NOTE / DISCLAIMER: This configuration should only be used for Dev / POC purposes this is NOT suitable for production use.
For Further Details Please Refer to the Official Documentation: Elasticsearch and Kibana
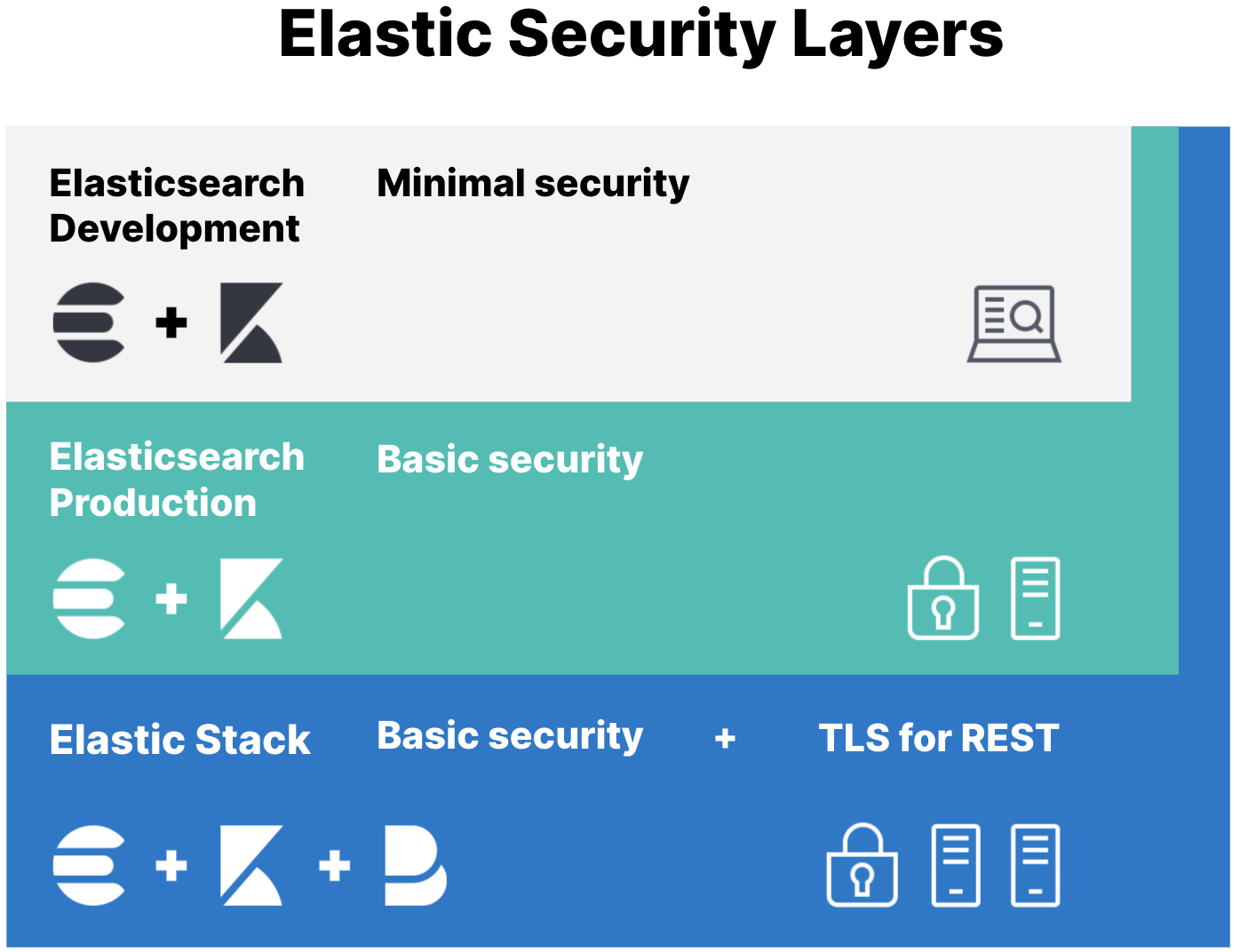
This is simple / minimal quickstart to create a single Elasticsearch node and Kibana with basic authentication and SSL/TLS enabled (we will enable SSL for both HTTPS and Transport layer even though it is just a single node). This is a condensed / direct path to the Basic Security + HTTPs shown in the diagram here and described Configure security for the Elastic Stack. We will then be able to bind the Elasticsearch and Kibana to the network so it can be safely reached from another system.
