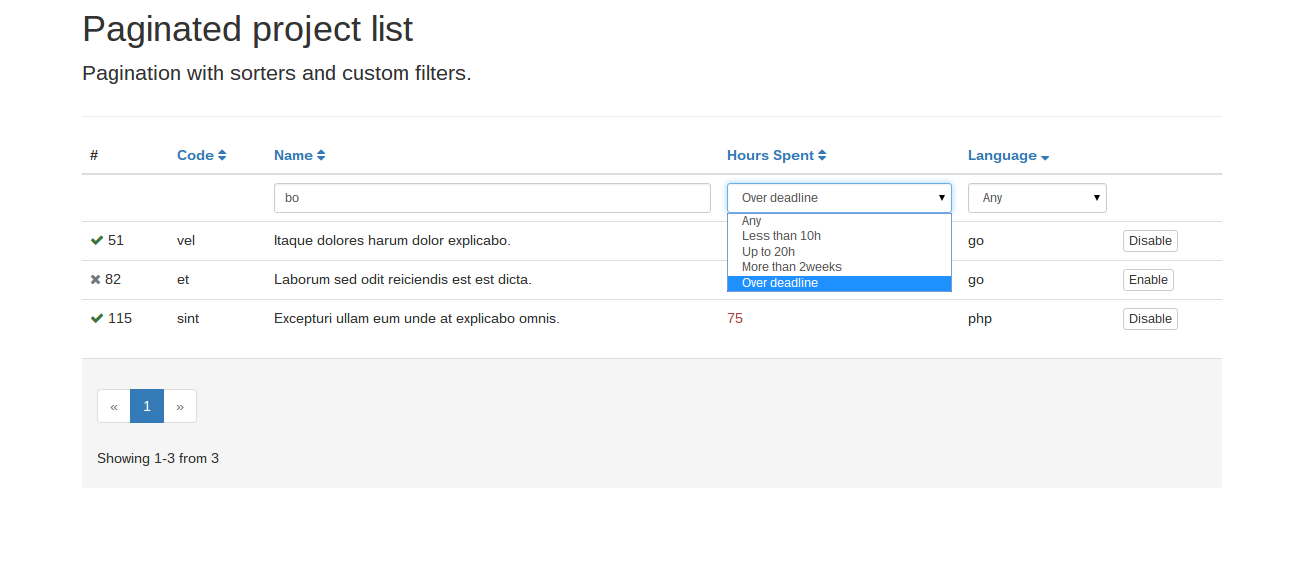
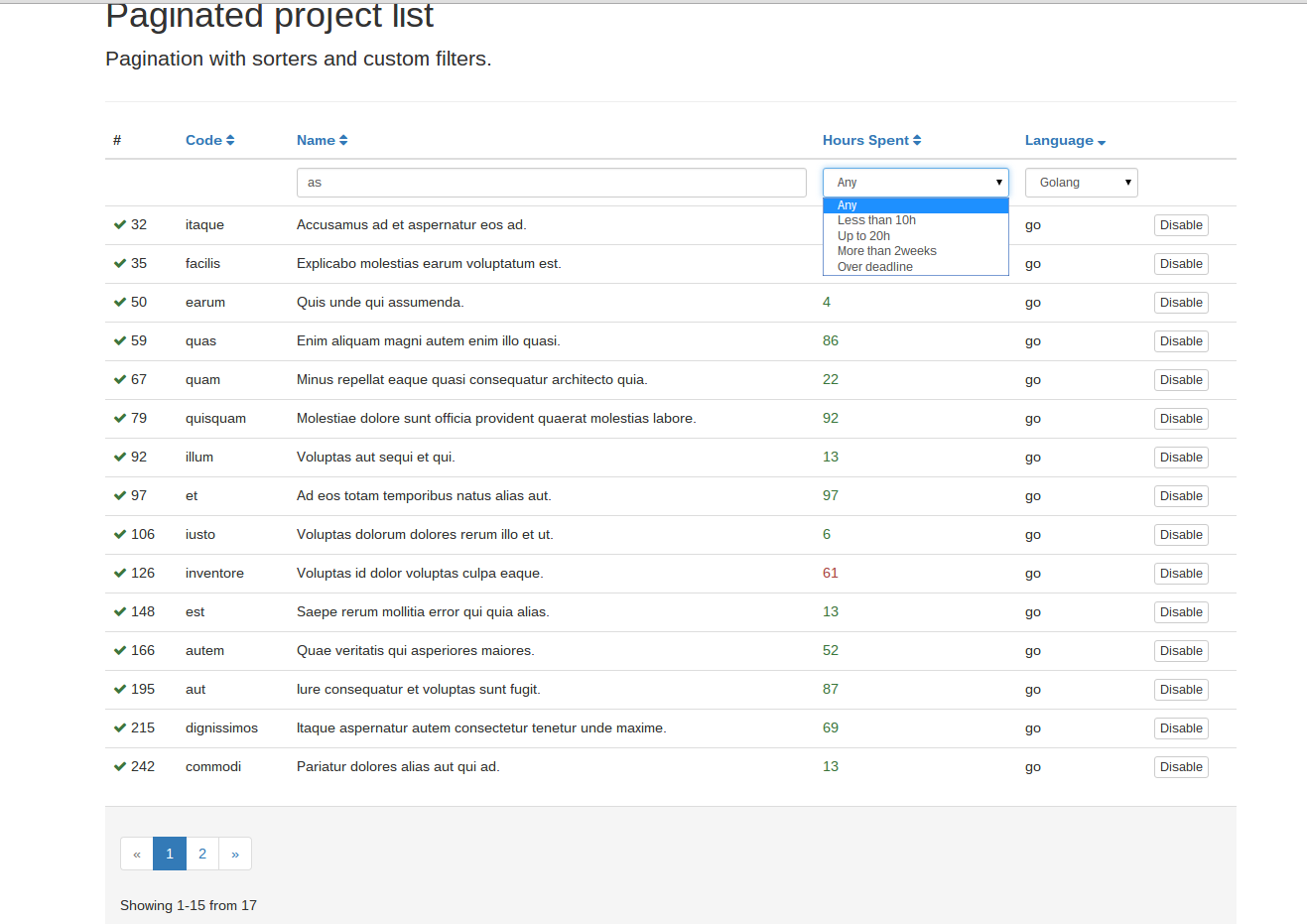
This paginator is different in the following ways:
- it has only one general class with around 300 lines of commented code. All the rest of the source code is specific to symfony2 framework, twig helpers and templates.
- it allows to create custom pagination filters - search, select.. and modify the database query based on the specific use cases.
- it also handles sorting in the traditional way.
- it is very small and may be reused in other frameworks with the modifications needed.
- it can only paginate Doctrine2 ORM QueryBuilder. Nothing else will be supported to maintain this library small and backward compatible. For your own customizations just fork or copy the source code.
- there may be only one pagination per request, because url query parameters are constant.
The best way to see features is to see the actual demo. Just clone the bundle and run:
make
Visit http://localhost:8000 to see the paginated fake projects with custom filters and sorters.
The demo application source is available in example directory and it is a basic symfony application.
First, install it with composer:
composer require data-dog/pager-bundle
Then, add it in your AppKernel bundles.
The general usage example in your controller:
<?php
namespace AppBundle\Controller;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Route;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Method;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Template;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Doctrine\ORM\QueryBuilder;
use DataDog\PagerBundle\Pagination;
class ProjectController extends Controller
{
/**
* @Method("GET")
* @Template
* @Route("/", name="homepage")
*/
public function indexAction(Request $request)
{
$qb = $this->getDoctrine()->getManager()->getRepository("AppBundle:Project")
->createQueryBuilder('p')
->addSelect('l')
->innerJoin('p.language', 'l');
$projects = new Pagination($qb, $request);
return compact('projects');
}
}All you need is to construct Pagination with doctrine query builder and the request. The Pagination object acts like an array, so you can pass it to the view and iterate over paginated items.
