##Dijkstra's Algorithm ("dike-straw") ###How to: ####Compute traversal costs for an expanding set of nodes till goal. 0. set current node to start.
- from current node look at all unvisited neighbors. a. add them to unvisited nodes list. b. and compute traversal cost from current node to each unvisited neighbor. c. (if traversal cost is less than existing traversal cost, replace with lower.)
- set current node to unvisited neighbor with lowest traversal cost. a. remove it from unvisted nodes list.
- repeat 1 and 2 until you've reached the end node. ####Nodes now have traversal costs; find the shortest path to complete the algorithm:
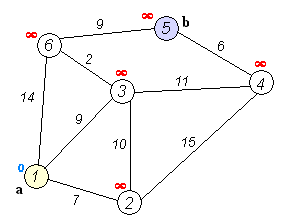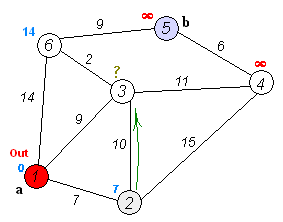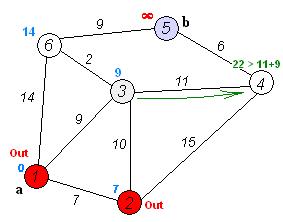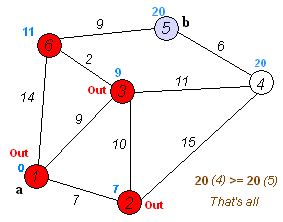
- set current node to end node and add it to the shortest path list.
- from the current node, choose the visited neighbor with the lowest traversal cost. a. add that node to the shortest path list. b. set it to the current node.
- repeat 5 until you've added the starting node to the shortest path list.
- the reversed shortest path list is your solution!
hint: recursion is not always the answer...
##A* ("a-star") ###How to: The same as Dijkstra's but traversal cost also includes an additional term (a heuristic, or guiding guess) to bias the pathfinder in a particular way.