Do NOT bind your Elasticsearch node or cluster to the network unless you secure your cluster and Kibana FIRST!
Notes:
- This example is using Elastic Stack 7.15.1 and Ubuntu 20.04 LTS using a Deb Package, if you use another method such as the tar.gz you will need to adjust the paths.
- We are colocating Elasticsearch and Kibana for POC / Dev purposes only.
- Many of these commands / directores require
rootaccess so either be prepared tosudomost of the commands or just do asudo -ifor the duration of the session... your choice... - There are many important settings for Elasticsearch that are not in the example please review them here before moving on from POC / Dev mode
- All the IP Adresses are just examples and are not to be taken literally.
- We are not setting any other setting than necessary.
The Macro Steps we are going to follow are below. These are documented in more detail in the Configure security for the Elastic Stack of the Elasticsearch documentation. I have also added a few other helpful hints.
- Install Elasticsearch.
- Enable Security and Setup SSL/TLS for both transport layer and HTTPS
- Setup Authentication
- Install Kibana
- Setup SSL/TLS
- Test
Download and Install Elasticsearch
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.15.1-amd64.deb
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.15.1-amd64.deb.sha512
shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-7.15.1-amd64.deb.sha512
sudo dpkg -i elasticsearch-7.15.1-amd64.debCheck the nework interfaces, the output should look something like the below. Note The nework interface name and the inet address in this case. We will use this information later in this case ens4 and 10.168.0.116
ifconfig
ens4: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1460
inet 10.168.0.116 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 0.0.0.0
....
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
...We will be setting up TLS on the node for both the Transport Layer and HTTPS. We will creating non-trusted / self-signed certs using the elasticsearch-certutil tool docs here. First we will create a CA (certificate authority) and then use that to generate the certificates.
Just take the defaults for all the question and skip the passwords for the .p12s, you can try that later if you like.
sudo -i
cd /usr/share/elasticsearch
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12Now we are going to generate the https certs this just shows the pertinent lines...
Note you will want to create the cert with the internal address, and loopback and a dns entry for localhost. If you have an addition external IP you would add to the ip list as well. We also specify the hostname for the DNS section.
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil http
...
Generate a CSR? [y/N]n
...
Use an existing CA? [y/N]y
...
CA Path: /usr/share/elasticsearch/elastic-stack-ca.p12
Password for elastic-stack-ca.p12:<none>
...
For how long should your certificate be valid? [5y]
Generate a certificate per node? [y/N]y
...
Enter all the hostnames that you need, one per line.
When you are done, press <ENTER> once more to move on to the next step.
my-hostname
localhost
...
Is this correct [Y/n]y
...
Enter all the IP addresses that you need, one per line.
When you are done, press <ENTER> once more to move on to the next step.
10.168.0.116
127.0.0.1
...
Is this correct [Y/n]y
...
Do you wish to change any of these options? [y/N]n
...
Provide a password for the "http.p12" file: [<ENTER> for none]
...
What filename should be used for the output zip file? [/usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip]
unzip elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
Now we will move the certs to the right directory and make sure they are readable
cp elastic-certificates.p12 /etc/elasticsearch/.
cp elasticsearch/http.p12 /etc/elasticsearch/.
cp kibana/elasticsearch-ca.pem /etc/elasticsearch/.
chmod 664 /etc/elasticsearch/*.p12
chmod 664 /etc/elasticsearch/*.pem
Configure the elasticsearch.yml. The _ens4_ is the name of the network interface, _local_ is the loopback. This means that elasticsearch will be available on both.
