Dart is a client-optimized language for developing fast apps on any platform. Its goal is to offer the most productive programming language for multi-platform development, paired with a flexible execution runtime platform for app frameworks.
MQTT is a lightweight IoT messaging protocol based on publish/subscribe model, which can provide real-time and reliable messaging services for connected devices with minimal code and bandwidth. It is widely used in industries, such as IoT, mobile Internet, smart hardware, Internet of vehicles, and power and energy.
This article mainly introduces how to use mqtt_client library in the Dart project to realize the connection, subscription, message sending and receiving between the client and MQTT Broker.
The examples in this article are based on the macOS environment.
Please refer to:Get the SDK
$ brew tap dart-lang/dart
$ brew install dart
$ dart --version
Dart SDK version: 2.13.0 (stable) (Wed May 12 12:45:49 2021 +0200) on "macos_x64"
$ dart create -t console-full mqtt_demo
$ cd mqtt_demo
The directory structure is as follows.
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── README.md
├── analysis_options.yaml
├── bin
│ └── mqtt_demo.dart
├── pubspec.lock
└── pubspec.yaml
In this article, we use mqtt_client as the MQTT client library and install it by running the following command.
$ dart pub add mqtt_client
This will add a line like this to the project's pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
mqtt_client: ^9.6.2
We will use the free public MQTT broker provided by EMQ. The service is created based on the MQTT Cloud Service - EMQX Cloud. The server access information is as follows:
- Broker: broker.emqx.io
- TCP Port: 1883
- Websocket Port: 8083
Edit bin/mqtt_demo.dart file.
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:mqtt_client/mqtt_client.dart';
import 'package:mqtt_client/mqtt_server_client.dart';
final client = MqttServerClient('broker-cn.emqx.io', '1883');
Future<int> main() async {
client.logging(on: true);
client.keepAlivePeriod = 60;
client.onDisconnected = onDisconnected;
client.onConnected = onConnected;
client.pongCallback = pong;
final connMess = MqttConnectMessage()
.withClientIdentifier('dart_client')
.withWillTopic('willtopic')
.withWillMessage('My Will message')
.startClean()
.withWillQos(MqttQos.atLeastOnce);
print('client connecting....');
client.connectionMessage = connMess;
try {
await client.connect();
} on NoConnectionException catch (e) {
print('client exception - $e');
client.disconnect();
} on SocketException catch (e) {
print('socket exception - $e');
client.disconnect();
}
if (client.connectionStatus!.state == MqttConnectionState.connected) {
print('client connected');
} else {
print('client connection failed - disconnecting, status is ${client.connectionStatus}');
client.disconnect();
exit(-1);
}
return 0;
}
/// The unsolicited disconnect callback
void onDisconnected() {
print('OnDisconnected client callback - Client disconnection');
if (client.connectionStatus!.disconnectionOrigin ==
MqttDisconnectionOrigin.solicited) {
print('OnDisconnected callback is solicited, this is correct');
}
exit(-1);
}
/// The successful connect callback
void onConnected() {
print('OnConnected client callback - Client connection was sucessful');
}
/// Pong callback
void pong() {
print('Ping response client callback invoked');
}
Then, execute
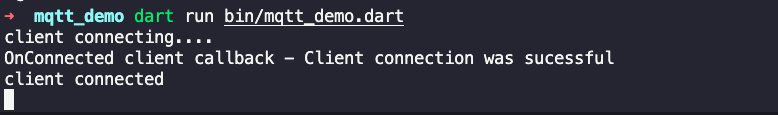
$ dart run bin/mqtt_demo.dart
We will see that the client has successfully connected to the MQTT broker.
Instructions
MqttConnectMessage: set connection options, including timeout settings, authentication, and last wish messages.
Example of certificate connection
/// Security context
SecurityContext context = new SecurityContext()
..useCertificateChain('path/to/my_cert.pem')
..usePrivateKey('path/to/my_key.pem', password: 'key_password')
..setClientAuthorities('path/to/client.crt', password: 'password');
client.secure = true;
client.securityContext = context;
Add the following code.
client.onSubscribed = onSubscribed;
const topic = 'topic/test';
print('Subscribing to the $topic topic');
client.subscribe(topic, MqttQos.atMostOnce);
client.updates!.listen((List<MqttReceivedMessage<MqttMessage?>>? c) {
final recMess = c![0].payload as MqttPublishMessage;
final pt = MqttPublishPayload.bytesToStringAsString(recMess.payload.message);
print('Received message: topic is ${c[0].topic}, payload is $pt');
});
/// The subscribed callback
void onSubscribed(String topic) {
print('Subscription confirmed for topic $topic');
}
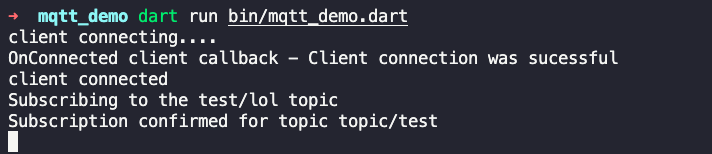
Then, execute
$ dart run bin/mqtt_demo.dart
We see that we have successfully subscribed to the MQTT topic.