The view:
<table class="table table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.code", "Code") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.name", "Name") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.hoursSpent", "Hours Spent") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "l.code", "Language") }}</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for project in projects %}
<tr>
<td>{{ project.id }}</td>
<td>{{ project.code }}</td>
<td>{{ project.name }}</td>
{% if project.isOverDeadline %}
<td class="text-danger">{{ project.hoursSpent }}</td>
{% else %}
<td class="text-success">{{ project.hoursSpent }}</td>
{% endif %}
<td>{{ project.language.code }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="panel-footer">
{{ pagination(projects) }}
</div>There are twig helper functions used:
- sorter_link - which uses the twig template to generate a link with the sorting order class and such.
- pagination - which creates a pagination html code to navigate pages.
These templates may be modified in standard symfony ways, see the configuration section.
In order to filter paginated results in different kinds of ways, you may extend the code. In the controller, provide some pagination options.
<?php
namespace AppBundle\Controller;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Route;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Method;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Template;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Doctrine\ORM\QueryBuilder;
use DataDog\PagerBundle\Pagination;
class ProjectController extends Controller
{
/**
* Our filter handler function, which allows us to
* modify the query builder specifically for our filter option
*/
public function projectFilters(QueryBuilder $qb, $key, $val)
{
switch ($key) {
case 'p.name':
if ($val) {
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->like('p.name', ':name'));
$qb->setParameter('name', "%$val%");
}
break;
case 'p.hoursSpent':
switch ($val) {
case 'lessThan10':
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->lt('p.hoursSpent', 10));
break;
case 'upTo20':
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->lte('p.hoursSpent', 20));
break;
case 'moreThan2weeks':
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->gte('p.hoursSpent', 80));
break;
case 'overDeadline':
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->gt('p.hoursSpent', 'p.deadline'));
break;
}
break;
case 'l.code':
$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->eq('l.code', ':code'));
$qb->setParameter('code', $val);
break;
default:
// Do not allow filtering by anything else
throw new \Exception("filter not allowed");
// You can also enable automatic filtering
//$paramName = preg_replace('/[^A-z]/', '_', $key);
//$qb->andWhere($qb->expr()->eq($key, ":$paramName"));
//$qb->setParameter($paramName, $val);
}
}
/**
* @Method("GET")
* @Template
* @Route("/", name="homepage")
*/
public function indexAction(Request $request)
{
$qb = $this->getDoctrine()->getManager()->getRepository("AppBundle:Project")
->createQueryBuilder('p')
->addSelect('l')
->innerJoin('p.language', 'l');
$options = [
'sorters' => ['l.code' => 'ASC'], // sorted by language code by default
'filters' => ['p.hoursSpent' => 'overDeadline'], // we can apply a filter option by default
'applyFilter' => [$this, 'projectFilters'], // custom filter handling
];
// our language filter options, the key will be used in where statemt by default
// and the value as title.
// The $filterAny key is a placeholder to skip the filter, so the any value could be ok.
$languages = [
Pagination::$filterAny => 'Any',
'php' => 'PHP',
'hs' => 'Haskell',
'go' => 'Golang',
];
// our spent time filter options, has specific keys so we know how to customize
$spentTimeGroups = [
Pagination::$filterAny => 'Any',
'lessThan10' => 'Less than 10h',
'upTo20' => 'Up to 20h',
'moreThan2weeks' => 'More than 2weeks',
'overDeadline' => 'Over deadline',
];
$projects = new Pagination($qb, $request, $options);
return compact('projects', 'languages', 'spentTimeGroups');
}
}Now here we have added three filters:
$languages and $spentTimeGroups will be used as filter_select options. The language options are simple and they
refer to direct values, so the where statement does not need to be modified. But spent time groups are custom so we
use custom options. In that case we need an applyFilter option to be set as a callable so the QueryBuilder could be modified
accordingly based on our custom options.
