ArrayList--------------------------------------------Mục lục
ArrayList (danh sách đặc) là một mảng có khả năng thay đổi kích thước nằm trong gói java.util
⚠️ Sự khác nhau giữaArrayvàArrayListlà bạn không thể thay đổi kích thước phần tử củaArraynhưng vớiArrayListthì có thể.
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>(); // tạo một Object ArraylistLớp ArrayList có rất nhiều phương thức, nhưng một trong số đó là :
add(): thêm phần tửget(): lấy phần tửset(): thay đổi phần tửremove(): xoá phần tửclear(): xoá ArrayListsize(): trả về số lượng phần từ
 Thêm phần tử
Thêm phần tử
Sử dụng phương thức add() để thêm phần tử như sau :
import java.util.ArrayList;
import jdk.internal.jshell.tool.resources.l10n;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();
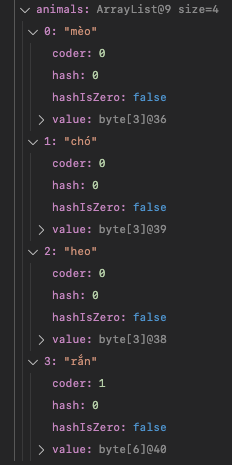
animals.add("mèo");
animals.add("chó");
animals.add("heo");
animals.add("rắn");
System.out.println(animals);
}
}
// Output : [mèo,chó,heo,rắn] Lấy phần tử
Lấy phần tử
Sử dụng phương thức get() để thêm phần tử như sau :
System.out.println(animals.get(0)); // mèo
System.out.println(animals.get(3)); // rắn Đổi phần tử
Đổi phần tử
Bạn có thể chỉnh sửa phần tử bằng cách sử dụng phương thức set() như sau :
set(<vị trí>,<chuỗi>)
animals.set(0,"voi"); // đổi phần tử vị tri 0 thành voi
System.out.println(animal);
//Output : [voi,chó,heo,rắn] Xoá phần tử
Xoá phần tử
Sử dụng phương thức remove() để xoá phần tử như sau :
remove(<vị trí>)
animals.remove(1);
System.out.println(animal);
// Output : [mèo,heo,rắn]Nếu bạn muốn xoá hết tất cả hãy dùng
clear():animals.clear(); System.out.println(animal); // Output : []
 Kiểm ta số phần tử
Kiểm ta số phần tử
Sử dụng phương thức size() để kiểm tra số phần tử hiện có trong mảng
System.out.println(animals.size());
//Output : 4Bạn có thể dùng vòng lặp để duyệt qua Arraylist theo 2 cách sau :
☲ Sử dụng for
for(int i = 0; i < animals.size(); i++){
System.out.println(animals.get(i));
}
/* mèo
chó
heo
rắn */☲ Sử dụng for..Each
for(String index : animals){
System.out.println(index);
}
/* mèo
chó
heo
rắn */💡 Vậy thì sử dụng
for..Eachsẽ đơn giản hơn rất nhiều đúng không nào
 Trả lời
Trả lời
Bản chất của ArrayList là một Object vậy nên nó ó thể lữu trữ nhiều kiểu dữ liệu khác.
ArrayList<Integer> myNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //kiểu số nguyên
ArrayList<Double> myNumbers = new ArrayList<Double>(); // kiểu số thực
ArrayList<String> myNumbers = new ArrayList<String>(); // kiểu chuỗi
ArrayList<Character> myNumbers = new ArrayList<Character>(); // kiểu ký tựSử dụng lớp Collections trong gói java.util, trong đó có phương thức sort() giúp bạn có thể sắp xếp theo chữ cái hoặc số.
☲ Sắp xếp theo chữ cái
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();
animals.add("mèo");
animals.add("chó");
animals.add("heo");
animals.add("rắn");
Collections.sort(animals);
for (String index : animals) {
System.out.println(index);
}
}
}
//Output : chó heo mèo rắn☲ Sắp xếp theo số thứ tự
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> numberic = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numberic.add(33);
numberic.add(5);
numberic.add(8);
numberic.add(1);
Collections.sort(numberic);
for (String index : numberic) {
System.out.println(index);
}
}
}
//Output : 1 5 8 33| 🔙 Bài 3.Date | Bài 5.LinkedList 🔜 |
|---|