-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 345
Debugging
Debugging is a powerful technique allowing you to interactively run your code and be able to see much more information about the things that went wrong.
In order to debug applications based on Sming Framework make sure that you are using Sming version 3.8.0 or newer.
If you want to debug inside of the Sming Framework library make sure to (re)compile it with ENABLE_GDB=1 directive.
cd $SMING_HOME
make dist-clean
make ENABLE_GDB=1
The commands above will re-compile Sming with debug symbols and optimizations for debugging. These commands need to be executed once.
To use, (re)compile your application with the ENABLE_GDB option and flash it to the board. For this example we will use the LiveDebug application.
cd $SMING_HOME/../samples/LiveDebug
make clean
make ENABLE_GDB=1 # -- recompiles your application with debugging support
make flashapp # flashes ONLY the (re)compiled application
The application will start running on your device and will wait for a debugger to pause its execution. To connect a debugger to the remote application use the provided command:
make gdb
This will start a new debugging session where you can run your code interactively. Once the debugger is connect it will pause the execution and you will be able to take control.
Remote debugging using /dev/ttyUSB0
gdbstub_init () at /home/slavey/dev/esp8266.dev.box/dev/Sming/Sming//gdb/gdbstub.cpp:914
914 gdb_do_break();
(gdb)
There are multiple commands supported in GDB and we will mention only some of them.
One possibility is to see the source code of the current line where the execution has stopped. To achieve this you should type "list" in the gdb console.
(gdb) list
909 SD(GDBSTUB_ENABLE_HOSTIO);
910 #undef SD
911
912 #if GDBSTUB_BREAK_ON_INIT
913 if(gdb_state.enabled) {
914 gdb_do_break();
915 }
916 #endif
917 }
918
This command will pause the debugger once it reaches a specific function or line in the code. This is called "breakpoint" and can be set using a command like the one below:
(gdb) break blink
Breakpoint 1 at 0x40105d4c: file app/application.cpp, line 66.
Notice: "break" sets a software breakpoint. This means that the blink function must be in IRAM. Otherwise the execution will fail. If you take a look at the Live Debug application you will see a in the definition of the init function the following attribute GDB_IRAM_ATTR. As shown below.
void GDB_IRAM_ATTR init()
This attribute is used to put the init function in IRAM when the code is compiled with the ENABLE_GDB=1 directive.
To continue the execution of the application we can use the continue command. As shown below:
(gdb) continue
Continuing.
LiveDebug sample
Explore some capabilities of the GDB debugger.
[OS] mode : sta..
...
[OS] cnt
Breakpoint 1, blink () at app/application.cpp:66
66 {
(gdb)
Because we have set already a breakpoint for the blink function the execution will be paused when the blink function is reached and from here you can go to the next line or see the current values of the variables.
This can be done using next
(gdb) next
67 digitalWrite(LED_PIN, ledState);
The command to see a value is print followed by the name of the value. For example to see the value of the ledState variable inside the blink function we could type:
(gdb) print ledState
$1 = true
You can see more useful commands from here.
Or watch the following short video
A good visualization helps us understand things faster. What we can do is use Eclipse CDT and its debugging plugins to do remote debugging as we did from the command line.
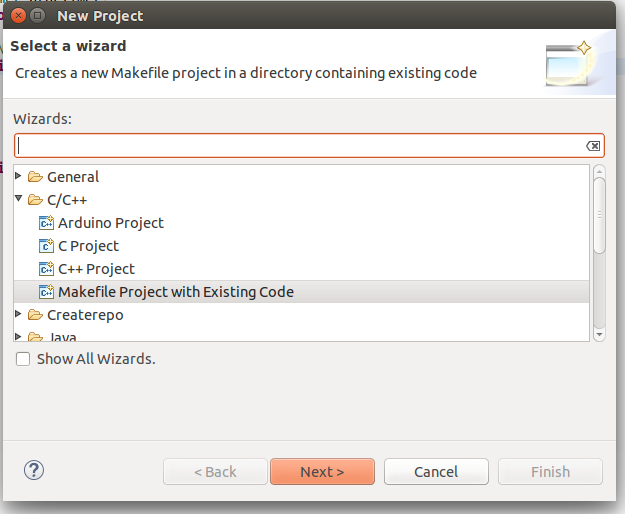
Here is how this can be done. Start Eclipse CDT. Import the LiveDebug sample. This can be done by calling File->New->Project->C/C++ -> Makefile Project with Existing Code. And then point Eclipse to the location of the LiveDebug sample. After that import the Sming Framework if you haven't done it yet.
Once the two projects are in Eclipse set the LiveDebug project to reference the Sming project.