NOTE: if you manage custom filtering, be sure to use parameters or use $qb->expr()->literal("string") to prevent
SQL injections. Also if you have custom filter handler, you must manage all your filters, the default handler will not
be active.
So how the view has changed:
<table class="table table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.code", "Code") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.name", "Name") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "p.hoursSpent", "Hours Spent") }}</th>
<th>{{ sorter_link(projects, "l.code", "Language") }}</th>
</tr>
<tr role="row" class="filter">
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td>{{ filter_search(projects, "p.name") }}</td>
<td>{{ filter_select(projects, "p.hoursSpent", spentTimeGroups) }}</td>
<td>{{ filter_select(projects, "l.code", languages) }}</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for project in projects %}
<tr>
<td>{{ project.id }}</td>
<td>{{ project.code }}</td>
<td>{{ project.name }}</td>
{% if project.isOverDeadline %}
<td class="text-danger">{{ project.hoursSpent }}</td>
{% else %}
<td class="text-success">{{ project.hoursSpent }}</td>
{% endif %}
<td>{{ project.language.code }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="panel-footer">
{{ pagination(projects) }}
</div>We have used two new twig functions for filters:
- filter_search - for searching projects by name.
- filter_select - for basic option filters.
These functions are rendering twig templates for our filters.
In case if you need to make a link and maintain search filters and sorters applied, use the $pagination->query()
function to get all the necessary url parameters and merge it with your link parameters.
The demo example handles enable and disable toggling for projects in a separate controller action and maintains all pagination properties.
There is no necessary configuration for a general usage. But in order to customize pagination there may be global options set in app.php for example:
<?php
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Symfony\Component\Debug\Debug;
use DataDog\PagerBundle\Pagination;
$loader = require_once __DIR__.'/../app/autoload.php';
Debug::enable();
Pagination::$defaults = array_merge(Pagination::$defaults, [
'limit' => 15,
'range' => 9,
]);
Pagination::$maxPerPage = 200;
require_once __DIR__.'/../app/AppKernel.php';
$kernel = new AppKernel('prod', false);
$kernel->loadClassCache();
$request = Request::createFromGlobals();
$response = $kernel->handle($request);
$response->send();
$kernel->terminate($request, $response);The default templates for filters and pagination are based on twitter bootstrap and fontawesome. You can customize them same as any other bundle template, for example:
- pagination - app/Resources/DataDogPagerBundle/views/pagination.html.twig
- search filter - app/Resources/DataDogPagerBundle/views/filters/search.html.twig
The best way to customize your filters is to extend twig extension, or create a new extension. If we would provide many options, that would confuse people in the end, so instead we add a little boilerplate. In your bundle services.yml update parameters:
parameters:
datadog.pager.twig_extension.class: AppBundle\Twig\PaginationExtensionThen create a class:
<?php
namespace AppBundle\Twig;
use DataDog\PagerBundle\Twig\PaginationExtension as Base;
use DataDog\PagerBundle\Pagination;
class PaginationExtension extends Base
{
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getFunctions()
{
$defaults = [
'is_safe' => ['html'],
'needs_environment' => true,
];
$funcs = parent::getFunctions();
$funcs['filter_search_placeholder'] = new \Twig_Function_Method($this, 'filterSearchPlaceholder', $defaults);
return $funcs;
}
public function filterSearchPlaceholder(\Twig_Environment $twig, Pagination $pagination, $key, $placeholder)
{
$value = isset($pagination->query()['filters'][$key]) ? $pagination->query()['filters'][$key] : '';
return $twig->render('AppBundle::filters/search_placeholder.html.twig', compact('key', 'pagination', 'value', 'placeholder'));
}
}And finally copy and modify the template based on your needs
The pager is free to use and is licensed under the MIT license