Add all this at the bottom of the default elasticsearch.yml
cd /etc/elasticsearch
vi elasticsearch.yml# Update this setting
network.host: ["_ens4_", "_local_"]
# Add the rest of these settings at the bottom of the file
discovery.type: single-node
# Enable security
xpack.security.enabled: true
# Enable auditing if you want, uncomment
# xpack.security.audit.enabled: true
# SSL HTTP Settings
xpack.security.http.ssl.enabled: true
xpack.security.http.ssl.keystore.path: http.p12
# SSL Transport Settings
xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate
xpack.security.transport.ssl.client_authentication: required
xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
Start elasticseearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.serviceFor reference here is the stop and status commands as well
sudo systemctl stop elasticsearch.service
sudo systemctl status elasticsearch.serviceElasticsearch Setup Basic Authentication. At this point the is a random bootstrap password and now you are required to set the passwords for all the built in users... make sure you keep track of them all.
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactiveTest with curl. If you have done everything right you should get an out similar to this, if so congratulations you have a single elasticsearch node with authentication and SSL/TLS!
cd /etc/elasticsearch
curl -u "elastic:mypassword" --cacert ./elasticsearch-ca.pem https://localhost:9200
{
"name" : "my-hostname",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "VzQIjzZvTpO5XL7ngo1wDg",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.15.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "83c34f456ae29d60e94d886e455e6a3409bba9ed",
"build_date" : "2021-10-07T21:56:19.031608185Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.9.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}If you need to debug / it is not working you view the Elasticsearchlogs with /var/log/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.log or sudo journalctl --unit elasticsearch -f
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.15.1-amd64.deb
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.15.1-amd64.deb.sha512
shasum -a 512 -c kibana-7.15.1-amd64.deb.sha512
sudo dpkg -i kibana-7.15.1-amd64.debSetup / Create Kibana Certs
- You can use the already elasticsearch generated cert. This cert will needed to be added "trusted" on the Browser side as they are generated from a non-trusted (self-signed) CA
- OR You will need to create real certs from a Trusted CA like Lets Encrypt
In this example we will use the already generated certs
sudo -i
cd /etc/kibana
cp /etc/elasticsearch/http.p12 .
cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-ca.pem .
chmod 644 *.pem *.p12Create a Kibana keystore and put the elasticsearch password in it, this way it is not exposed in the kibana.yml file. And then make sure it is readable by the kibana user
/usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-keystore create
/usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-keystore add elasticsearch.passwordUpdate the kibana setting in kibana.yml
cd /etc/kibana
vi kibana.ymlThese are just the settings you need to change, you do not need to change any other settings.
# Note bind to nic address
server.host: "10.168.0.116"
# The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries.
elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://10.168.0.116:9200"]
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide
# the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana
# index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which
# is proxied through the Kibana server.
elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system"
#elasticsearch.password: "password" #<- Leave this commented out, it will come from the keystore
# Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively.
# These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser.
server.ssl.enabled: true
server.ssl.keystore.path: /etc/kibana/http.p12
server.ssl.keystore.password: ""
# Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate
# authority for your Elasticsearch instance.
elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: /etc/kibana/elasticsearch-ca.pem
# Saved Object Encryption Key : Pick your own
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: "salkdjfhasldfkjhasdlfkjhasdflkasjdfhslkajfhasldkfjhasdlaksdjfh"
Start, stop and status commands
sudo systemctl start kibana.service
sudo systemctl stop kibana.service
sudo systemctl status kibana.serviceAt this point you should have a secured Kibana running as well.
Navigate in this example to https://10.168.0.116:5601 You will need to accept the self signed cert and there you have it
A Secured Elasticsearch Node configured with a secured Kibana
All the cert issues can be solved if you create real certs from a real CA.
Note if you need to debug you can use
sudo journalctl --unit kibana -fTo connect Logstash to an Elasticsearch cluster that is secured with the elasticsearch generated signed certificate you will need to reference the the elasticsearch CA that you created earlier. This will allow vaildation of the CA and a secure connection. Same goes for any of the beats like Filebeat or Metricbeat
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["https://10.168.0.116:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "password"
cacert => "/<path-to-ca>/elasticsearch-ca.pem"
}
stdout {codec => rubydebug}
}