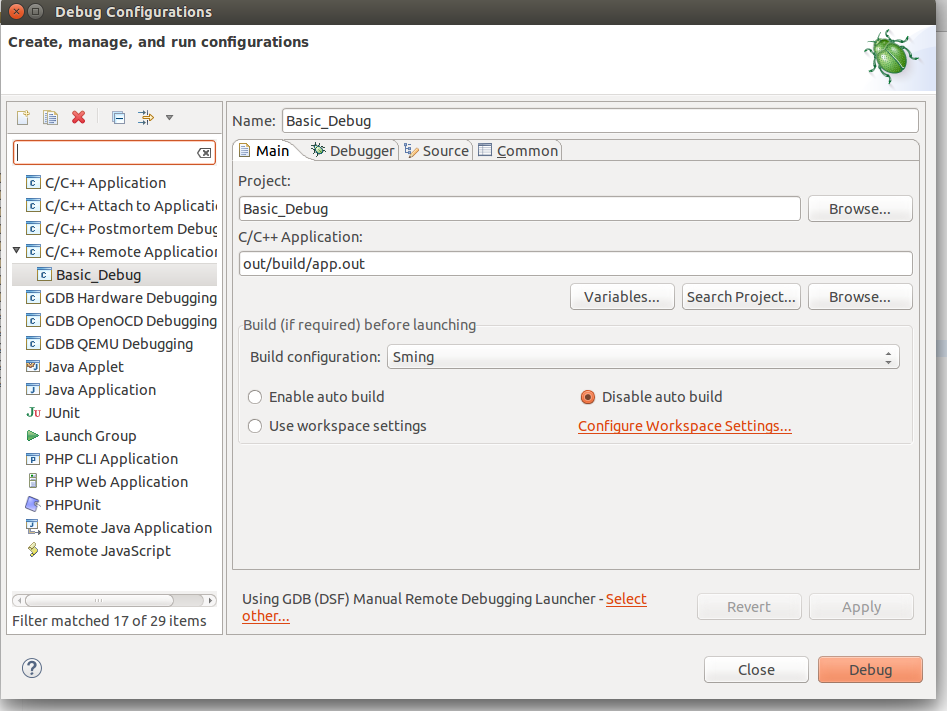
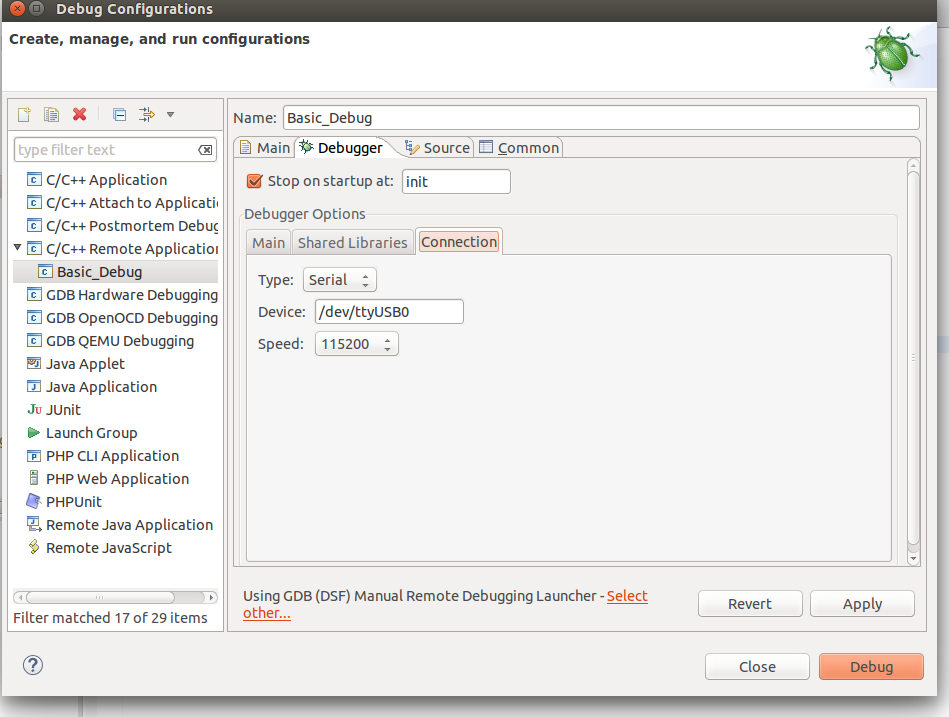
Now create a new Remote Debugging Configuration. This can be done from Run -> Debug Configurations -> C/C++ Remote Application. In there right click and create a new C/C++ Remote Application. In the Main tab set the Project to Basic_Build, the C/C++ Application to out/build/app.out and disable for now the auto build.
