切片(Slice)是一种没有所有权的资料型别。切片参照连续的记忆体分配而不是整个集合。它允许安全,高效地存取阵列而无需复制。切片不是直接建立的,而是从现有变数建立的。切片由长度组成,并且可以是可变的或不可变的。切片的行为与阵列相同。
字串切片指的是字串的一部分。切片看起来像:
let str=String::from("Tw511.com tutorial");
let yiibai=&str[0..10];
let tutorial=&str[11,18];如果想要取一部分字串,而不是整个字串。语法是一个从开始但不包括结束的范围。因此,可以通过指定括号内的范围来建立切片,例如 如果想要包含字串的结尾,那么必须使用[start..end]``[start..end]``start``end``..=``..
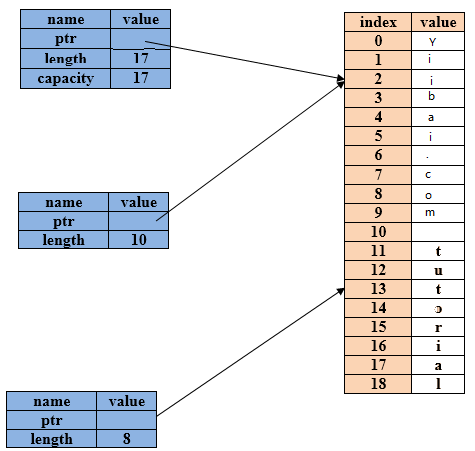
let str= String::from("tw511.com tutorial");
let yiibai = &str[0..=9];
let tutorial= &str[11..=18] ;图解表示:
如果要从 看起来如下:0
let str= String::from("hello world");
let hello = &str[0..5];
let hello=&str[..5];如果 看起来如下:slice
let str= String::from("hello world") ;
let hello=&str[6..len];
let world = &str[6..];下面来看一个字串切片的简单范例:
fn main(){
let str=String::from("Tw511.com tutorial");
let yiibai=&str[..=9];
println!("first word of the given string is {}",yiibai);
}执行上面范例程式码,得到以下结果 -
first word of the given string is Tw511.com字串切片是文字
字串文字储存在二进位制档案中,字串文字仅作为字串切片。如下:
let str = "Hello Yiibai" ;
str`的型别是 字串文字是不可变的,`&str``&str如果有一个字串切片,那么可以直接传递它作为引数。将字串切片作为引数传递给函式,而不是传递参照,以使API更通用和有用,而不会失去其功能。
fn main()
{
let str= String:: from("Computer Science");
let first_word= first_word(&str[..]); //first_word function finds the first word of the string.
let s="Computer Science" ; //string literal
let first_word=first_word(&s[..]); // first_word function finds the first word of the string.
let first_word=first_word(s) ; //string slice is same as string literal. Therefore, it can also be written in this way also.
}阵列也可以视为切片。它们的行为类似于字串切片。切片的型别为 它们通过将参照储存为第一个元素并将长度储存为第二个元素,类似于字串切片。[&i32]
考虑下面一个阵列:
let arr = [100,200,300,400,500]; // array initialization
let a = &arr[1..=3]; // retrieving second,third and fourth element下面来看一个简单的例子。
fn main()
let arr = [100,200,300,400,500,600];
let mut i=0;
let a=&arr[1..=3];
let len=a.len();
println!("Elements of 'a' array:");
while i<len
{
println!("{}",a[i]);
i=i+1;
}
}执行上面范例程式码,得到以下结果 -
Elements of 'a' array:
200
300
400