OpenConnect VPN server is an SSL VPN server that is secure, small, fast and configurable. It implements the OpenConnect SSL VPN protocol and has also (currently experimental) compatibility with clients using the AnyConnect SSL VPN protocol. The OpenConnect protocol provides a dual TCP/UDP VPN channel and uses the standard IETF security protocols to secure it. The OpenConnect client is multi-platform and available here. Alternatively, you can try connecting using the official Cisco AnyConnect client (Confirmed working on Android).
The dockerfile was written to always download and compile the latest release of OpenConnect VPN server when built.*
* OpenConnect dev team has taken to listing unreleased versions on the page I pull with curl to get the current version so I had to modify the command to pull the second most recent version instead. Since I dont control this page it is subject to change back at anytime, keep that in mind if you fork this container.
- Base: Alpine 3.13
- Latest OpenConnect Server 1.1.2
- Size: 63.6MB
- Modification of the listening port for more networking versatility
- Customizing the DNS servers used for queries over the VPN
- Supports tunneling all traffic over the VPN or tunneling only specific routes via split-include
- Config directory can be mounted to a host directory for persistence
- Create certs automatically using default or provided values, or drop your own certs in /config/certs
- Advanced manual configuration for power users
The container is available from the Docker registry and this is the simplest way to get it.
$ docker run --privileged -d \
-p 4443:4443 \
-p 4443:4443/udp \
markusmcnugen/openconnect
$ docker run --privileged -d \
-p 4443:4443 \
-p 4443:4443/udp \
-e "CA_CN=VPN CA" \
-e "CA_ORG=OCSERV" \
-e "CA_DAYS=9999" \
-e "SRV_CN=vpn.example.com" \
-e "SRV_ORG=MyCompany" \
-e "SRV_DAYS=9999" \
markusmcnugen/openconnect
Cert files are stored in /config/certs. It will automatically generate certs if the following two files are not present in the cert directory:
server-key.pem
server-cert.pem
$ docker run --privileged -d \
-v /your/config/path/:/config \
-e "LISTEN_PORT=443" \
-e "DNS_SERVERS=192.168.1.190" \
-e "TUNNEL_MODE=split-include" \
-e "TUNNEL_ROUTES=192.168.1.0/24" \
-e "SPLIT_DNS_DOMAINS=example.com" \
-p 443:443 \
-p 443:443/udp \
markusmcnugen/openconnect
This container allows for advanced configurations for power users who know what they are doing by mounting the /config volume to a host directory. Users can then drop in their own certs and modify the configuration. The POWER_USER environmental variable is required to stop the container from overwriting options set from container environment variables. Some advanced features include setting up site to site VPN links, User Groups, Proxy Protocol support and more.
| Variable | Required | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
LISTEN_PORT |
No | Listening port for VPN connections | LISTEN_PORT=4443 |
DNS_SERVERS |
No | Comma delimited name servers | DNS_SERVERS=8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4 |
TUNNEL_MODE |
No | Tunnel mode (all / split-include) | TUNNEL_MODE=split-include |
TUNNEL_ROUTES |
No | Comma delimited tunnel routes in CIDR notation | TUNNEL_ROUTES=192.168.1.0/24 |
SPLIT_DNS_DOMAINS |
No | Comma delimited dns domains | SPLIT_DNS_DOMAINS=example.com |
POWER_USER |
No | Allows for advanced manual configuration via host mounted /config volume | POWER_USER=no |
| Volume | Required | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
config |
No | OpenConnect config files | /your/config/path/:/config |
| Port | Proto | Required | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
4443 |
TCP | Yes | OpenConnect server TCP listening port | 4443:4443 |
4443 |
UDP | Yes | OpenConnect server UDP listening port | 4443:4443/udp |
Install and run the docker container with your chosen options. Port forward incoming traffic on your router, some outside port to the containers IP and the listening port on the inside. After port forwarding is established you will need to create VPN accounts for users to login with usernames and passwords.
Incoming Outside Port 4443 Forwarding TCP and UDP to the OpenConnect Servers inside IP address and listening port
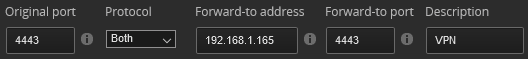
Add users by executing the following command on the host running the docker container
docker exec -ti openconnect ocpasswd -c /config/ocpasswd markusmcnugen
Enter password:
Re-enter password:
Delete users by executing the following command on the host running the docker container
docker exec -ti openconnect ocpasswd -c /config/ocpasswd -d markusmcnugen
After a user successfully logins to the VPN a message will be logged in the docker log.
Example of login message:
[info] User markusmcnugen Connected - Server: 192.168.1.165 VPN IP: 192.168.255.194 Remote IP: 107.92.120.188
Example of logoff message:
[info] User markusmcnugen Disconnected - Bytes In: 175856 Bytes Out: 4746819 Duration:63
To build this container, clone the repository and cd into it.
$ cd /repo/location/openconnect
$ docker build -t openconnect .
$ docker run --privileged -d \
-p 4443:4443 \
-p 4443:4443/udp \
openconnect
This will start a container as described in the "Run container from Docker registry" section. View the other run configurations for more advanced setups.