client.published!.listen((MqttPublishMessage message) {
print('Published topic: topic is ${message.variableHeader!.topicName}, with Qos ${message.header!.qos}');
});
const pubTopic = 'test/topic';
final builder = MqttClientPayloadBuilder();
builder.addString('Hello from mqtt_client');
print('Subscribing to the $pubTopic topic');
client.subscribe(pubTopic, MqttQos.exactlyOnce);
print('Publishing our topic');
client.publishMessage(pubTopic, MqttQos.exactlyOnce, builder.payload!);
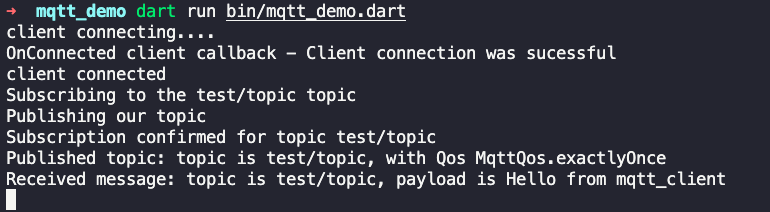
We see that the message has been published successfully and we receive it.
We use the following code for the complete test.
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:mqtt_client/mqtt_client.dart';
import 'package:mqtt_client/mqtt_server_client.dart';
final client = MqttServerClient('broker-cn.emqx.io', '1883');
Future<int> main() async {
client.logging(on: false);
client.keepAlivePeriod = 60;
client.onDisconnected = onDisconnected;
client.onConnected = onConnected;
client.onSubscribed = onSubscribed;
client.pongCallback = pong;
final connMess = MqttConnectMessage()
.withClientIdentifier('dart_client')
.withWillTopic('willtopic')
.withWillMessage('My Will message')
.startClean()
.withWillQos(MqttQos.atLeastOnce);
print('Client connecting....');
client.connectionMessage = connMess;
try {
await client.connect();
} on NoConnectionException catch (e) {
print('Client exception: $e');
client.disconnect();
} on SocketException catch (e) {
print('Socket exception: $e');
client.disconnect();
}
if (client.connectionStatus!.state == MqttConnectionState.connected) {
print('Client connected');
} else {
print('Client connection failed - disconnecting, status is ${client.connectionStatus}');
client.disconnect();
exit(-1);
}
const subTopic = 'topic/sub_test';
print('Subscribing to the $subTopic topic');
client.subscribe(subTopic, MqttQos.atMostOnce);
client.updates!.listen((List<MqttReceivedMessage<MqttMessage?>>? c) {
final recMess = c![0].payload as MqttPublishMessage;
final pt = MqttPublishPayload.bytesToStringAsString(recMess.payload.message);
print('Received message: topic is ${c[0].topic}, payload is $pt');
});
client.published!.listen((MqttPublishMessage message) {
print('Published topic: topic is ${message.variableHeader!.topicName}, with Qos ${message.header!.qos}');
});
const pubTopic = 'topic/pub_test';
final builder = MqttClientPayloadBuilder();
builder.addString('Hello from mqtt_client');
print('Subscribing to the $pubTopic topic');
client.subscribe(pubTopic, MqttQos.exactlyOnce);
print('Publishing our topic');
client.publishMessage(pubTopic, MqttQos.exactlyOnce, builder.payload!);
print('Sleeping....');
await MqttUtilities.asyncSleep(80);
print('Unsubscribing');
client.unsubscribe(subTopic);
client.unsubscribe(pubTopic);
await MqttUtilities.asyncSleep(2);
print('Disconnecting');
client.disconnect();
return 0;
}
/// The subscribed callback
void onSubscribed(String topic) {
print('Subscription confirmed for topic $topic');
}
/// The unsolicited disconnect callback
void onDisconnected() {
print('OnDisconnected client callback - Client disconnection');
if (client.connectionStatus!.disconnectionOrigin ==
MqttDisconnectionOrigin.solicited) {
print('OnDisconnected callback is solicited, this is correct');
}
exit(-1);
}
/// The successful connect callback
void onConnected() {
print('OnConnected client callback - Client connection was sucessful');
}
/// Pong callback
void pong() {
print('Ping response client callback invoked');
}
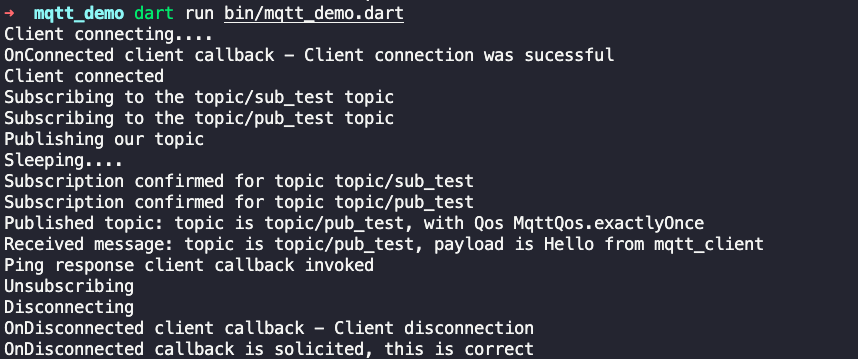
Console output.
At this point, we have finished connecting to the public MQTT server using the mqtt_client library in Dart, and implemented the connection, message publishing, subscription, and test between client and MQTT server.
Next, readers can check out The Easy-to-understand Guide to MQTT Protocol series of articles provided by EMQ to learn about MQTT protocol features, explore more advanced applications of MQTT, and get started with MQTT application and service development.