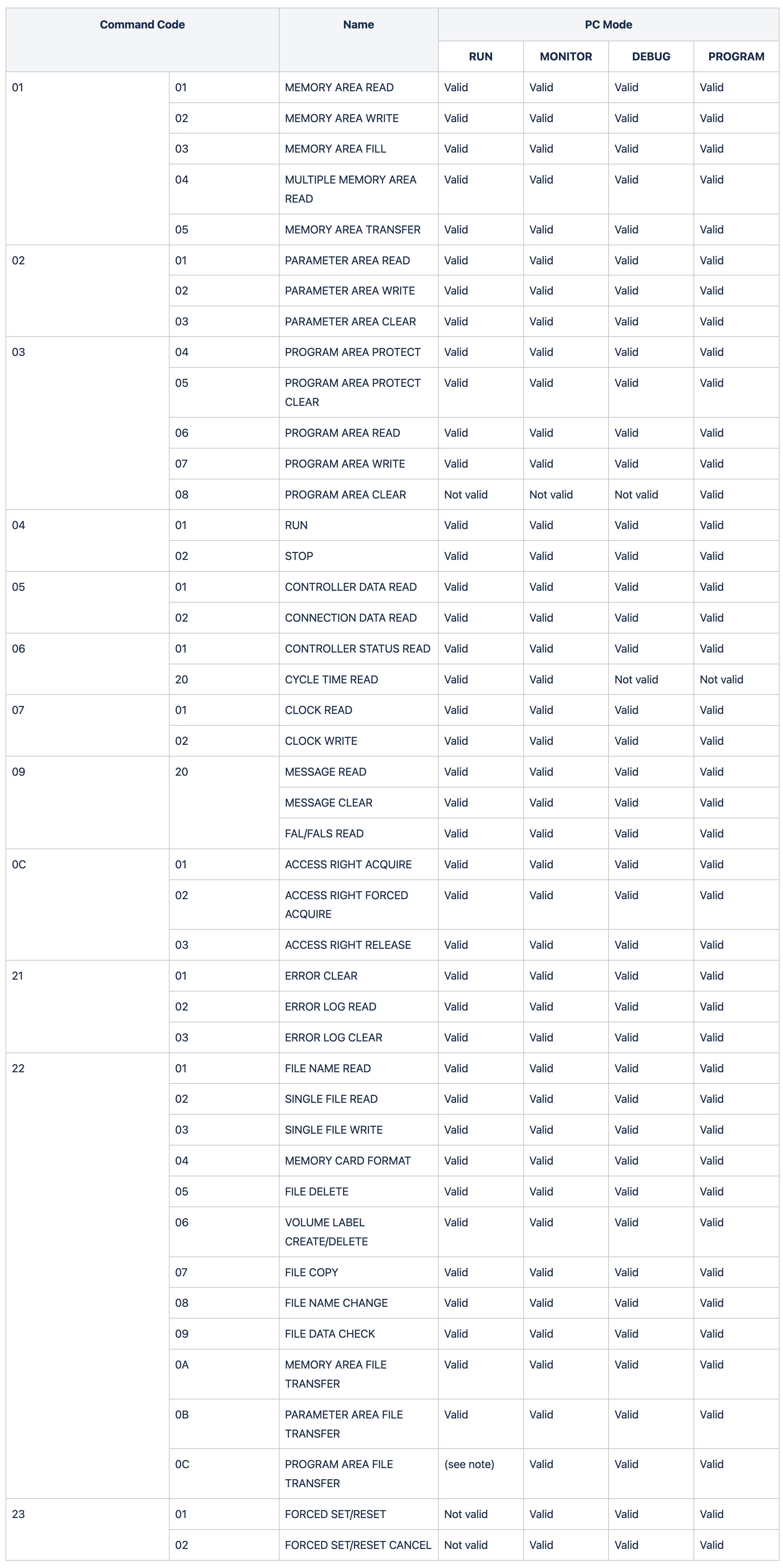
In the Command Code field column in the table below, each cell represents a byte (two hexadecimal digits). The following table lists the FINS commands supported by CV-series PCs and the PC operating modes during which they are enabled.
Note: When the PC is in RUN mode, data transfers from files to the program area are not possible, but transfers from the program area to files are possible.
With the arrival of the wave of Industry 4.0, there is a growing demand for data intelligence, interconnectivity, and cloud-edge collaboration in the industrial sector. Against this backdrop, the FINS protocol may face some issues.
Firstly, as an intranet application protocol, FINS was not designed with security in mind, and its communication methods are simple, making it vulnerable to hacker attacks and data tampering that could pose a threat to the production environment.
In addition, FINS can only perform one-to-one communication in complex application architectures and cannot effectively support the development of distributed and cloud-native applications.
Compared to FINS, MQTT has significant advantages. MQTT is a lightweight publish-subscribe message transport protocol commonly used for remote monitoring and communication in IoT applications. It provides a simple and flexible way to transfer messages between devices while effectively handling a large number of concurrent connections. It is currently used in various fields such as IoT, mobile internet, smart hardware, connected vehicles, smart cities, remote medicine, power, oil, and energy.
In the IoT field, MQTT is obviously more suitable for message transmission in distributed systems. Therefore, we can bridge FINS to MQTT to complement each other.
This article provides essential knowledge about the FINS protocol. Bridging FINS data to MQTT can bring more benefits to industrial scenarios and make them more efficient. You can get a detailed guide here to learn how to bridge the two.