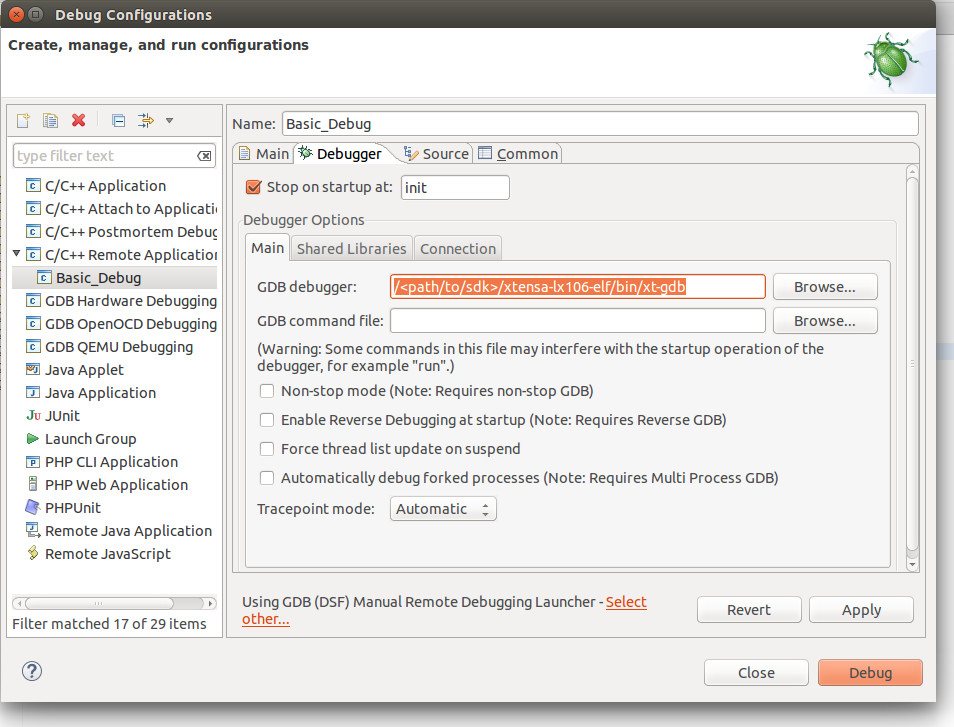
Then go to the Debugger tab and point the GDB debugger to your Xtensa-gdb binary.
Make sure to load also "GDB command file". The one that you will need is located in under Sming/gdb/gdbcmds .
Finally we should configure the remote connection. Go to the Debugger->Connection tab and set the type to be Serial, the device to be /dev/ttyUSB0 and set the speed to 115200. Make sure to replace /dev/ttyUSB0 with the correct device name on your operating system.
We are now ready for debugging. Press the Debug button. In the screenshot above the Debug button is on the bottom-right corner. After some seconds your debugging session should be up and running and you can enjoy live debugging.
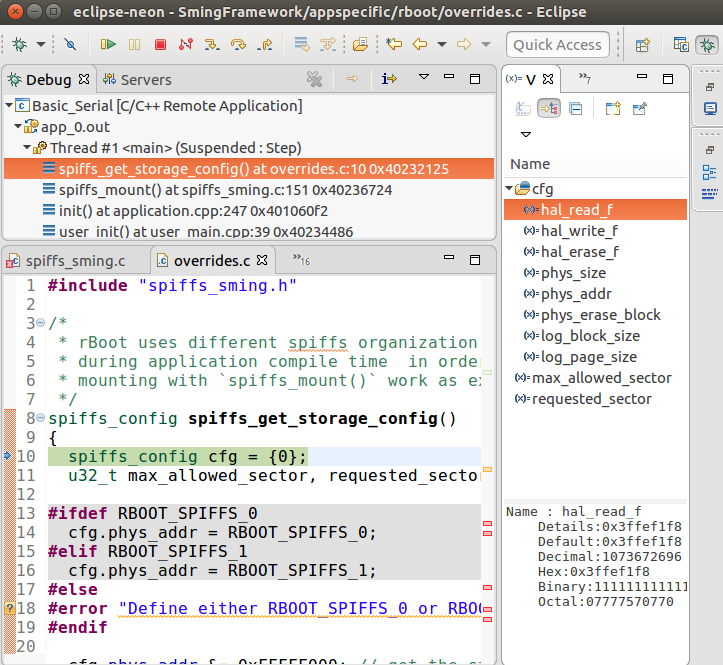
You will be able to see the current variables and their values. You should be able to go step by step, go inside of functions, add breakpoints to code in RAM or add breakpoints to code that was in FLASH, after it was executed executed at least once.
Enjoy!